
Oxidation numbers of ${\text{P}}$ in ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$, of ${\text{S}}$ in ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ and that of ${\text{Cr}}$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$are respectively:
A) $ + 3, + 6{\text{ and }} + 5$
B) $ + 5, + 3{\text{ and }} + 6$
C) $ + 3, + 6{\text{ and }} + 6$
D) $ + 5, + 6{\text{ and }} + 6$
Answer
561.6k+ views
Hint: Oxidation number is the charge acquired by the species may be positive, negative or zero by gain or loss of electrons. To solve this we must know the oxidation number of oxygen. The charge on oxygen atoms is $ - 2$.
Complete answer:
First let us draw the structures of ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$, ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ and ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$. The structures are as follows:
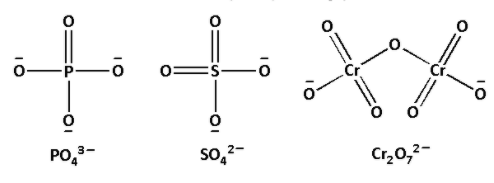
We are given a polyatomic anion ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$. In the given polyatomic anion, we have to find the oxidation number of ${\text{P}}$.
We know that the charge on an oxygen atom is $ - 2$.
We know that the sum of all the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion. Thus, the total charge on the polyatomic anion is $ - 3$. Thus,
Charge on ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ $ = {\text{ON of P}} + 4 \times \left( {{\text{ON of O}}} \right)$
Substitute $ - 3$ for the charge on ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$, x for the oxidation number of ${\text{P}}$ and $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{O}}$. Thus,
$\Rightarrow - 3 = \left( x \right) + \left( {{\text{4}} \times \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)$
$\Rightarrow x = - 3 + 8$
$\Rightarrow x = + 5$
Thus, the oxidation number of ${\text{P}}$ in ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ is $ + 5$.
We are given a polyatomic anion ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$. In the given polyatomic anion, we have to find the oxidation number of ${\text{S}}$.
We know that the charge on an oxygen atom is $ - 2$.
We know that the sum of all the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion. Thus, the total charge on the polyatomic anion is $ - 2$. Thus,
Charge on ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ $ = {\text{ON of S}} + 4 \times \left( {{\text{ON of O}}} \right)$
Substitute $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$, x for the oxidation number of ${\text{S}}$ and $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{O}}$. Thus,
$\Rightarrow - 2 = \left( x \right) + \left( {{\text{4}} \times \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)$
$\Rightarrow x = - 2 + 8$
$\Rightarrow x = + 6$
Thus, the oxidation number of ${\text{S}}$ in ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ is $ + 6$.
We are given a polyatomic anion ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$. In the given polyatomic anion, we have to find the oxidation number of ${\text{Cr}}$.
We know that the charge on an oxygen atom is $ - 2$.
We know that the sum of all the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion. Thus, the total charge on the polyatomic anion is $ - 2$. Thus,
Charge on ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$ $ = 2 \times \left( {{\text{ON of Cr}}} \right) + 7 \times \left( {{\text{ON of O}}} \right)$
Substitute $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$, x for the oxidation number of ${\text{Cr}}$ and $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{O}}$. Thus,
$\Rightarrow - 2 = \left( {2x} \right) + \left( {{\text{7}} \times \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)$
$\Rightarrow 2x = - 2 + 14$
$\Rightarrow 2x = - 12$
$\Rightarrow x = + 6$
The oxidation number of ${\text{Cr}}$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$ is $ + 6$.
Thus, oxidation numbers of ${\text{P}}$ in ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$, of ${\text{S}}$ in ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ and that of ${\text{Cr}}$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$are respectively $ + 5, + 6{\text{ and }} + 6$.
Thus, the correct answer is option (D) $ + 5, + 6{\text{ and }} + 6$.
