
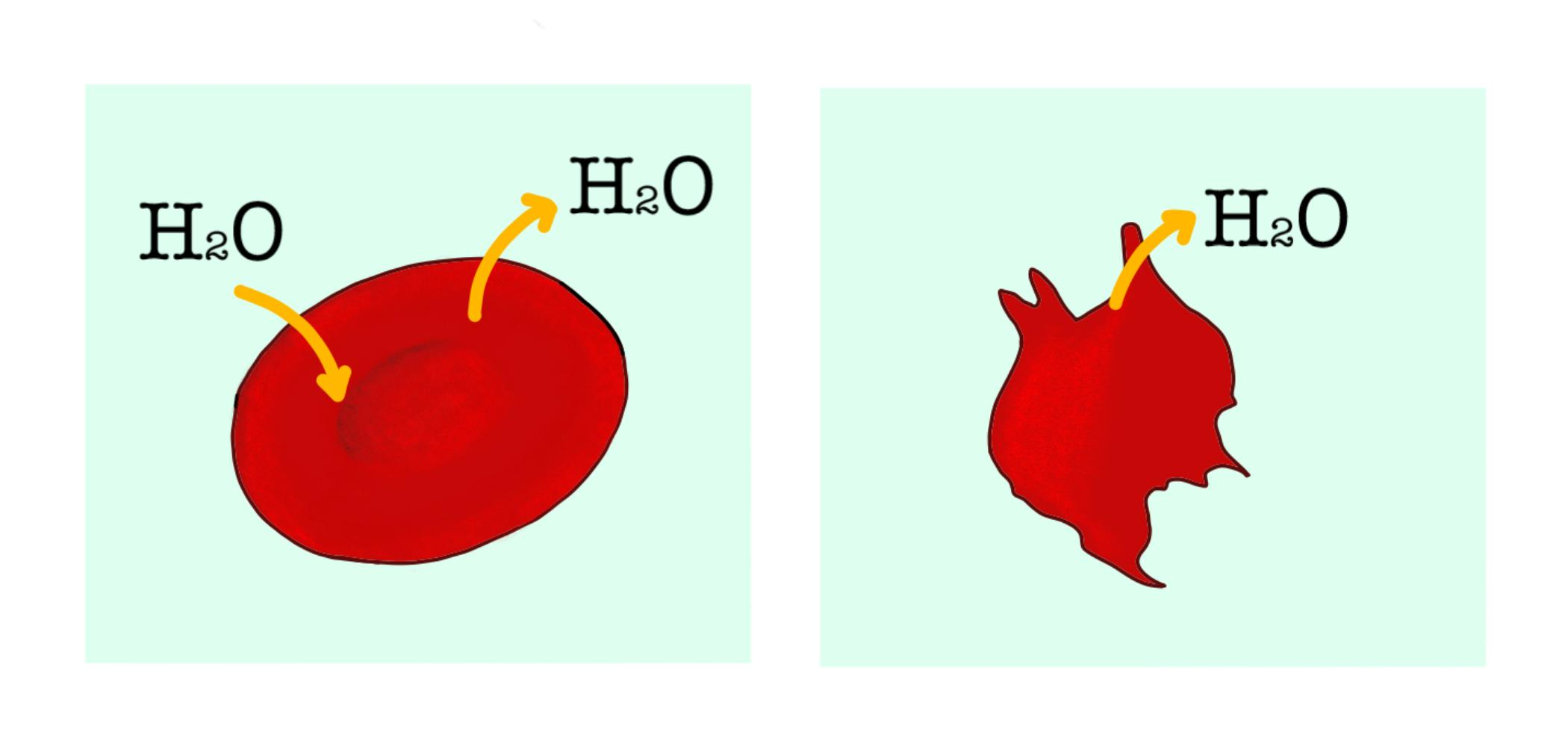
Observe the given figure and answer the question. Explain what has happened to the cell. Consider the cells as A and B respectively.

Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: As seen in the figure A, the ${ H }_{ 2 }O$ molecule is seen going in and out of the red blood cell, in its intact shape. In figure B, ${ H }_{ 2 }O$ is seen leaving the cell and the cell shape looks abnormal. Hence, the entry and exit of water from the cell is a phenomenon that explains the change in the cell shape.
Complete answer:
The red blood cell in the figure is seen to undergo osmosis. Osmosis is defined as the movement of water from a high water potential to low water potential.
- When a cell is present in a solution, osmosis occurs to and from the cell and the solution.
- When the solution outside the cell has a higher concentration than the medium inside the cell, the solution is hypertonic which causes the water from the cells to flow to the solution to create equal osmotic pressure. When the solution outside the cell has a lower concentration than the medium inside the cell, the solution is hypotonic which causes water from the solution to flow through the membrane inside the cell.
- When the concentration of the solution both inside and outside the cell are equal, there is no flow of the water or solvent molecules making the solution isotonic.
- When the solution outside the red blood cell is hypertonic, the water moves from within the cell to outside the cell, resulting in plasmolysis and thus shrinkage of the cell.
Additional Information:
The osmotic pressure is the pressure applied to a solution to stop the flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane.
- When the red blood cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the water moves from the outside of the cell into the inside, resulting in the swelling of the cell making it turgid.
- Red blood cells or any physiological cells need to be placed in a medium with an isotonic concentration, or else it leads to swelling or shriveling of cells, which may result in permanent damage.
Note: There are organisms that can survive in high salt environments without facing the loss of water through osmosis. They are known as halophiles.
- Halophiles are of two kinds. Obligate halophiles can only survive in high salt concentration environments while facultative halophiles are able to survive in both high and normal salt concentration environments.
Complete answer:
The red blood cell in the figure is seen to undergo osmosis. Osmosis is defined as the movement of water from a high water potential to low water potential.
- When a cell is present in a solution, osmosis occurs to and from the cell and the solution.
- When the solution outside the cell has a higher concentration than the medium inside the cell, the solution is hypertonic which causes the water from the cells to flow to the solution to create equal osmotic pressure. When the solution outside the cell has a lower concentration than the medium inside the cell, the solution is hypotonic which causes water from the solution to flow through the membrane inside the cell.
- When the concentration of the solution both inside and outside the cell are equal, there is no flow of the water or solvent molecules making the solution isotonic.
- When the solution outside the red blood cell is hypertonic, the water moves from within the cell to outside the cell, resulting in plasmolysis and thus shrinkage of the cell.
Additional Information:
The osmotic pressure is the pressure applied to a solution to stop the flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane.
- When the red blood cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the water moves from the outside of the cell into the inside, resulting in the swelling of the cell making it turgid.
- Red blood cells or any physiological cells need to be placed in a medium with an isotonic concentration, or else it leads to swelling or shriveling of cells, which may result in permanent damage.
Note: There are organisms that can survive in high salt environments without facing the loss of water through osmosis. They are known as halophiles.
- Halophiles are of two kinds. Obligate halophiles can only survive in high salt concentration environments while facultative halophiles are able to survive in both high and normal salt concentration environments.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




