
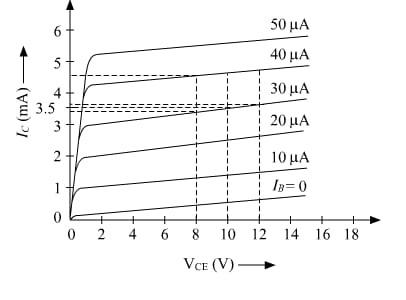
Output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration are shown in the figure. Determine:
i. Dynamic output resistance
ii. Dc current gain
iii. Ac current gain at an operating point ${{V}_{CE}}=10V,{{I}_{B}}=30\mu A$

Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: Output characteristics graph is the plot between output current and output voltage at a constant input current. This graph shows the variation in output current according to the output voltage keeping constant input current. We can find the value of current and voltage at different intervals of time.
Formulae used:
\[{{R}_{o}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{CE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{C}}} \right)}_{{{I}_{B}}=\text{constant}}}\]
${{\beta }_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}$
${{\beta }_{AC}}=\dfrac{\Delta {{I}_{C}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Output characteristics are the variation of collector current, say ${{I}_{C}}$, with the collector emitter voltage, say ${{V}_{CE}}$.
Dynamic output resistance or output impedance is defined as a measure of the source’s propensity to drop in voltage when the load draws some current through the circuit. It can also be called as source impedance.
Calculating dynamic resistance,
\[\begin{align}
& {{R}_{o}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{CE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{C}}} \right)}_{{{I}_{B}}=\text{constant}}} \\
& =\dfrac{12-8}{(3.6-3.4)\times {{10}^{-3}}} \\
& =\dfrac{4}{0.2\times {{10}^{-3}}}=20\times {{10}^{3}}
\end{align}\]
${{R}_{o}}=20k\Omega $
For an n-p-n transistor, current gain is the ratio of the two currents ${{I}_{C}}$ (Collector current) and ${{I}_{B}}$ (Base current). It is denoted by the symbol Beta, $\beta $ .
Calculating DC current gain,
${{\beta }_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}$
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{CE}}=10V,\text{ and }{{I}_{B}}=30\mu A \\
& {{I}_{C}}=3.5m\alpha \\
\end{align}$
Now, ${{\beta }_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}=\dfrac{3.5mA}{30\mu A}=\dfrac{3.5\times {{10}^{-3}}}{30\times {{10}^{-6}}}=117$
${{\beta }_{DC}}=117$
Since current gain is the ratio of similar quantities, it has no units.
AC current gain of a transistor is defined as the ratio of change in Collector current and change in base current for a fixed time interval.
Calculating AC current gain,
${{\beta }_{AC}}=\dfrac{\Delta {{I}_{C}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}}$
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{C}}=10V,\Delta {{I}_{B}}=40-30=10 \\
& \Delta {{I}_{B}}=10\mu A \\
& \Delta {{I}_{C}}=4.7-3.5=1.2 \\
& \Delta {{I}_{C}}=1.2mA \\
\end{align}$
Now,
\[\begin{align}
& {{\beta }_{AC}}=\dfrac{\Delta {{I}_{C}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}}=\dfrac{1.2mA}{10\mu A}=\dfrac{1.2\times {{10}^{-3}}}{10\times {{10}^{-6}}}=120 \\
& {{\beta }_{AC}}=120 \\
\end{align}\]
Value of dynamic resistance is ${{R}_{o}}=20k\Omega $
Value of DC current gain ${{\beta }_{DC}}=117$
Value of AC current gain \[{{\beta }_{AC}}=120\]
Note: Students should know the difference between DC current gain and AC current gain and how to find their values. DC current gain is calculated at fixed values of Collector current and Base current while AC current gain is calculated taking the change in values of Collector current and Base current for some fixed interval of time.
Formulae used:
\[{{R}_{o}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{CE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{C}}} \right)}_{{{I}_{B}}=\text{constant}}}\]
${{\beta }_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}$
${{\beta }_{AC}}=\dfrac{\Delta {{I}_{C}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Output characteristics are the variation of collector current, say ${{I}_{C}}$, with the collector emitter voltage, say ${{V}_{CE}}$.
Dynamic output resistance or output impedance is defined as a measure of the source’s propensity to drop in voltage when the load draws some current through the circuit. It can also be called as source impedance.
Calculating dynamic resistance,
\[\begin{align}
& {{R}_{o}}={{\left( \dfrac{\Delta {{V}_{CE}}}{\Delta {{I}_{C}}} \right)}_{{{I}_{B}}=\text{constant}}} \\
& =\dfrac{12-8}{(3.6-3.4)\times {{10}^{-3}}} \\
& =\dfrac{4}{0.2\times {{10}^{-3}}}=20\times {{10}^{3}}
\end{align}\]
${{R}_{o}}=20k\Omega $
For an n-p-n transistor, current gain is the ratio of the two currents ${{I}_{C}}$ (Collector current) and ${{I}_{B}}$ (Base current). It is denoted by the symbol Beta, $\beta $ .
Calculating DC current gain,
${{\beta }_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}$
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{CE}}=10V,\text{ and }{{I}_{B}}=30\mu A \\
& {{I}_{C}}=3.5m\alpha \\
\end{align}$
Now, ${{\beta }_{DC}}=\dfrac{{{I}_{C}}}{{{I}_{B}}}=\dfrac{3.5mA}{30\mu A}=\dfrac{3.5\times {{10}^{-3}}}{30\times {{10}^{-6}}}=117$
${{\beta }_{DC}}=117$
Since current gain is the ratio of similar quantities, it has no units.
AC current gain of a transistor is defined as the ratio of change in Collector current and change in base current for a fixed time interval.
Calculating AC current gain,
${{\beta }_{AC}}=\dfrac{\Delta {{I}_{C}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}}$
$\begin{align}
& {{V}_{C}}=10V,\Delta {{I}_{B}}=40-30=10 \\
& \Delta {{I}_{B}}=10\mu A \\
& \Delta {{I}_{C}}=4.7-3.5=1.2 \\
& \Delta {{I}_{C}}=1.2mA \\
\end{align}$
Now,
\[\begin{align}
& {{\beta }_{AC}}=\dfrac{\Delta {{I}_{C}}}{\Delta {{I}_{B}}}=\dfrac{1.2mA}{10\mu A}=\dfrac{1.2\times {{10}^{-3}}}{10\times {{10}^{-6}}}=120 \\
& {{\beta }_{AC}}=120 \\
\end{align}\]
Value of dynamic resistance is ${{R}_{o}}=20k\Omega $
Value of DC current gain ${{\beta }_{DC}}=117$
Value of AC current gain \[{{\beta }_{AC}}=120\]
Note: Students should know the difference between DC current gain and AC current gain and how to find their values. DC current gain is calculated at fixed values of Collector current and Base current while AC current gain is calculated taking the change in values of Collector current and Base current for some fixed interval of time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




