
What is the oxidation product of thiols?
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: As we know that oxidation can be defined as the loss of electrons by the chemical species. It can also be done by the gain of oxygen atom or by the loss of hydrogen atom. Since thiol is the organosulfur compound which can also be said as a sulphur derivative of alcohol group. So we need to find the oxidation product of this compound.
Complete answer:
We should know that various product formations take place during the oxidation of a thiol compound. There are two methods for the oxidation of thiols:-
(A) Oxidation of thiol by gain of oxygen atom:-
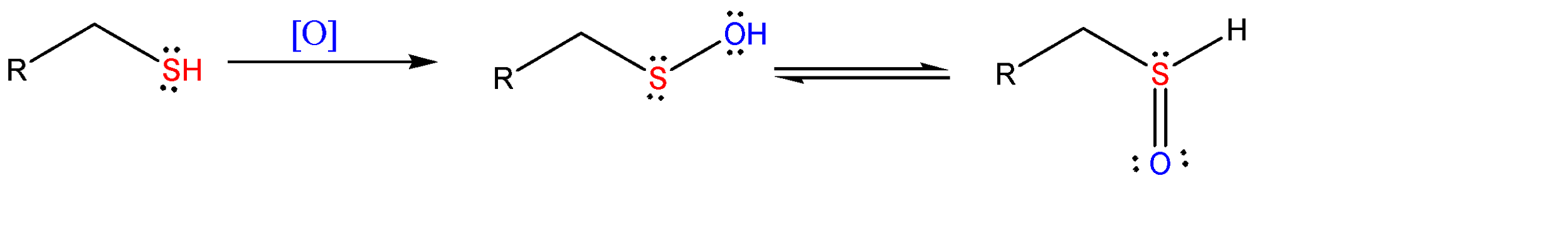
When a thiol is oxidized by using an oxidizing agent, it forms a short lived intermediate species which is known as sulfenic acid. This sulfenic acid keeps tautomerising and forms keto-enol intermediates for a short time..
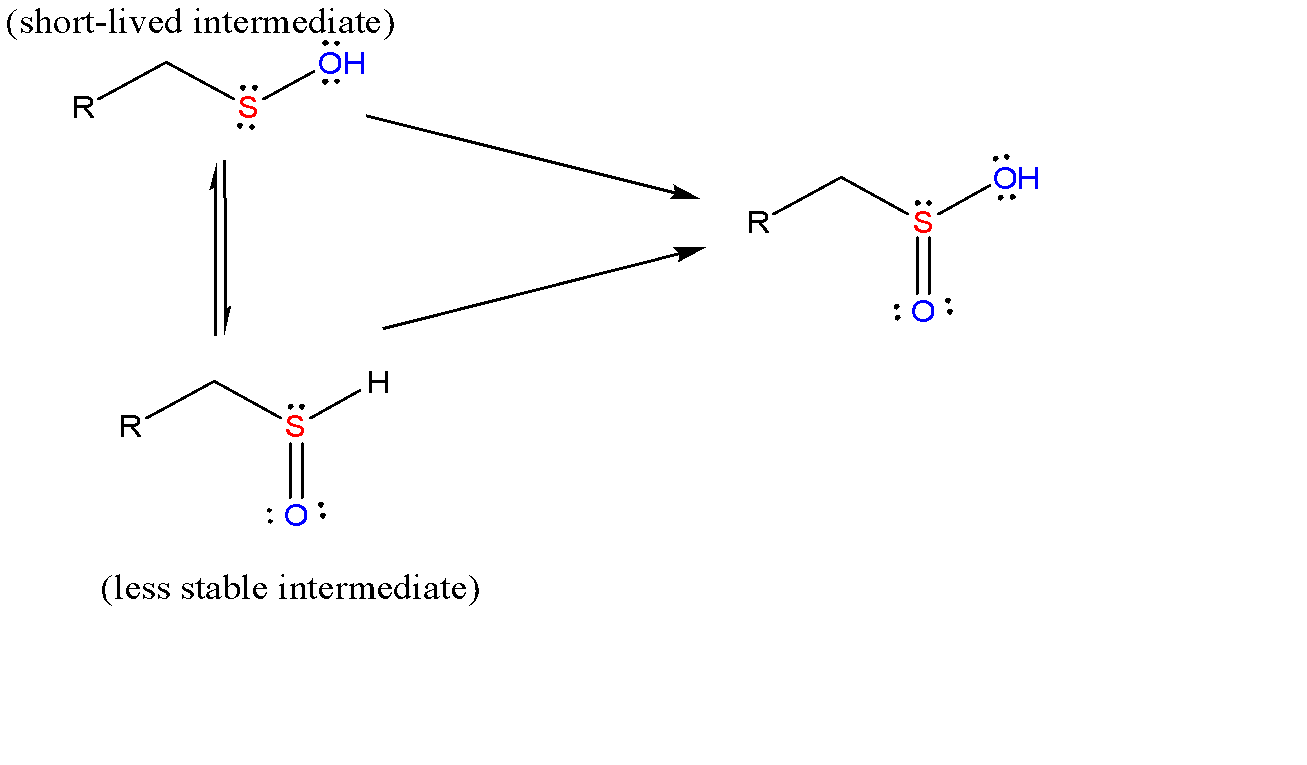
Then this sulfenic acid further oxidizes to give sulfinic acid. These are the oxoacids of sulphur where sulphur is in pyramidal shape.
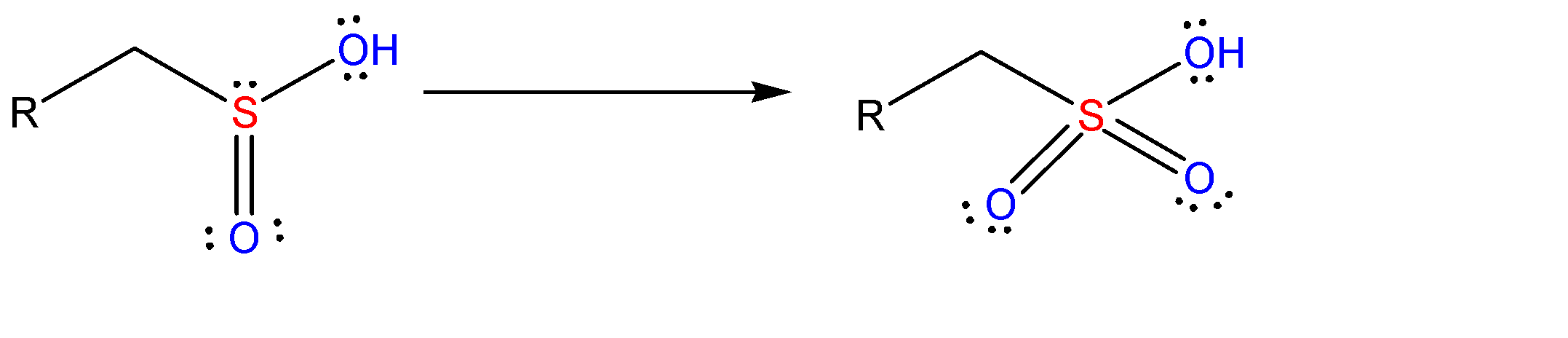
At the end it forms sulfonic acid which is the final product of this reaction. These are very strong acids.
(B) Oxidation of thiol by loss of hydrogen atom:-

