
Open vascular bundles are those which
A. Are surrounded by pericycle but no endodermis
B. Are capable of producing secondary xylem and phloem
C. Are not surrounded by pericycle
D. Possess conjunctive tissue between xylem and phloem
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Open vascular bundles are present only in dicotyledonous plants . Gymnosperms and dicot angiosperms undergo secondary growth in their later phase of life. Monocotyledons lack secondary growth.
Complete answer:
Xylem and phloem constitute the vascular bundles in a plant. Xylem mostly translocates water, nutrients, and hormones. Phloem is associated with the transport of food and other materials.
While xylem translocates water in only one direction, phloem translocates food materials in both directions. Hence, the movement of substances in the xylem is unidirectional while that in the phloem is bidirectional.
In the mature regions of roots and shoots of plants, there is a presence of meristems or meristematic tissues. These meristems produce woody axis and they appear later in the life of plants that are later than primary meristems.
These meristems are called secondary or lateral meristems. These are cylindrical meristems. These are responsible for producing the secondary tissues to the plant body. Interfascicular cambium and cork cambium is the secondary meristems.
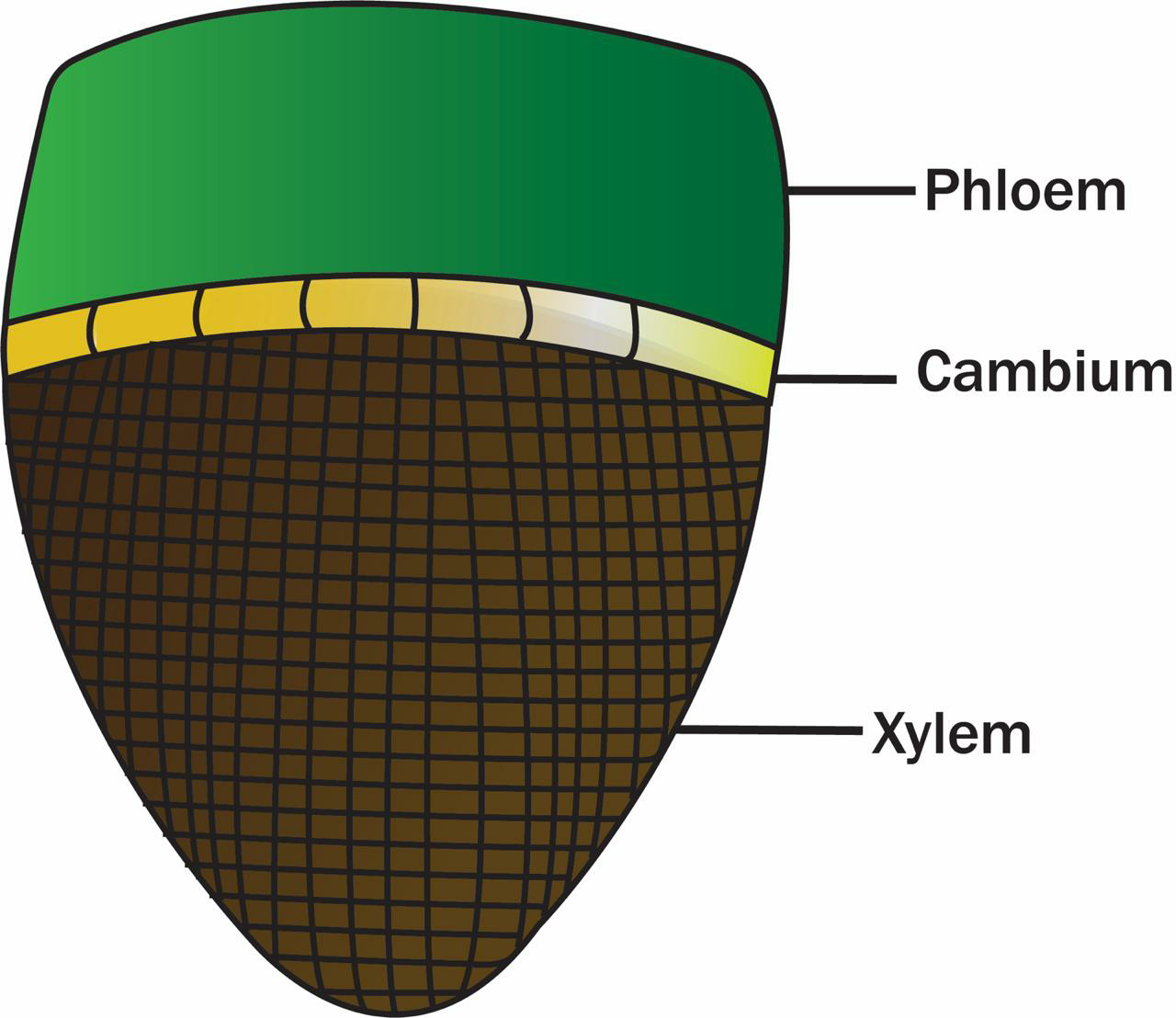
In dicotyledonous stems, cambium is present between the xylem and the phloem which are responsible for secondary growth in the stem. Secondary growth increases the girth of the plant and primary growth increases the height of the plant.
