
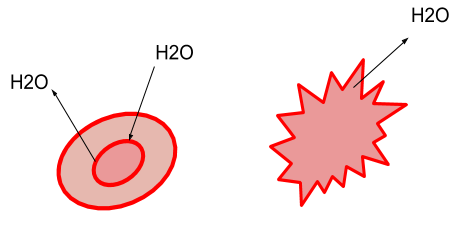
Observe the given figure and answer the following question. What has happened to cells? Explain.

Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: Tonicity is the concentration of a solution compared to another solution. Concentration describes the amount of solution dissolved.In biology, the tonicity of the environment as compared to the cell determines how water moves across the membrane.
Complete answer:
The graph illustrates the tonicity of different settings, and how water flows. To regulate the concentration gradient of solutes, water runs. It can switch from a high concentration of solute to a low concentration of solute. Three concepts, hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic, determine whether a solution allows water to pass into or out of a cell.
During a hypertonic solution, if a cell is put, there will be a net flow of water from the cell, and thus the cell will lose volume. If the solute concentration is greater than that within the cell, solutions are hypertonic to a cell, and hence the solutes do not cross the membrane.
There would be a net flow of water into the cell if a cell is put in a highly hypotonic solution, and the cell will thus gain volume. If the concentration of the solutes outside the cell is less than inside the cell and the solutes are also unable to cross the membrane, the solution is hypotonic to the cell.
There will be no net flow of water into or out of the cell if a cell is put in an isosmotic solution, and the volume of the cell will therefore remain constant. If the concentration of the solution outside the cell is the same as within the cell and the solutes are unable to cross the membrane as well, then the solution is isotonic to the cell.
During a hypertonic solution, if a cell is put, water will exit the cell, and thus the cell will shrink. There's no net water movement in an isotonic setting, so there is no change in the size of the cell. Water will enter the cell when a cell is put in a very hypotonic environment, and the cell will swell as well.
Note: Isotonic conditions are optimum in the case of a red blood corpuscle, and our body has homeostatic (stability-maintaining) mechanisms to confirm that these conditions remain stable. A red blood corpuscle, if put during a hypotonic solution, will bloat up and burst, while it will shrink in an extremely hypertonic solution, making the cytoplasm dense and its contents concentrated, and will die.
Complete answer:
The graph illustrates the tonicity of different settings, and how water flows. To regulate the concentration gradient of solutes, water runs. It can switch from a high concentration of solute to a low concentration of solute. Three concepts, hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic, determine whether a solution allows water to pass into or out of a cell.
During a hypertonic solution, if a cell is put, there will be a net flow of water from the cell, and thus the cell will lose volume. If the solute concentration is greater than that within the cell, solutions are hypertonic to a cell, and hence the solutes do not cross the membrane.
There would be a net flow of water into the cell if a cell is put in a highly hypotonic solution, and the cell will thus gain volume. If the concentration of the solutes outside the cell is less than inside the cell and the solutes are also unable to cross the membrane, the solution is hypotonic to the cell.
There will be no net flow of water into or out of the cell if a cell is put in an isosmotic solution, and the volume of the cell will therefore remain constant. If the concentration of the solution outside the cell is the same as within the cell and the solutes are unable to cross the membrane as well, then the solution is isotonic to the cell.
During a hypertonic solution, if a cell is put, water will exit the cell, and thus the cell will shrink. There's no net water movement in an isotonic setting, so there is no change in the size of the cell. Water will enter the cell when a cell is put in a very hypotonic environment, and the cell will swell as well.
Note: Isotonic conditions are optimum in the case of a red blood corpuscle, and our body has homeostatic (stability-maintaining) mechanisms to confirm that these conditions remain stable. A red blood corpuscle, if put during a hypotonic solution, will bloat up and burst, while it will shrink in an extremely hypertonic solution, making the cytoplasm dense and its contents concentrated, and will die.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




