
What is an orbital? Draw the shapes of the 1s, 2s, $\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}_{\text{x}}}\text{ }$ , $\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}_{\text{y}}}\text{ }$,$\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}_{\text{z}}}\text{ }$, $\text{ 3}{{\text{d}}_{\text{xy}}}\text{ }$ , $\text{ 3}{{\text{d}}_{\text{yz}}}\text{ }$, $\text{ 3}{{\text{d}}_{\text{xz }}}\text{ }$,$\text{ 3}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}-{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}\text{ }$and $\text{ 3}{{\text{d}}_{{{z}^{2}}}}\text{ }$orbitals.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Orbitals are the regions in the atom in which electrons are more likely to be found. Three are four different types of orbitals. These are s, p , d , and f .s is a spherical orbital, p is a dumbbell-shaped orbital, d are a double dumbbell-shaped orbital and f orbitals have a more complex structure.
Complete Solution :
An orbital is a three-dimensional representation of a region in which the electrons are more likely to be found around the atom.in atomic orbitals, the orbital is the mathematical function that describes the location of an electron in the atom. Each orbital of an atom has a unique set of three quantum numbers which are principal quantum number(n), azimuthal quantum number (l), and magnetic quantum number (m) .this orbitals have a characteristic shape. This is as follows:
1) s-orbital:
