
Oxygen molecule is formed by:
A.One axial s-s overlap and one p-p axial overlap
B.Two p-p axial overlap
C.Two p-p sidewise overlap
D.One p-p axial and one p-p sidewise overlap
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: Each oxygen atom has three p orbitals which are perpendicular to each other and hence can overlap axially as well as sidewise.
Complete step by step answer:
The electronic configuration of Oxygen is \[{\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 2}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 2p}}_x^2{\text{ 2p}}_y^1{\text{ 2p}}_z^1{\text{ }}\].
So, p orbitals of a single oxygen atom would look like –
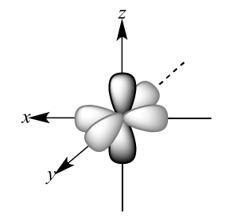
All the 2p orbitals are perpendicular to each other. So, \[{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}_z}{\text{ }}\]orbitals of each oxygen atom will overlap sidewise to form a sigma bond. \[{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}_y}\] orbitals of each oxygen would overlap axially forming a pi bond. So, a double bond will be formed between the two oxygen atoms, out of which one will be \[{{\text{p}}_z}{\text{ - }}{{\text{p}}_z}\] sigma bond and the other will be \[{{\text{p}}_y}{\text{ - }}{{\text{p}}_y}\] pi bond. So, the structure of the molecule will be –
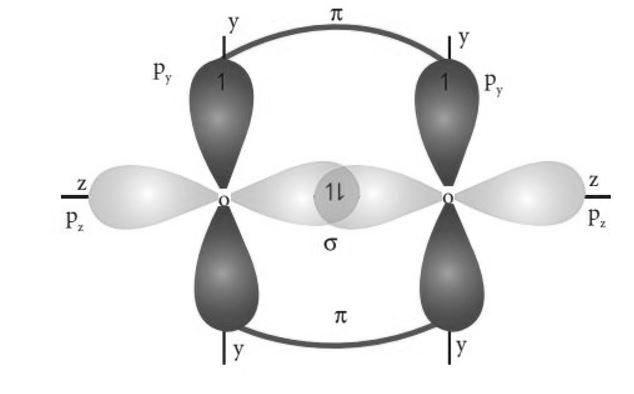
Hence, option D is correct.
Additional information: Oxygen is the most abundant available element in the earth. It is denoted by the symbol O and is categorized under the chalcogen group in the periodic table. It is colourless, odourless, tasteless gas which easily dissolves in water. It is essential for survival of human beings.
It is used in the production and manufacturing of glass and stone products, and in mining. Special oxygen chambers are used in case of high pressure to increase the partial pressure of oxygen around the patient. The primary applications of oxygen include melting, refining, and manufacture of steel along with other metals.
Note: Oxygen requires two electrons to complete its octet. It shares these two electrons with another oxygen atom and hence always exists as a diatomic molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
The electronic configuration of Oxygen is \[{\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 2}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 2p}}_x^2{\text{ 2p}}_y^1{\text{ 2p}}_z^1{\text{ }}\].
So, p orbitals of a single oxygen atom would look like –

All the 2p orbitals are perpendicular to each other. So, \[{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}_z}{\text{ }}\]orbitals of each oxygen atom will overlap sidewise to form a sigma bond. \[{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}_y}\] orbitals of each oxygen would overlap axially forming a pi bond. So, a double bond will be formed between the two oxygen atoms, out of which one will be \[{{\text{p}}_z}{\text{ - }}{{\text{p}}_z}\] sigma bond and the other will be \[{{\text{p}}_y}{\text{ - }}{{\text{p}}_y}\] pi bond. So, the structure of the molecule will be –

Hence, option D is correct.
Additional information: Oxygen is the most abundant available element in the earth. It is denoted by the symbol O and is categorized under the chalcogen group in the periodic table. It is colourless, odourless, tasteless gas which easily dissolves in water. It is essential for survival of human beings.
It is used in the production and manufacturing of glass and stone products, and in mining. Special oxygen chambers are used in case of high pressure to increase the partial pressure of oxygen around the patient. The primary applications of oxygen include melting, refining, and manufacture of steel along with other metals.
Note: Oxygen requires two electrons to complete its octet. It shares these two electrons with another oxygen atom and hence always exists as a diatomic molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




