
Parabolas are drawn to touch two given straight lines which are inclined at an angle w; if the chords of contact all pass through a fixed point, prove that
A. Their directrices all pass through another fixed point and
B. Their foci all lie on a circle which goes through the intersection of the two given straight lines.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Equation of directrix for parabola touching two different lines at angle ‘w’ can be given as
$\dfrac{x+y\cos w}{a}+\dfrac{y+x\cos w}{b}=1$
Where (a, b) are constants.
Use $\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1$ for supposing a line as chord of contact to get rid of solving complex equations. Focus of the same parabola with the same conditions can be given by the relation
$ax=by={{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}$
Complete step by step answer:
As, we are drawing parabolas for touching two straight lines, which are inclined at angle w, and we are given that the chord of contacts all passes through a fixed point.
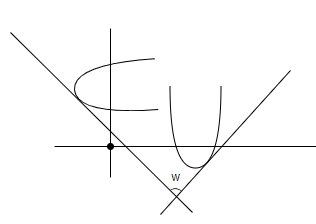
As, we know the equation of directrix, for a parabola touching two lines can be given as
$\dfrac{x+y\cos w}{a}+\dfrac{y+x\cos w}{b}=1$………………..(i)
Where, a, b are constants.
As the chord of contact is passing through a fixed point. Let us suppose coordinates of it as (h, k).
So, as we know, any straight line $\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1$, will pass through (h, k) if,
$\dfrac{h}{a}+\dfrac{k}{b}=1$…………………(ii)
Now, we can directly compare equation (i) and (ii). So, we get
$x+y\cos w=h,y+x\cos w=k$ …………….(iii)
Now, the first equation represents all the directrics. It means the above two equations in $\left( {{x}_{1}},y \right)$ can be solved and we will get exactly one intersecting point of it. So, directrics will pass through a fixed point.
Let us solve both the equations in equation (iii) to get $\left( {{x}_{1}},y \right)$ i.e. fixed point through which the directrix will pass.
Hence, we have
$x+y\cos w=h,y+x\cos w=k$
Value of x from first equation:
\[x=h-y\cos w\]
Putting value of x in another equation, we get
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow y+\left( h-y\operatorname{cosw} \right)\cos w=k \\
&\Rightarrow y\left[ 1-{{\cos }^{2}}w \right]+h\cos w=k \\
&\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{k-h\cos w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \\
\end{align}$
So, we can put value of ‘y’ in first equation, to get ‘x’ as
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow x=h-y\cos w \\
&\Rightarrow x=h-\left( \dfrac{k-h{{\cos }^{2}}w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \right)\cos w \\
&\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{h-h{{\cos }^{2}}w-k\cos w+h{{\cos }^{2}}w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \\
&\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{h-k\cos w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \\
\end{align}$
So, the directrix will pass through a 0 fixed point
$\left( \dfrac{h-k\cos w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w},\dfrac{k-h\cos w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \right)$
So, the first part of the problem is proved.
Now, coming to the second part:
As, we know focus of any parabola with the help of angle between two given lines is given by relation:
$ax=by={{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}$ ………………..(iv)
Where, a, b are constants.
Now, we can compare the first two terms of the equation (iv) to the third term of the same equation individually. So, we get
$ax={{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}$
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}}{x}, \\
&\Rightarrow by={{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}}{y} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can substitute ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the equation (ii), so, we get
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow \dfrac{hx}{{{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}}+\dfrac{ky}{{{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}}=1 \\
&\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}=hx+ky, \\
&\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}2xy\cos w-hx-ky=0 \\
\end{align}$
So, clearly the above equation is representing a circle with the rotation of the axis and it is passing through (o, o) as well. Hence, the second statement is also proved.
Note: One may suppose the equation of both the lines as ${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0,{{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$ and relate the angle between them, but it will be very complex to involve six variable in this question. So, using direct results of writing directrix and focus help the problem to get solved easily.
One may confuse with the equation of circle, ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cos w-hx-ky=0$, by the involvement of xy term with it. This type of equation of circle can be found only if the axis is rotated to solve angle. So, it also represents a circle, which passes through origin as well.
One may need not to find the intersection of $x+y\cos w=h,y+x\cos w=k$; As, we have two equations in two variables, it means there will be an unique solution; So, we do not need to solve them further. It is solved in solution for the better understanding of the given problem.