It is a completely spherical and symmetrical orbital. These orbitals are closest to the nucleus.as the principal quantum number increases these orbitals get bigger. The order of the s-orbitals is as follows,
$\text{ 1s }<\text{ 2s }<\text{ 3s }<\text{ 4s }$
S orbitals do not have a node. The s orbital is as shown below,
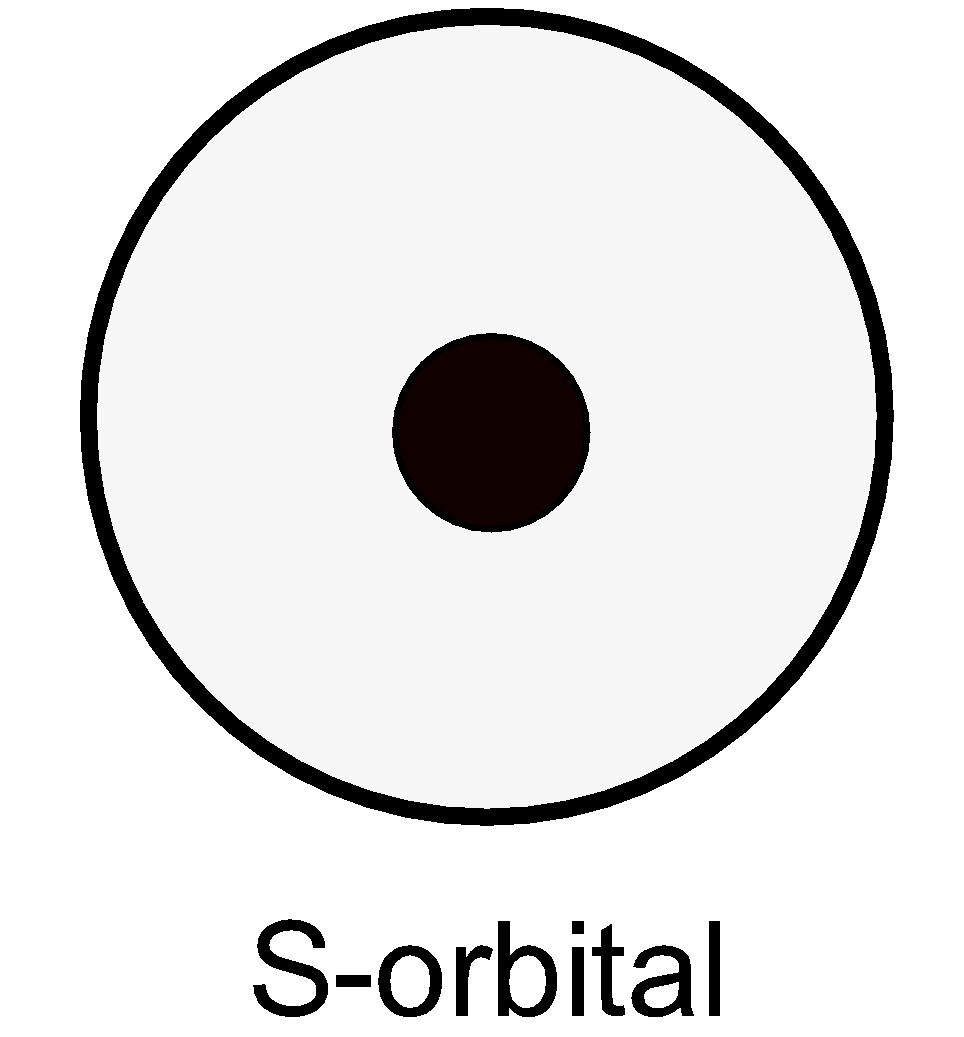
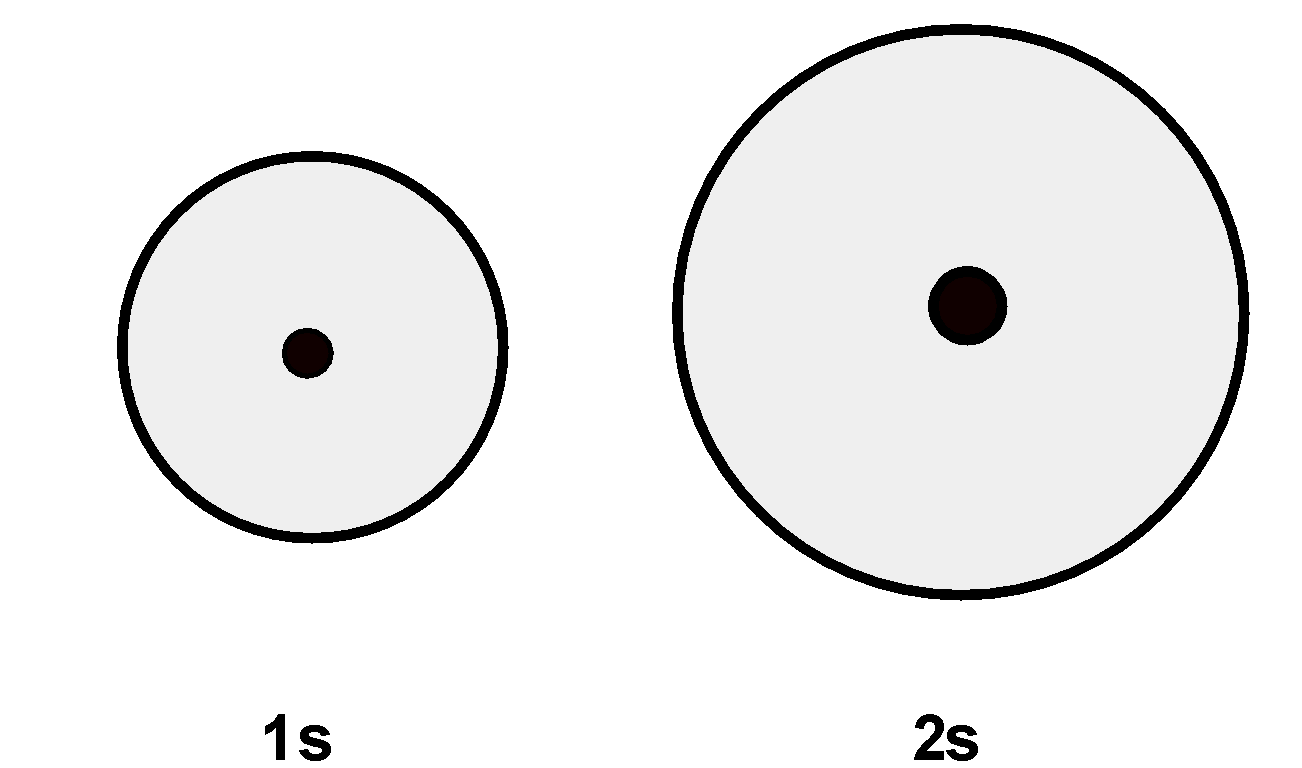
The 1 s and 2s orbital are drawn as follows,
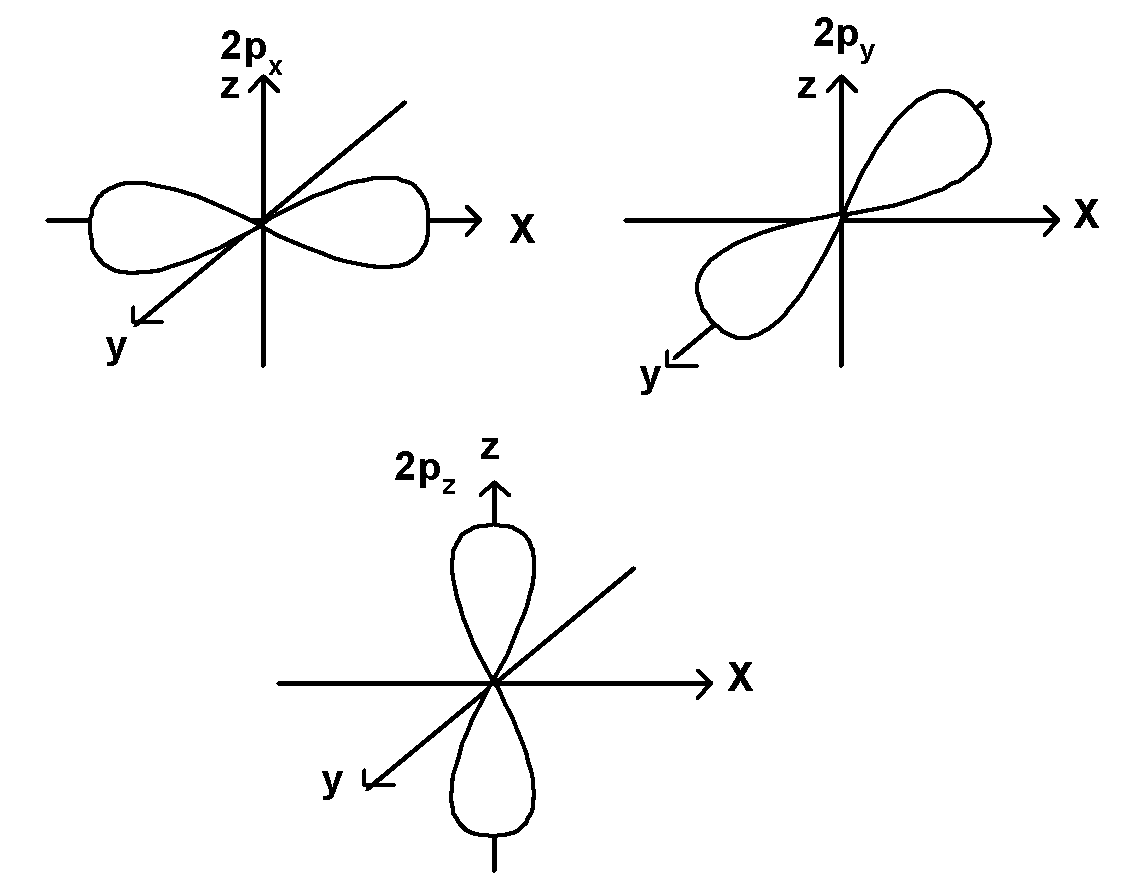
2) p-orbital:
It is a dumbbell-shaped orbital. p orbitals have a node. The p orbitals can occupy six electrons as there are a total of three p orbitals. This three p orbitals are mutually perpendicular to each other and aligned towards the three axes x, y and these three p-orbitals are shown below,
3) d-orbital:
d orbital is double dumbbell-shaped orbitals. This has a cloverleaf shape in the plane. ‘d’ orbitals have an azimuthal quantum number equal to 2 and the minimum quantum number for d-orbitals are 3.the value for the ‘l’ can range from $\text{ }-2\text{ , }-1\text{ , 0 , +1 , +2 }$ . Thus there are a total of five d-orbitals. These 5 d orbitals are designated as $\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{\text{xy}}}\text{ }$ , $\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{\text{yz}}}\text{ }$, $\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{\text{xz }}}\text{ }$,$\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}-{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}\text{ }$ and $\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{{{z}^{2}}}}\text{ }$. The five orbitals for principal quantum number 3 are as shown below,
