
Oxygen dissociation curve of hemoglobin is
A. Sigmoid
B. Hyperbolic.
C. Linear
D. Hyperbolic
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Hemoglobin in the combination of heme and globin, which red pigment present in the cytoplasm of the red blood cells, where it helps in the transport of oxygen to all body parts and to carry deoxygenated blood to purify to the lungs.
Complete answer:
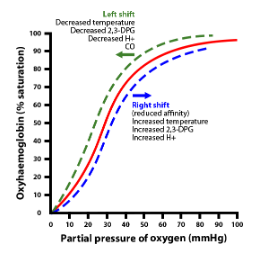
The hemoglobin dissociation curve is also known as the oxy dissociation curve.
The curve is obtained by plotting the graph where the saturation of oxygen in the vertical axis and oxygen affinity or partial pressure in the horizontal axis.
The Oxyhemoglobin curve which obtains is usually a sigmoid in shape.
Mainly it tells about the affinity of oxygen to the hemoglobin and how the hemoglobin carries oxygen.
One heme can carry the four oxygen molecules, the association of oxygen with heme is very difficult, but it occurs if the partial pressure is high, once one oxygen molecule attaches to the hemoglobin, it’s shape changes so that 2nd, 3rd and 4th is easily attached.
In case of more dissolved carbon dioxide, the affinity of oxygen decreases as the partial pressure of oxygen is low, the shape of hemoglobin changes and the slowly carbon dioxide gets attached with hemoglobin and all oxygen molecules get released.
Left shift occurs in the lungs, where the affinity of the oxygen is more.
Right shift occurs in case of low oxygen affinity, and high carbon dioxide concentration, and increase in the body temperature, increase in hydrogen ions and increase in 2- bisphosphoglycerate.
Note:
Oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve is somewhat different in the fetus, compare to adults, in fetus the affinity of oxygen is more and left relative shifting occurs because in fetal hemoglobin, it consists of 2 alpha and 2 gamma chains, while in adults it is 2 alpha and 2 beta chains.
Complete answer:

The hemoglobin dissociation curve is also known as the oxy dissociation curve.
The curve is obtained by plotting the graph where the saturation of oxygen in the vertical axis and oxygen affinity or partial pressure in the horizontal axis.
The Oxyhemoglobin curve which obtains is usually a sigmoid in shape.
Mainly it tells about the affinity of oxygen to the hemoglobin and how the hemoglobin carries oxygen.
One heme can carry the four oxygen molecules, the association of oxygen with heme is very difficult, but it occurs if the partial pressure is high, once one oxygen molecule attaches to the hemoglobin, it’s shape changes so that 2nd, 3rd and 4th is easily attached.
In case of more dissolved carbon dioxide, the affinity of oxygen decreases as the partial pressure of oxygen is low, the shape of hemoglobin changes and the slowly carbon dioxide gets attached with hemoglobin and all oxygen molecules get released.
Left shift occurs in the lungs, where the affinity of the oxygen is more.
Right shift occurs in case of low oxygen affinity, and high carbon dioxide concentration, and increase in the body temperature, increase in hydrogen ions and increase in 2- bisphosphoglycerate.
Note:
Oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve is somewhat different in the fetus, compare to adults, in fetus the affinity of oxygen is more and left relative shifting occurs because in fetal hemoglobin, it consists of 2 alpha and 2 gamma chains, while in adults it is 2 alpha and 2 beta chains.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