$\dfrac{x+y\cos w}{a}+\dfrac{y+x\cos w}{b}=1$
Where (a, b) are constants.
Use $\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1$ for supposing a line as chord of contact to get rid of solving complex equations. Focus of the same parabola with the same conditions can be given by the relation
$ax=by={{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}$
Complete step by step answer:
As, we are drawing parabolas for touching two straight lines, which are inclined at angle w, and we are given that the chord of contacts all passes through a fixed point.
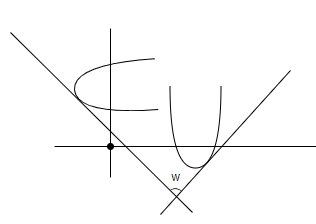
As, we know the equation of directrix, for a parabola touching two lines can be given as
$\dfrac{x+y\cos w}{a}+\dfrac{y+x\cos w}{b}=1$………………..(i)
Where, a, b are constants.
As the chord of contact is passing through a fixed point. Let us suppose coordinates of it as (h, k).
So, as we know, any straight line $\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1$, will pass through (h, k) if,
$\dfrac{h}{a}+\dfrac{k}{b}=1$…………………(ii)
Now, we can directly compare equation (i) and (ii). So, we get
$x+y\cos w=h,y+x\cos w=k$ …………….(iii)
Now, the first equation represents all the directrics. It means the above two equations in $\left( {{x}_{1}},y \right)$ can be solved and we will get exactly one intersecting point of it. So, directrics will pass through a fixed point.
Let us solve both the equations in equation (iii) to get $\left( {{x}_{1}},y \right)$ i.e. fixed point through which the directrix will pass.
Hence, we have
$x+y\cos w=h,y+x\cos w=k$
Value of x from first equation:
\[x=h-y\cos w\]
Putting value of x in another equation, we get
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow y+\left( h-y\operatorname{cosw} \right)\cos w=k \\
&\Rightarrow y\left[ 1-{{\cos }^{2}}w \right]+h\cos w=k \\
&\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{k-h\cos w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \\
\end{align}$
So, we can put value of ‘y’ in first equation, to get ‘x’ as
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow x=h-y\cos w \\
&\Rightarrow x=h-\left( \dfrac{k-h{{\cos }^{2}}w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \right)\cos w \\
&\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{h-h{{\cos }^{2}}w-k\cos w+h{{\cos }^{2}}w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \\
&\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{h-k\cos w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \\
\end{align}$
So, the directrix will pass through a 0 fixed point
$\left( \dfrac{h-k\cos w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w},\dfrac{k-h\cos w}{1-{{\cos }^{2}}w} \right)$
So, the first part of the problem is proved.
Now, coming to the second part:
As, we know focus of any parabola with the help of angle between two given lines is given by relation:
$ax=by={{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}$ ………………..(iv)
Where, a, b are constants.
Now, we can compare the first two terms of the equation (iv) to the third term of the same equation individually. So, we get
$ax={{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}$
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}}{x}, \\
&\Rightarrow by={{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}} \\
&\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}}{y} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can substitute ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the equation (ii), so, we get
$\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow \dfrac{hx}{{{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}}+\dfrac{ky}{{{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}}=1 \\
&\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2xy\cos w+{{y}^{2}}=hx+ky, \\
&\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}2xy\cos w-hx-ky=0 \\
\end{align}$
So, clearly the above equation is representing a circle with the rotation of the axis and it is passing through (o, o) as well. Hence, the second statement is also proved.
Note: One may suppose the equation of both the lines as ${{a}_{1}}x+{{b}_{1}}y+{{c}_{1}}=0,{{a}_{2}}x+{{b}_{2}}y+{{c}_{2}}=0$ and relate the angle between them, but it will be very complex to involve six variable in this question. So, using direct results of writing directrix and focus help the problem to get solved easily.
One may confuse with the equation of circle, ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cos w-hx-ky=0$, by the involvement of xy term with it. This type of equation of circle can be found only if the axis is rotated to solve angle. So, it also represents a circle, which passes through origin as well.
One may need not to find the intersection of $x+y\cos w=h,y+x\cos w=k$; As, we have two equations in two variables, it means there will be an unique solution; So, we do not need to solve them further. It is solved in solution for the better understanding of the given problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




