
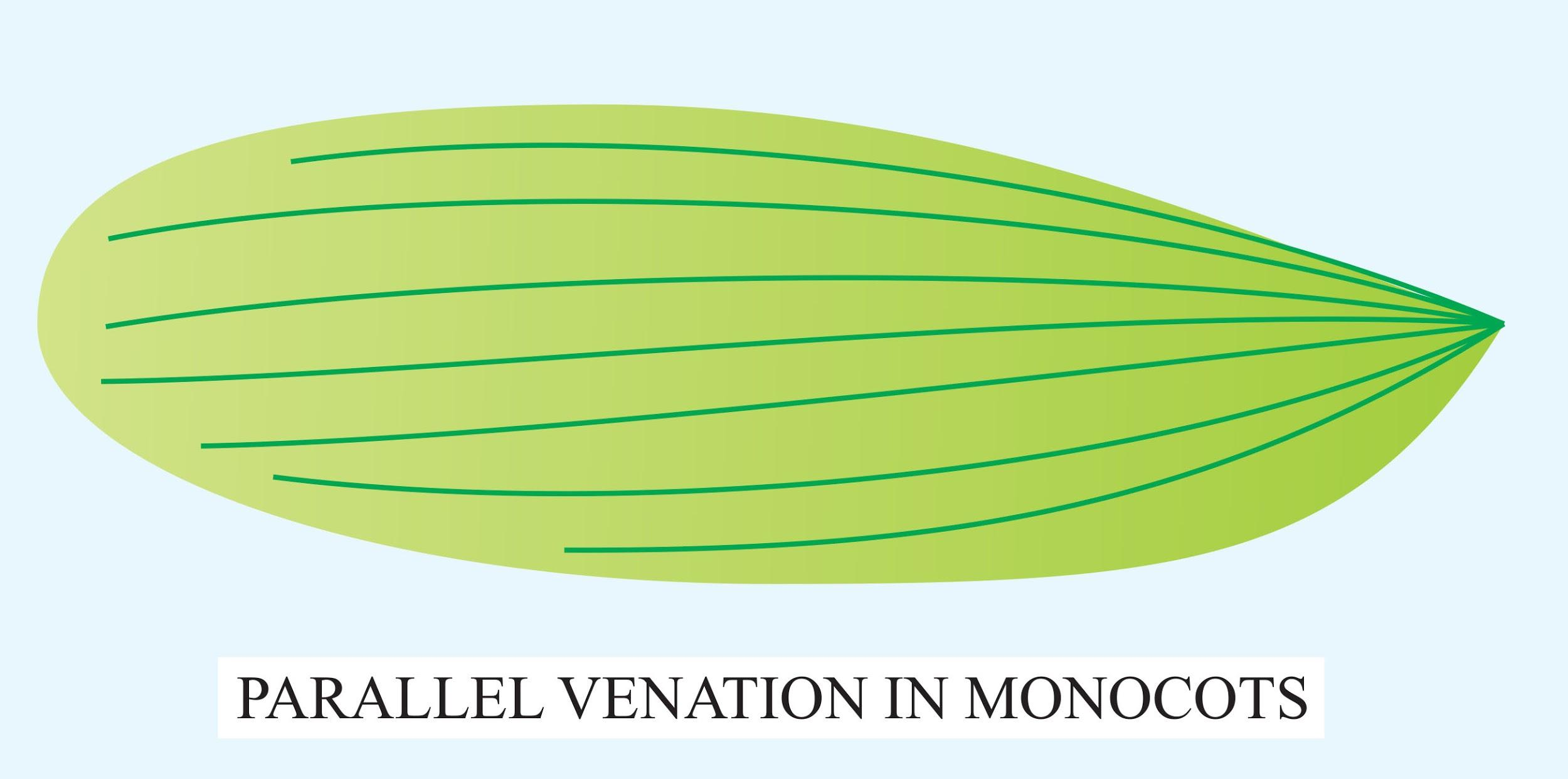
Parallel venation is a characteristic feature of
(a)Monocotyledon
(b)Dicotyledon
(c)Pteridophytes
(d)Bryophytes
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Parallel venation is a condition in which all the veins of a leaf are arranged parallel to each other. The leaves processing parallel venation consists of extended leaf shape and wide leaf base. The veins run parallel to each other from the base to the tip of the leaf.