In this reaction, the oxidation occurs by the loss of hydrogen atom that was attached to the sulfur atom and this sulfur atom combines with sulphur atom of another molecule to form disulfide bond (-S-S-).
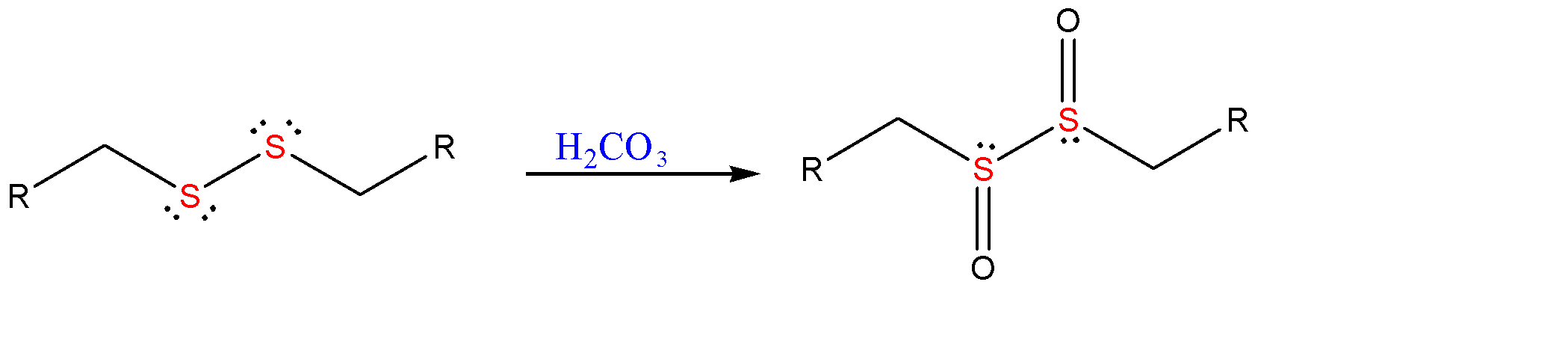
When disulfide bond is formed, it is further oxidized by the help of carbonic acid (${{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}$ ) to form a hypervalent species called sulfones.
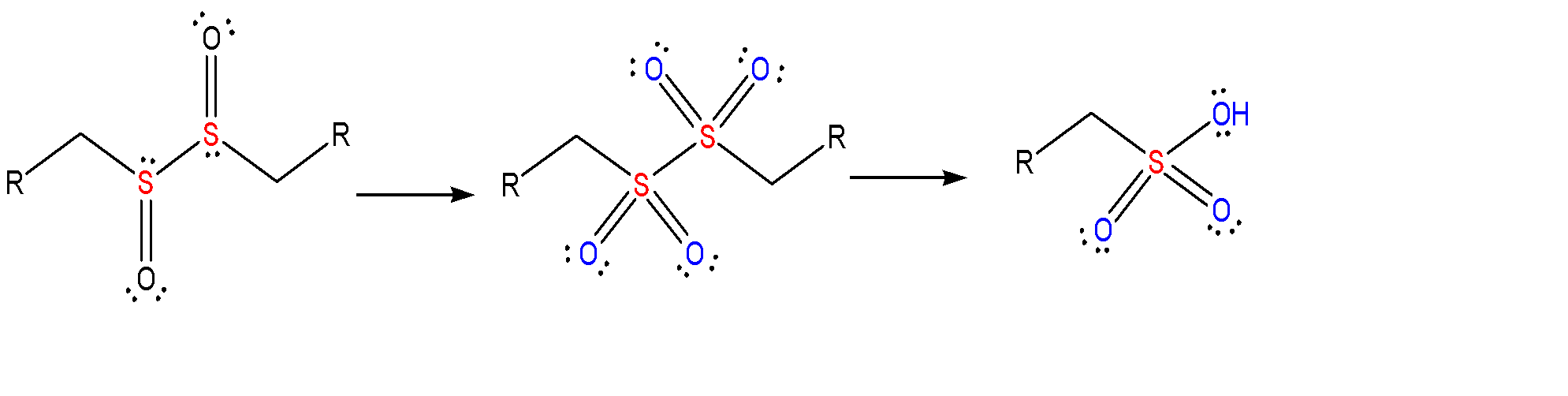
These sulfones continue to oxidize further which eventually leads to the formation of sulfonic acid.
Note:
-We can also use nitric acid instead of carbonic acid to further oxidize the disulfide bonds.
-Remember that oxidizing a thiol by using hydrogen peroxide (${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ ) is simple to perform but difficult to understand because many products can form during this reaction.
Complete answer:
We should know that various product formations take place during the oxidation of a thiol compound. There are two methods for the oxidation of thiols:-
(A) Oxidation of thiol by gain of oxygen atom:-

