
Part of the female reproductive system of frog which stores ova temporarily is _____.
A) Uterus
B) Ovary
C) Fallopian tube
D) Ovisac
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: In the female frog, there is a structure near the ureters. It is a part of the oviduct but is not coiled like an oviduct. It opens in the cloaca through its apertures and stores ova temporarily before their release.
Complete answer:
The reproductive system of the female frog consists of two oviducts and two ovaries. The posterior end of two oviducts opens into cloaca separately. Just before entering the cloaca, each oviduct forms a thin-walled enlargement that is not coiled like the rest of the part of the oviduct. This portion of the oviduct is known as ovisac. The eggs or ova of the female frog are collected here and stored temporarily before they are laid. A diagram of the female reproductive system has been shown below, the ovisac near the ureter and other parts of the reproductive and urinary system of a female frog can be seen in the diagram.
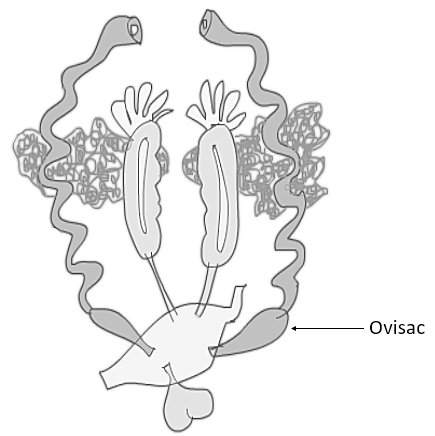
The two ovaries lie near the kidneys and are attached to the kidneys by mesovarium. This is a double fold of peritoneum. The ovary is a multilobed and irregularly folded structure, quite large and hollow sac with greyish or blackish appearance. The size of ovaries in the female frog varies considerably in different seasons as in breeding season they become greatly enlarged.
So, the correct answer is ‘Ovisac’.
Note:
-The uterus is found only in those animals which give birth to young ones and the term viviparous is used for these animals. In such animals, fertilization takes place internally and the fertilized egg is implanted in the uterus where it develops till birth. Frog is an oviparous animal because it lays eggs that develop outside the body after being fertilized.
-Fallopian tubes are also called uterine tubes and these are found only in female mammals. These tubes provide a passageway from the ovary to the uterus for the egg. These are also not a part of the female reproductive system of the frog.
Complete answer:
The reproductive system of the female frog consists of two oviducts and two ovaries. The posterior end of two oviducts opens into cloaca separately. Just before entering the cloaca, each oviduct forms a thin-walled enlargement that is not coiled like the rest of the part of the oviduct. This portion of the oviduct is known as ovisac. The eggs or ova of the female frog are collected here and stored temporarily before they are laid. A diagram of the female reproductive system has been shown below, the ovisac near the ureter and other parts of the reproductive and urinary system of a female frog can be seen in the diagram.

The two ovaries lie near the kidneys and are attached to the kidneys by mesovarium. This is a double fold of peritoneum. The ovary is a multilobed and irregularly folded structure, quite large and hollow sac with greyish or blackish appearance. The size of ovaries in the female frog varies considerably in different seasons as in breeding season they become greatly enlarged.
So, the correct answer is ‘Ovisac’.
Note:
-The uterus is found only in those animals which give birth to young ones and the term viviparous is used for these animals. In such animals, fertilization takes place internally and the fertilized egg is implanted in the uterus where it develops till birth. Frog is an oviparous animal because it lays eggs that develop outside the body after being fertilized.
-Fallopian tubes are also called uterine tubes and these are found only in female mammals. These tubes provide a passageway from the ovary to the uterus for the egg. These are also not a part of the female reproductive system of the frog.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




