
Passage cells are found in:
(a)Dicot stem
(b)Aerial root
(c)Monocot root
(d)Monocot stem
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Passage cells are certain endodermal cells of roots that have been modified for the transport of water. The function of these cells is to transport water and other mineral salts from the cortex to the xylem elements.
Complete answer:
Passage cells are present in the form of short cells. Endodermal cells which do not have Casparian strips are called passage cells.
A dicot stem has its vascular bundles arranged in the form of a ring, and the pith is at the core of the stem and is scattered in the interior region of the plant. The xylem and phloem of each vascular bundle are divided by a vascular cambium.
Aerial roots are roots that originate from the part of the plant which is above the earth’s surface or water. These roots absorb water from the air that the plant receives. Example: Banyan figs, Orchids, etc.
In the monocot root, passage cells are found in the endodermis of the root which is found the opposite to the protoxylem element. These cells are not thick and help in the transverse action of fluids through it.
A monocot stem has its vascular bundles near the outer area of the stem. Vascular bundles are tissues that are distributed in parenchymatous ground tissues. The pith region is absent in the monocot stem.
Additional information:
A dicot root has its vascular structures located in the middle of the root. The xylem is located in the middle of the root and phloem bundles are arranged around it. Dicot roots do not have a central pith area and the parenchyma serves as connective tissue in the region where the vascular structures are found.
So, the correct answer is ‘Monocot root’.
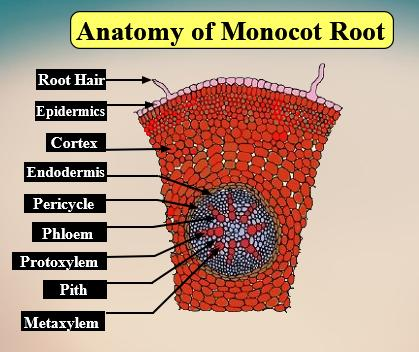
Note: Passage cells are also found in the endodermis of the dicot root. These cells allow passage between vascular tissue and the cortex. Hence, passage cells are found in both monocot root and dicot root.
Complete answer:
Passage cells are present in the form of short cells. Endodermal cells which do not have Casparian strips are called passage cells.
A dicot stem has its vascular bundles arranged in the form of a ring, and the pith is at the core of the stem and is scattered in the interior region of the plant. The xylem and phloem of each vascular bundle are divided by a vascular cambium.
Aerial roots are roots that originate from the part of the plant which is above the earth’s surface or water. These roots absorb water from the air that the plant receives. Example: Banyan figs, Orchids, etc.
In the monocot root, passage cells are found in the endodermis of the root which is found the opposite to the protoxylem element. These cells are not thick and help in the transverse action of fluids through it.
A monocot stem has its vascular bundles near the outer area of the stem. Vascular bundles are tissues that are distributed in parenchymatous ground tissues. The pith region is absent in the monocot stem.
Additional information:
A dicot root has its vascular structures located in the middle of the root. The xylem is located in the middle of the root and phloem bundles are arranged around it. Dicot roots do not have a central pith area and the parenchyma serves as connective tissue in the region where the vascular structures are found.
So, the correct answer is ‘Monocot root’.

Note: Passage cells are also found in the endodermis of the dicot root. These cells allow passage between vascular tissue and the cortex. Hence, passage cells are found in both monocot root and dicot root.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