When a thiol is oxidized by using an oxidizing agent, it forms a short lived intermediate species which is known as sulfenic acid. This sulfenic acid keeps tautomerising and forms keto-enol intermediates for a short time..

Then this sulfenic acid further oxidizes to give sulfinic acid. These are the oxoacids of sulphur where sulphur is in pyramidal shape.

At the end it forms sulfonic acid which is the final product of this reaction. These are very strong acids.
(B) Oxidation of thiol by loss of hydrogen atom:-

In this reaction, the oxidation occurs by the loss of hydrogen atom that was attached to the sulfur atom and this sulfur atom combines with sulphur atom of another molecule to form disulfide bond (-S-S-).
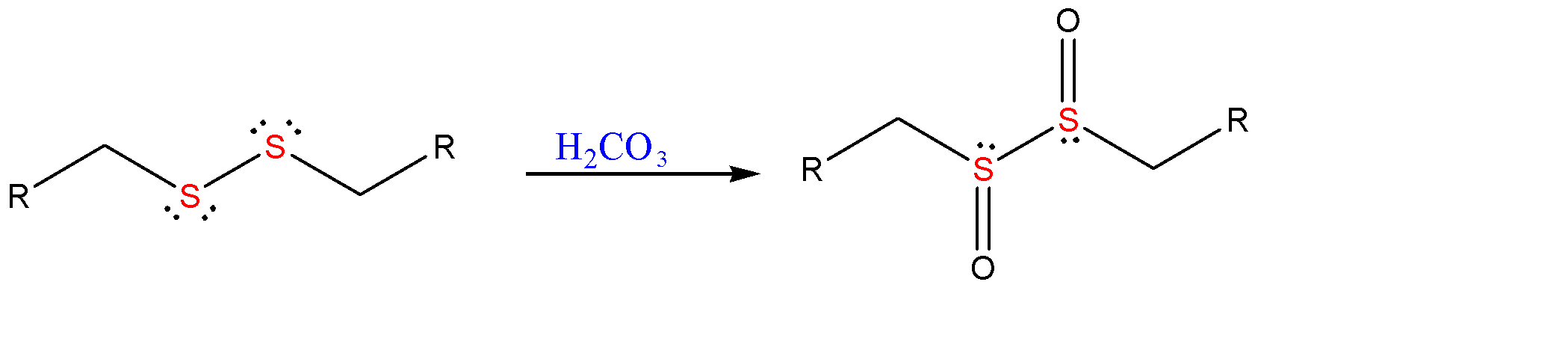
When disulfide bond is formed, it is further oxidized by the help of carbonic acid (${{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}$ ) to form a hypervalent species called sulfones.

These sulfones continue to oxidize further which eventually leads to the formation of sulfonic acid.
Note:
-We can also use nitric acid instead of carbonic acid to further oxidize the disulfide bonds.
-Remember that oxidizing a thiol by using hydrogen peroxide (${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ ) is simple to perform but difficult to understand because many products can form during this reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




