
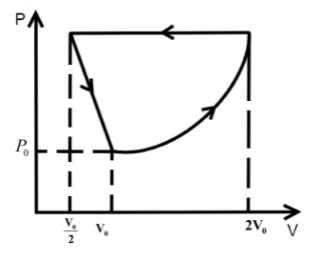
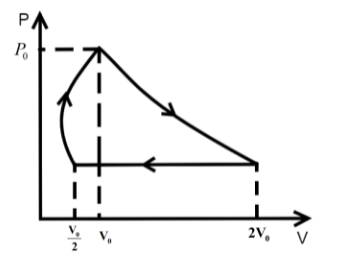
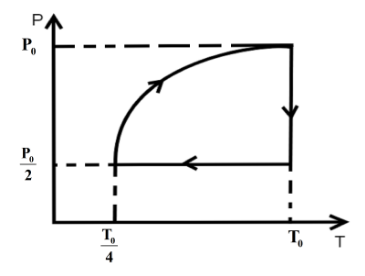
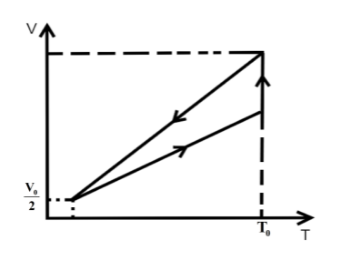
One mole of an ideal gas at pressure \[{P_0}\] and temperature \[{T_0}\] volume \[{V_0}\] is expanded isothermally to twice its volume and then compressed at constant pressure to (\[\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{2}\]) and the gas is brought to original state by a process in which \[P \propto V\] (Pressure is directly proportional to volume): The correct representation of process is :
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
523.2k+ views
Hint:In an isothermal process the temperature of the reaction is kept constant and the P-T or V-T curve is straight parallel to the T axis. For an isobaric process the pressure of the reaction is kept constant and the P-V or P-T curve is straight parallel to the P axis.
Formula used:
Boyle’s law for ideal gas is given by,
\[PV = k\]
where \[P\] is the pressure of the gas, \[V\]is the volume of the gas and \[k\]is constant.
Charles’s law for ideal gas is given by,
\[V = kT\]
where, \[V\] is the volume of the gas, \[T\] is the absolute temperature of the gas and \[k\]is constant.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that in an isothermal process the temperature of the reaction is kept constant while other parameters of the equation of state vary .So, for an isothermal process the P-T or V-T curve is straight parallel to the T axis. Here, it is expanded to keep the temperature constant. So, from Boyle’s law we can get the final pressure as, \[{P_0}{V_0} = {P_2}2{V_0}\] when, \[T = k\] is constant.
\[{P_2} = \dfrac{{{P_0}}}{2}\]
In the second step the pressure is kept constant and we know for an isobaric process the pressure of the reaction is kept constant while other parameters of the equation of state vary. So, the P-V or P-T curve is straight parallel to the P axis. So, from Charles law we can get final temperature in the process as, \[\dfrac{{2{V_0}}}{{{T_0}}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2{T_2}}}\] when \[P = k\] is constant.
\[{T_2} = \dfrac{{{T_0}}}{4}\]
In the third step the \[P \propto V\] so P-V curve is parabolic in this process so coming back to the initial state will be a parabolic path in the P-V curve. Since, \[P \propto V\] from ideal gas relation we can write \[P \propto \dfrac{T}{P}\] .
\[{P^2} \propto T\]
So, the state parameter of the gas changes as,
\[{P_0},{V_0},{T_0}\xrightarrow[{process}]{{isothermal}}\dfrac{{{P_0}}}{2},2{V_0},{T_0}\xrightarrow[{process}]{{isobaric}}\dfrac{{{P_0}}}{2},\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{2},\dfrac{{{T_0}}}{4}\xrightarrow{{P \propto V}}{P_0},{V_0},{T_0}\]
So, the P-T curve can be drawn as,
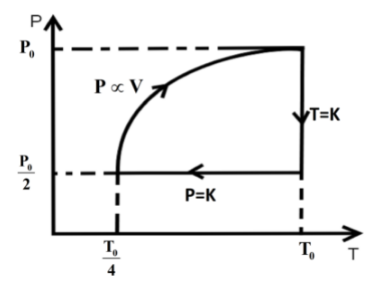
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note:To draw the curve, always deduce the state parameters \[P,V,T\] first using the equation of states at the end of each process to mark the values in the curve. In adiabatic processes the total exchange of heat in the process is always zero. Adiabatic process follows the equation \[P{V^\gamma } = k\] where \[\gamma \]is the ratio of the molar specific heats i.e. the ratio of the molar specific heat at constant pressure to the molar specific heat at constant volume.
Formula used:
Boyle’s law for ideal gas is given by,
\[PV = k\]
where \[P\] is the pressure of the gas, \[V\]is the volume of the gas and \[k\]is constant.
Charles’s law for ideal gas is given by,
\[V = kT\]
where, \[V\] is the volume of the gas, \[T\] is the absolute temperature of the gas and \[k\]is constant.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that in an isothermal process the temperature of the reaction is kept constant while other parameters of the equation of state vary .So, for an isothermal process the P-T or V-T curve is straight parallel to the T axis. Here, it is expanded to keep the temperature constant. So, from Boyle’s law we can get the final pressure as, \[{P_0}{V_0} = {P_2}2{V_0}\] when, \[T = k\] is constant.
\[{P_2} = \dfrac{{{P_0}}}{2}\]
In the second step the pressure is kept constant and we know for an isobaric process the pressure of the reaction is kept constant while other parameters of the equation of state vary. So, the P-V or P-T curve is straight parallel to the P axis. So, from Charles law we can get final temperature in the process as, \[\dfrac{{2{V_0}}}{{{T_0}}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{2{T_2}}}\] when \[P = k\] is constant.
\[{T_2} = \dfrac{{{T_0}}}{4}\]
In the third step the \[P \propto V\] so P-V curve is parabolic in this process so coming back to the initial state will be a parabolic path in the P-V curve. Since, \[P \propto V\] from ideal gas relation we can write \[P \propto \dfrac{T}{P}\] .
\[{P^2} \propto T\]
So, the state parameter of the gas changes as,
\[{P_0},{V_0},{T_0}\xrightarrow[{process}]{{isothermal}}\dfrac{{{P_0}}}{2},2{V_0},{T_0}\xrightarrow[{process}]{{isobaric}}\dfrac{{{P_0}}}{2},\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{2},\dfrac{{{T_0}}}{4}\xrightarrow{{P \propto V}}{P_0},{V_0},{T_0}\]
So, the P-T curve can be drawn as,

Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note:To draw the curve, always deduce the state parameters \[P,V,T\] first using the equation of states at the end of each process to mark the values in the curve. In adiabatic processes the total exchange of heat in the process is always zero. Adiabatic process follows the equation \[P{V^\gamma } = k\] where \[\gamma \]is the ratio of the molar specific heats i.e. the ratio of the molar specific heat at constant pressure to the molar specific heat at constant volume.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




