
…………. pairs of legs are found in Insects.
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: Insects or Insecta (derived from Latin insectum) are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates and also the largest group within the arthropod phylum. The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods that is usually used for walking.
Complete Answer:
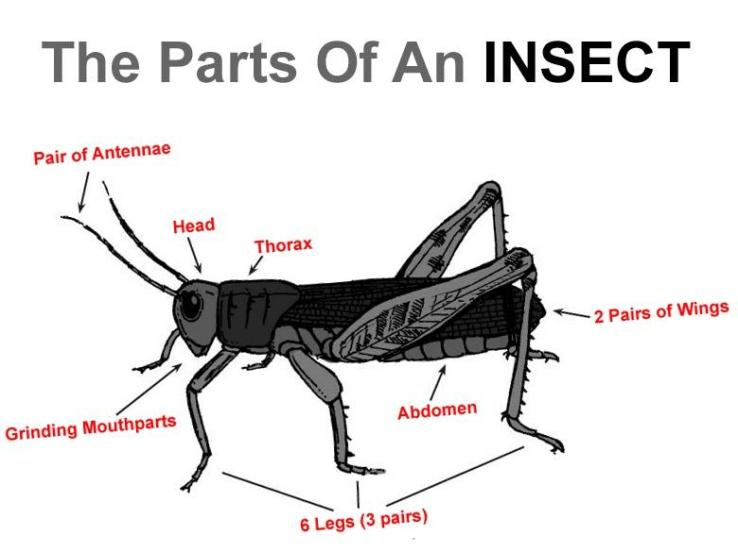
Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton with a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen) and three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes along with one pair of antennae. Many insects have a tripedal gait. The segments of the body are organized into three distinctive but interconnected units (tagmata): a head, a thorax and an abdomen. The thorax is made up of three segments: prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax. Each thoracic segment supports one pair of legs. The anterior segment which is closest to the head is the prothorax and has the first pair of legs and the pronotum. The middle segment is the mesothorax which has the second pair of legs and anterior wings. The third and posterior segment, abutting the abdomen, is the metathorax that features the third pair of legs and posterior wings. Each segment is delineated by an intersegmental suture. Thus, insects have 3 pairs of legs.
Insects and their relatives are, thereby, called hexapods, i.e., having six legs. Each leg has five components: the coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, and tarsus. Each of them is a single segment, except the tarsus which can be three to seven segments, each referred to as a tarsomere. Some larval insects, however, have extra walking legs on their abdominal segments called prolegs.
Note:
Insect walking is an alternative form of locomotive option in robots. This may allow robots to traverse terrain that robots with wheels may be unable to handle. A few insects have evolved to walk on the surface of the water (especially members of the Gerridae family) commonly known as water striders. A few species of ocean-skaters in the genus Halobates even live on the surface of open oceans.
Complete Answer:
Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton with a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen) and three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes along with one pair of antennae. Many insects have a tripedal gait. The segments of the body are organized into three distinctive but interconnected units (tagmata): a head, a thorax and an abdomen. The thorax is made up of three segments: prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax. Each thoracic segment supports one pair of legs. The anterior segment which is closest to the head is the prothorax and has the first pair of legs and the pronotum. The middle segment is the mesothorax which has the second pair of legs and anterior wings. The third and posterior segment, abutting the abdomen, is the metathorax that features the third pair of legs and posterior wings. Each segment is delineated by an intersegmental suture. Thus, insects have 3 pairs of legs.
Insects and their relatives are, thereby, called hexapods, i.e., having six legs. Each leg has five components: the coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, and tarsus. Each of them is a single segment, except the tarsus which can be three to seven segments, each referred to as a tarsomere. Some larval insects, however, have extra walking legs on their abdominal segments called prolegs.

Note:
Insect walking is an alternative form of locomotive option in robots. This may allow robots to traverse terrain that robots with wheels may be unable to handle. A few insects have evolved to walk on the surface of the water (especially members of the Gerridae family) commonly known as water striders. A few species of ocean-skaters in the genus Halobates even live on the surface of open oceans.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




