
When p- aminophenol reacts with one molar equivalent of acetic anhydride, a compound A $({{C}_{8}}{{H}_{9}}N{{O}_{2}})$is formed that dissolves in dilute NaOH. When A is treated with one equivalent of NaOH followed by ethyl iodide, an ethyl ether B is formed.
Calculate the total number of delocalized $\pi \,{{e}^{-}}s$ in compound B.
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint:Delocalized pi electrons are the electrons that are present in the pi bond. These electrons get delocalized to provide stability to the molecule in the condition of resonance. These electrons move from the nuclei of one atom to another.
Complete step-by-step answer:We have been given a series of reactions that the compound, para- aminophenol undergoes. First it reacts with 1 equimolar of acetic anhydride, ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}}CO \right)}_{2}}O$, through this reaction it forms compound A which has a amide bond in place of amine with hydroxyl on para position. This compound dissolves in NaOH and removes the proton from the hydroxyl group. Now this compound reacts with ethyl iodide to form an aromatic compound that contains an amide group and an ethyl ether. The reactions are as follows:
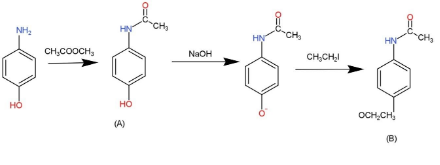
The delocalization of pi bonds in compound B is, as, the amide bond contains 1 double bond so, 2 pi electrons, the carbon ring has 3 double bonds that means 6 pi electrons, while the ether contains 1 double bond in carbonyl group so 2 pi electrons.
So, number of $\pi \,{{e}^{-}}s$= 2 + 6 + 2
Number of $\pi \,{{e}^{-}}s$= 10
Hence, the compound B contains 10$\pi \,{{e}^{-}}s$ that results in delocalization.
Note:As sigma bond is the basis of pi bond, so wherever there is a double bond, that means 2 pi electrons, and in triple bonds 4 pi electrons. The compound A formed is known as paracetamol, which is used as a medicine.
Complete step-by-step answer:We have been given a series of reactions that the compound, para- aminophenol undergoes. First it reacts with 1 equimolar of acetic anhydride, ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}}CO \right)}_{2}}O$, through this reaction it forms compound A which has a amide bond in place of amine with hydroxyl on para position. This compound dissolves in NaOH and removes the proton from the hydroxyl group. Now this compound reacts with ethyl iodide to form an aromatic compound that contains an amide group and an ethyl ether. The reactions are as follows:

The delocalization of pi bonds in compound B is, as, the amide bond contains 1 double bond so, 2 pi electrons, the carbon ring has 3 double bonds that means 6 pi electrons, while the ether contains 1 double bond in carbonyl group so 2 pi electrons.
So, number of $\pi \,{{e}^{-}}s$= 2 + 6 + 2
Number of $\pi \,{{e}^{-}}s$= 10
Hence, the compound B contains 10$\pi \,{{e}^{-}}s$ that results in delocalization.
Note:As sigma bond is the basis of pi bond, so wherever there is a double bond, that means 2 pi electrons, and in triple bonds 4 pi electrons. The compound A formed is known as paracetamol, which is used as a medicine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