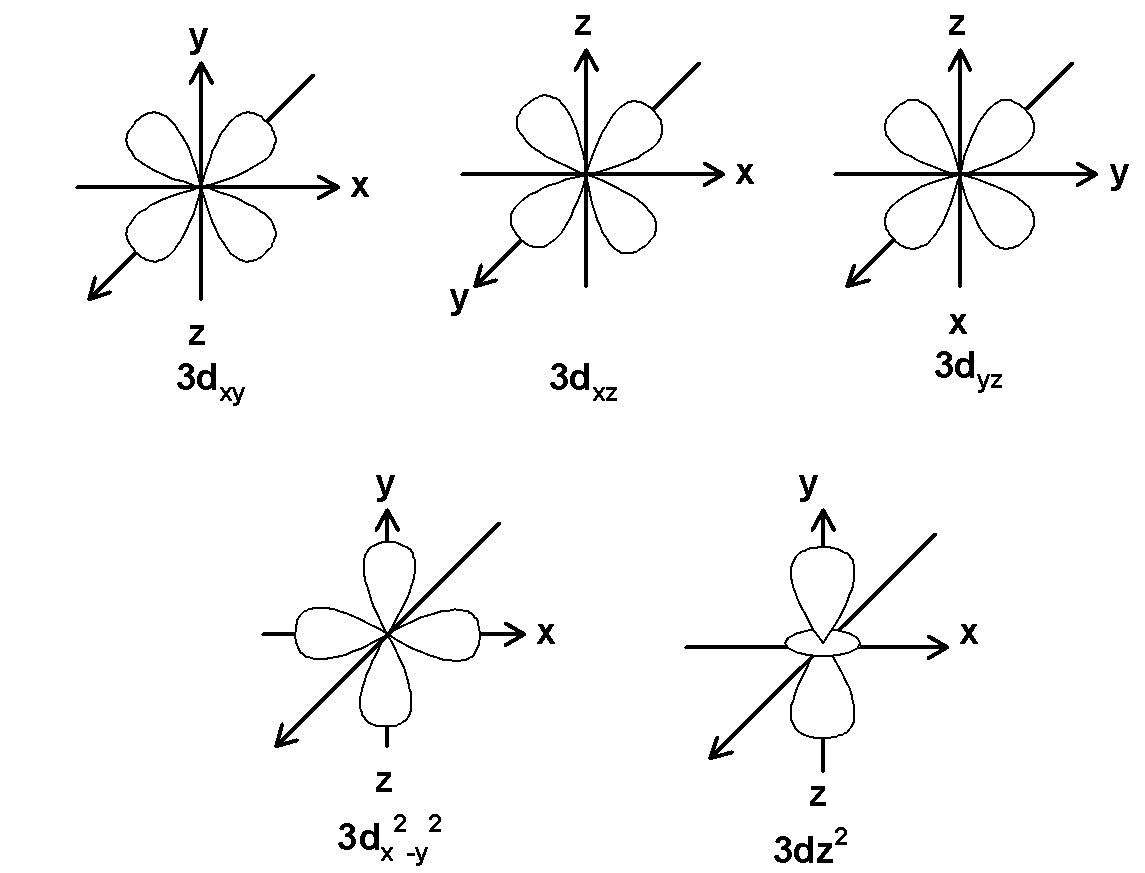
Note: Note that, orbitals show the probability of finding an electron in an atom. There are 4 orbitals and their names as s stand for sharp, p for principle, d for diffuse, and f for fundamental. S orbital shield nucleus well but p, d, or f orbitals have a diffused shape thus shields the nucleus poorly.
Complete Solution :
An orbital is a three-dimensional representation of a region in which the electrons are more likely to be found around the atom.in atomic orbitals, the orbital is the mathematical function that describes the location of an electron in the atom. Each orbital of an atom has a unique set of three quantum numbers which are principal quantum number(n), azimuthal quantum number (l), and magnetic quantum number (m) .this orbitals have a characteristic shape. This is as follows:
1) s-orbital:
It is a completely spherical and symmetrical orbital. These orbitals are closest to the nucleus.as the principal quantum number increases these orbitals get bigger. The order of the s-orbitals is as follows,
$\text{ 1s }<\text{ 2s }<\text{ 3s }<\text{ 4s }$
S orbitals do not have a node. The s orbital is as shown below,

The 1 s and 2s orbital are drawn as follows,

2) p-orbital:
It is a dumbbell-shaped orbital. p orbitals have a node. The p orbitals can occupy six electrons as there are a total of three p orbitals. This three p orbitals are mutually perpendicular to each other and aligned towards the three axes x, y and these three p-orbitals are shown below,

3) d-orbital:
d orbital is double dumbbell-shaped orbitals. This has a cloverleaf shape in the plane. ‘d’ orbitals have an azimuthal quantum number equal to 2 and the minimum quantum number for d-orbitals are 3.the value for the ‘l’ can range from $\text{ }-2\text{ , }-1\text{ , 0 , +1 , +2 }$ . Thus there are a total of five d-orbitals. These 5 d orbitals are designated as $\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{\text{xy}}}\text{ }$ , $\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{\text{yz}}}\text{ }$, $\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{\text{xz }}}\text{ }$,$\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}-{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}\text{ }$ and $\text{ }{{\text{d}}_{{{z}^{2}}}}\text{ }$. The five orbitals for principal quantum number 3 are as shown below,

Note: Note that, orbitals show the probability of finding an electron in an atom. There are 4 orbitals and their names as s stand for sharp, p for principle, d for diffuse, and f for fundamental. S orbital shield nucleus well but p, d, or f orbitals have a diffused shape thus shields the nucleus poorly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




