
Pasture effect is due to
(a) Change from aerobic to anaerobic
(b) Providing oxygen to anaerobically respiring structure
(c) Rapid utilization of ATP
(d) Nonsynthetic of ATP
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: Under anaerobic conditions, the conversion of glucose to pyruvate is much higher than under aerobic conditions like yeast cells produce more ethanol and muscle cells accumulate lactate.
Complete step by step answer:
The inhibition of glycolysis by oxygen that is an aerobic condition is known as the pasteur effect. Pasteur effect is the result of the inhibition of the enzyme phosphofructokinase. Glycolytic intermediates from fructose 1,6- bisphosphate onwards decrease while the sooner intermediates accumulate.
The pasteur effect is the slowing of glycolysis in the presence of oxygen. More ATP is produced aerobic conditions than under anaerobic conditions, therefore, less glucose is consumed aerobically.
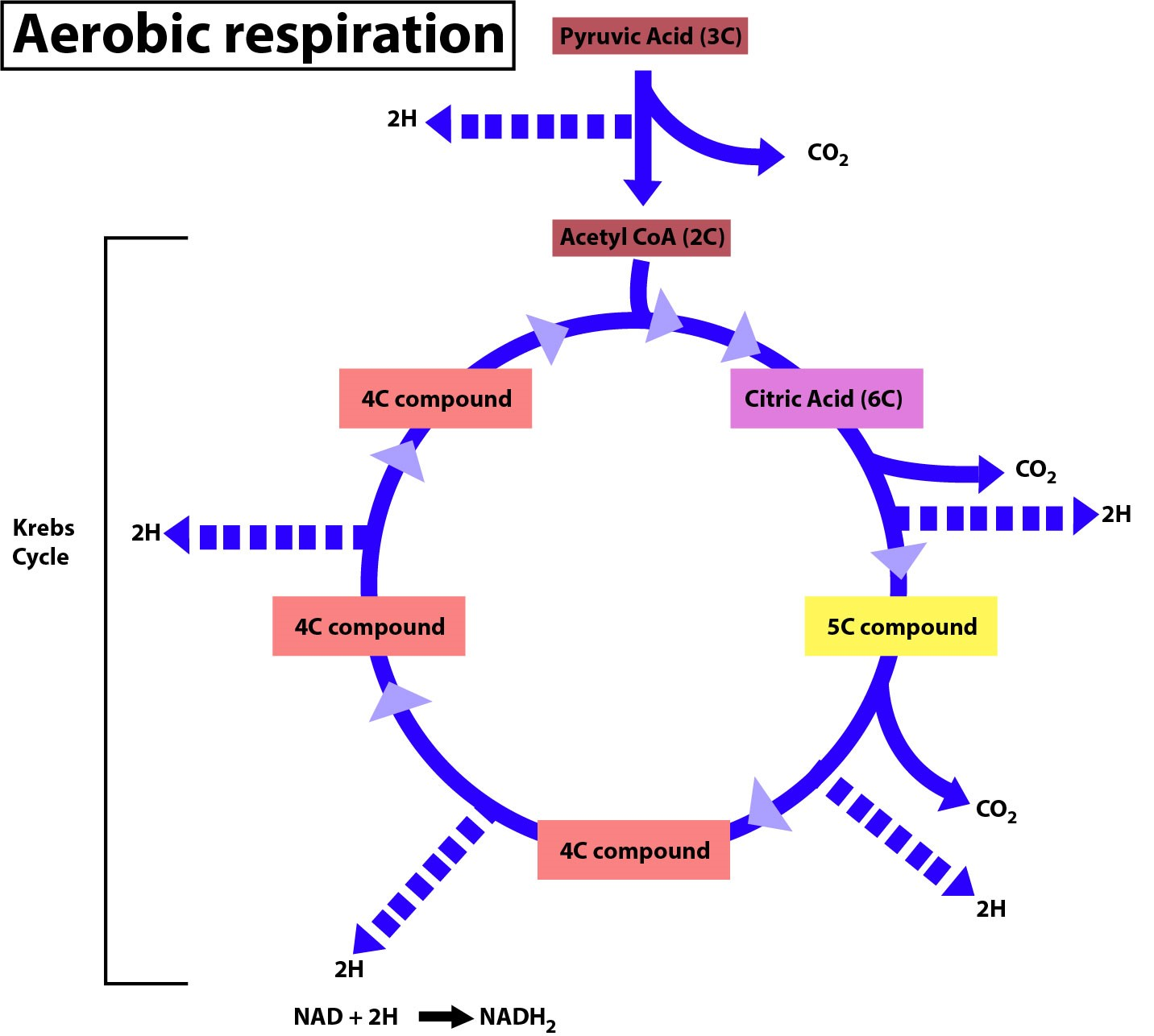
Additional Information:
- The Fate of Pyruvate
Aerobic conditions pyruvate oxidized to acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle for further oxidation. Anaerobic conditions in microorganisms, pyruvate conversion take place to ethanol.
Anaerobic conditions in muscles, red blood cells, pyruvate conversion take place to lactate.
- Reduction of Pyruvate to Lactate in muscles under anaerobic.
Muscles lack pyruvate dehydrogenase and can’t produce ethanol from pyruvate.
Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate.
This reaction regenerates NAD+ to be used by GAPDH in glycolysis.
- Recycling of lactate
Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is then transported to the liver.
Liver lactate dehydrogenase can reconvert lactate to pyruvate.
Lactic acidosis can result from insufficient oxygen which causes an increase in lactic acid and a decrease in blood pH.
So, the correct answer is ‘Providing oxygen to the anaerobically respiring structure.’
Note: Crabtree effect: Inhibition of oxygen consumption by the addition of glucose to tissues having high aerobic glycolysis is known as the Crabtree effect. Opposite to that of Pasteur effect. Crabtree effect is because of the increased competition of glycolysis for inorganic phosphate (Pi) & NAD+ which limits their availability for phosphorylation and oxidation.
Complete step by step answer:
The inhibition of glycolysis by oxygen that is an aerobic condition is known as the pasteur effect. Pasteur effect is the result of the inhibition of the enzyme phosphofructokinase. Glycolytic intermediates from fructose 1,6- bisphosphate onwards decrease while the sooner intermediates accumulate.
The pasteur effect is the slowing of glycolysis in the presence of oxygen. More ATP is produced aerobic conditions than under anaerobic conditions, therefore, less glucose is consumed aerobically.

Additional Information:
- The Fate of Pyruvate
Aerobic conditions pyruvate oxidized to acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle for further oxidation. Anaerobic conditions in microorganisms, pyruvate conversion take place to ethanol.
Anaerobic conditions in muscles, red blood cells, pyruvate conversion take place to lactate.
- Reduction of Pyruvate to Lactate in muscles under anaerobic.
Muscles lack pyruvate dehydrogenase and can’t produce ethanol from pyruvate.
Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate.
This reaction regenerates NAD+ to be used by GAPDH in glycolysis.
- Recycling of lactate
Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is then transported to the liver.
Liver lactate dehydrogenase can reconvert lactate to pyruvate.
Lactic acidosis can result from insufficient oxygen which causes an increase in lactic acid and a decrease in blood pH.
So, the correct answer is ‘Providing oxygen to the anaerobically respiring structure.’
Note: Crabtree effect: Inhibition of oxygen consumption by the addition of glucose to tissues having high aerobic glycolysis is known as the Crabtree effect. Opposite to that of Pasteur effect. Crabtree effect is because of the increased competition of glycolysis for inorganic phosphate (Pi) & NAD+ which limits their availability for phosphorylation and oxidation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