Since the vascular bundles in dicot stems possess cambium between them, the cambium helps to create secondary xylem and secondary phloem during the secondary growth of the plant.
These vascular bundles, due to secondary growth, are called open vascular bundles. The vascular bundles of the plants which do not undergo secondary growth in the later phase of their life are called closed vascular bundles.
Monocotyledonous plants of angiosperms do not possess cambium between their vascular bundles. Therefore no secondary growth occurs in these plants, hence the vascular bundles in these plants are closed vascular bundles.
If the xylem and the phloem of the vascular bundles are joint to each other and situated along the same radius of vascular bundles, then it is called a conjoint type of vascular bundles. Conjoint vascular bundles are found in stems and leaves.
Roots possess radial vascular bundles, in which the xylem and the phloem are arranged in an alternate manner along the different radii within the vascular bundle.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (B)
Note: The cells between two vascular bundles are called medullary rays. During the secondary growth of the dicot stems, these medullary rays become meristematic and form the interfascicular cambium. Hence, interfascicular and intrafascicular cambium together constitute a cambial ring in the stem.

Complete answer:
Xylem and phloem constitute the vascular bundles in a plant. Xylem mostly translocates water, nutrients, and hormones. Phloem is associated with the transport of food and other materials.
While xylem translocates water in only one direction, phloem translocates food materials in both directions. Hence, the movement of substances in the xylem is unidirectional while that in the phloem is bidirectional.
In the mature regions of roots and shoots of plants, there is a presence of meristems or meristematic tissues. These meristems produce woody axis and they appear later in the life of plants that are later than primary meristems.
These meristems are called secondary or lateral meristems. These are cylindrical meristems. These are responsible for producing the secondary tissues to the plant body. Interfascicular cambium and cork cambium is the secondary meristems.
In dicotyledonous stems, cambium is present between the xylem and the phloem which are responsible for secondary growth in the stem. Secondary growth increases the girth of the plant and primary growth increases the height of the plant.
Since the vascular bundles in dicot stems possess cambium between them, the cambium helps to create secondary xylem and secondary phloem during the secondary growth of the plant.
These vascular bundles, due to secondary growth, are called open vascular bundles. The vascular bundles of the plants which do not undergo secondary growth in the later phase of their life are called closed vascular bundles.
Monocotyledonous plants of angiosperms do not possess cambium between their vascular bundles. Therefore no secondary growth occurs in these plants, hence the vascular bundles in these plants are closed vascular bundles.
If the xylem and the phloem of the vascular bundles are joint to each other and situated along the same radius of vascular bundles, then it is called a conjoint type of vascular bundles. Conjoint vascular bundles are found in stems and leaves.
Roots possess radial vascular bundles, in which the xylem and the phloem are arranged in an alternate manner along the different radii within the vascular bundle.
Hence, the correct answer is an option (B)
Note: The cells between two vascular bundles are called medullary rays. During the secondary growth of the dicot stems, these medullary rays become meristematic and form the interfascicular cambium. Hence, interfascicular and intrafascicular cambium together constitute a cambial ring in the stem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