Complete answer:
Parallel venation is a characteristic feature of monocotyledon. Monocots are the angiosperm plants that contain only one embryonic leaf or cotyledon. They consist of flowering plants which are traditionally divided. They include about 60000 species and are the largest family of the flowering plants such as the species of orchids with more than 20000 species. They are economically important and sometimes mistaken for grasses. The biomass in agriculture is produced by monocotyledons which not only include major grains but also the forage grasses, sugarcane, and bamboo. Due to uniformity and diversity, monocots are distinguished from other angiosperms. They provide leaf structure, floral configuration, and organization of the shoots to a diversity of NGO sperms and indicates a high degree of evolutionary success. They lack lateral Meristem which allows them for continual growth in diameter with height.
Additional information:
Dicotyledon: They are the group of flowering plants which are known as dicots and have two embryonic leaves or cotyledons. They have reticulate venation and have characteristics of monocots such as vascular bundles, non-tricolpate pollen and trimerous flowers. They consist of pentamerous or tetramerous flowers and three numbers of poles in the pollen. The arrangement of vascular bundles in the stem is in concentric circles and the roots are developed from the radicle. The venation of leaves is reticulate and the secondary growth is often present.
Pteridophytes: They are vascular plants that disperse spores because they do not produce flowers and seeds and are known as cryptogams. They do not form a monophyletic group and are closely related to the seed plants. The sporophyte body is differentiated into root, stem, and leaves and the root system is adventitious. Pteridophytes share common ancestors and do not form a clade but constitute a paraphyletic group. The undergoes alternation of generation in which a diploid generation is followed by a haploid generation that produces gametes.
Bryophytes: They are non-vascular land plants that consist of about 20,000 plant species and do not produce flowers or seed. Reproduction in bryophytes takes place through spores and is considered to be a paraphyletic group. Sporophytes produced are unbranched and the lifecycle gets dominated by the gametophyte stage. They do not have true vascular tissue which contains lignin which helps in the transport of water.
So, the correct answer is 'Monocotyledon'.
Note: The largest bryophyte is Dawsonia and the smallest bryophyte is Zoopsis. Fern is a pteridophyte with 10560 known species and some of them constitute the oldest plant in the world. Dekhen lives for about a hundred years and does not produce seeds.
Complete answer:
Parallel venation is a characteristic feature of monocotyledon. Monocots are the angiosperm plants that contain only one embryonic leaf or cotyledon. They consist of flowering plants which are traditionally divided. They include about 60000 species and are the largest family of the flowering plants such as the species of orchids with more than 20000 species. They are economically important and sometimes mistaken for grasses. The biomass in agriculture is produced by monocotyledons which not only include major grains but also the forage grasses, sugarcane, and bamboo. Due to uniformity and diversity, monocots are distinguished from other angiosperms. They provide leaf structure, floral configuration, and organization of the shoots to a diversity of NGO sperms and indicates a high degree of evolutionary success. They lack lateral Meristem which allows them for continual growth in diameter with height.
Additional information:
Dicotyledon: They are the group of flowering plants which are known as dicots and have two embryonic leaves or cotyledons. They have reticulate venation and have characteristics of monocots such as vascular bundles, non-tricolpate pollen and trimerous flowers. They consist of pentamerous or tetramerous flowers and three numbers of poles in the pollen. The arrangement of vascular bundles in the stem is in concentric circles and the roots are developed from the radicle. The venation of leaves is reticulate and the secondary growth is often present.
Pteridophytes: They are vascular plants that disperse spores because they do not produce flowers and seeds and are known as cryptogams. They do not form a monophyletic group and are closely related to the seed plants. The sporophyte body is differentiated into root, stem, and leaves and the root system is adventitious. Pteridophytes share common ancestors and do not form a clade but constitute a paraphyletic group. The undergoes alternation of generation in which a diploid generation is followed by a haploid generation that produces gametes.
Bryophytes: They are non-vascular land plants that consist of about 20,000 plant species and do not produce flowers or seed. Reproduction in bryophytes takes place through spores and is considered to be a paraphyletic group. Sporophytes produced are unbranched and the lifecycle gets dominated by the gametophyte stage. They do not have true vascular tissue which contains lignin which helps in the transport of water.
So, the correct answer is 'Monocotyledon'.

Note: The largest bryophyte is Dawsonia and the smallest bryophyte is Zoopsis. Fern is a pteridophyte with 10560 known species and some of them constitute the oldest plant in the world. Dekhen lives for about a hundred years and does not produce seeds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