Note: Rules for assigning the oxidation number to elements are as follows:
i) The oxidation number of an element in its free or uncombined state is always zero.
ii) The oxidation number of monatomic ions is the same as that of the positive or negative charge on the ion.
iii) The sum of all the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is zero.
iv) The sum of oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the total charge on the polyatomic ion.
v) The oxidation number of alkali metals is always $ + 1$.
vi) The oxidation number of alkaline earth metals is always $ + 2$.
vii) The oxidation number of hydrogen is always $ + 1$.
viii) The oxidation number of oxygen is always $ - 2$.
Complete answer:
First let us draw the structures of ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$, ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ and ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$. The structures are as follows:

We are given a polyatomic anion ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$. In the given polyatomic anion, we have to find the oxidation number of ${\text{P}}$.
We know that the charge on an oxygen atom is $ - 2$.
We know that the sum of all the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion. Thus, the total charge on the polyatomic anion is $ - 3$. Thus,
Charge on ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ $ = {\text{ON of P}} + 4 \times \left( {{\text{ON of O}}} \right)$
Substitute $ - 3$ for the charge on ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$, x for the oxidation number of ${\text{P}}$ and $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{O}}$. Thus,
$\Rightarrow - 3 = \left( x \right) + \left( {{\text{4}} \times \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)$
$\Rightarrow x = - 3 + 8$
$\Rightarrow x = + 5$
Thus, the oxidation number of ${\text{P}}$ in ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$ is $ + 5$.
We are given a polyatomic anion ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$. In the given polyatomic anion, we have to find the oxidation number of ${\text{S}}$.
We know that the charge on an oxygen atom is $ - 2$.
We know that the sum of all the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion. Thus, the total charge on the polyatomic anion is $ - 2$. Thus,
Charge on ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ $ = {\text{ON of S}} + 4 \times \left( {{\text{ON of O}}} \right)$
Substitute $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$, x for the oxidation number of ${\text{S}}$ and $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{O}}$. Thus,
$\Rightarrow - 2 = \left( x \right) + \left( {{\text{4}} \times \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)$
$\Rightarrow x = - 2 + 8$
$\Rightarrow x = + 6$
Thus, the oxidation number of ${\text{S}}$ in ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ is $ + 6$.
We are given a polyatomic anion ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$. In the given polyatomic anion, we have to find the oxidation number of ${\text{Cr}}$.
We know that the charge on an oxygen atom is $ - 2$.
We know that the sum of all the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge on the ion. Thus, the total charge on the polyatomic anion is $ - 2$. Thus,
Charge on ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$ $ = 2 \times \left( {{\text{ON of Cr}}} \right) + 7 \times \left( {{\text{ON of O}}} \right)$
Substitute $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$, x for the oxidation number of ${\text{Cr}}$ and $ - 2$ for the charge on ${\text{O}}$. Thus,
$\Rightarrow - 2 = \left( {2x} \right) + \left( {{\text{7}} \times \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)$
$\Rightarrow 2x = - 2 + 14$
$\Rightarrow 2x = - 12$
$\Rightarrow x = + 6$
The oxidation number of ${\text{Cr}}$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$ is $ + 6$.
Thus, oxidation numbers of ${\text{P}}$ in ${\text{PO}}_4^{3 - }$, of ${\text{S}}$ in ${\text{SO}}_4^{2 - }$ and that of ${\text{Cr}}$ in ${\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }$are respectively $ + 5, + 6{\text{ and }} + 6$.
Thus, the correct answer is option (D) $ + 5, + 6{\text{ and }} + 6$.
Note: Rules for assigning the oxidation number to elements are as follows:
i) The oxidation number of an element in its free or uncombined state is always zero.
ii) The oxidation number of monatomic ions is the same as that of the positive or negative charge on the ion.
iii) The sum of all the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is zero.
iv) The sum of oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the total charge on the polyatomic ion.
v) The oxidation number of alkali metals is always $ + 1$.
vi) The oxidation number of alkaline earth metals is always $ + 2$.
vii) The oxidation number of hydrogen is always $ + 1$.
viii) The oxidation number of oxygen is always $ - 2$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




