
On which side of the body may we see the Navel?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: The position of our belly button depicts the position of Navel. Our belly button denotes the spot where our umbilical cord was attached before our birth. This cord is a soft and bendable tube that carries nutrients and vitamins and minerals from the mother to the baby when the baby is in her womb. It is also called Umbilicus.
Complete answer:
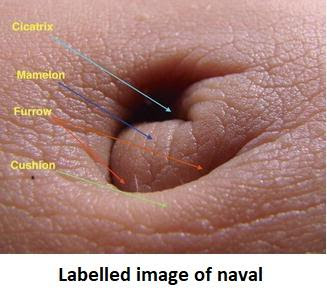
The Umbilicus is a natural scar due to the detachment of the umbilical cord. The periumbilical area is distinguished by an ellipsoid or a round shape, with a slight depression of 2.5–3.0 centimetres in diameter. It represents an essential feature in the overall body curve. It exists as one of the most important landmarks on the abdominal wall. Through the navel we can separate the abdomen into different quadrants.
The umbilical region contains the navel and many parts of the small intestine. It contains part of the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. It also contains the transverse colon and the bottom portions of both the kidneys.
Anatomical Position of Navel –
We can see the umbilicus at the anterior part of a human body. It lies along the midline at the level of the intervertebral discs between the L3 and L4 vertebrae. According to the anatomy the Navel is considered as the only acceptable scar on the human body.
The navel body position is relatively the same amongst humans. It is clearly seen that it is typically located vertically, corresponding to the junction present between the Third Lumbar vertebrae and Fourth Lumbar vertebrae with some normal variation amongst the people between the Third Lumbar vertebrae and Fifth Lumbar vertebrae.
Note:
Just behind our navel or umbilicus there is a thick fibrous cord. This cord is formed from the umbilical cord called the Urachus. It originates from the bladder. Navel or umbilicus balances all forces. It is the centre of physical gravity while standing, walking, sitting, running or in any other posture.
Complete answer:
The Umbilicus is a natural scar due to the detachment of the umbilical cord. The periumbilical area is distinguished by an ellipsoid or a round shape, with a slight depression of 2.5–3.0 centimetres in diameter. It represents an essential feature in the overall body curve. It exists as one of the most important landmarks on the abdominal wall. Through the navel we can separate the abdomen into different quadrants.
The umbilical region contains the navel and many parts of the small intestine. It contains part of the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. It also contains the transverse colon and the bottom portions of both the kidneys.
Anatomical Position of Navel –
We can see the umbilicus at the anterior part of a human body. It lies along the midline at the level of the intervertebral discs between the L3 and L4 vertebrae. According to the anatomy the Navel is considered as the only acceptable scar on the human body.
The navel body position is relatively the same amongst humans. It is clearly seen that it is typically located vertically, corresponding to the junction present between the Third Lumbar vertebrae and Fourth Lumbar vertebrae with some normal variation amongst the people between the Third Lumbar vertebrae and Fifth Lumbar vertebrae.

Note:
Just behind our navel or umbilicus there is a thick fibrous cord. This cord is formed from the umbilical cord called the Urachus. It originates from the bladder. Navel or umbilicus balances all forces. It is the centre of physical gravity while standing, walking, sitting, running or in any other posture.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




