
$PC{{l}_{3}}$ on hydrolysis gives fumes of:
(A)-${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}+HCl$
(B)-${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}+HCl$
(C)-${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}}\,\text{and}\,{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$
(D)-${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}}+HCl$
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The hydrolysis reaction involves the addition of water molecules to the given compound through nucleophilic attack and forming a new bond with the hydroxide ion of water.
Complete step by step answer:
Phosphorus trichloride, $PC{{l}_{3}}$ has one phosphorus atom having $(+3)$charge linked to three chlorine atoms having $(-1)$ charge on each atom. Thus, having a lone pair on the phosphorus atom leading to its trigonal pyramidal geometry from the VSEPR theory.
It acts as both an electrophile or nucleophile depending on the reaction condition, where the electrophilic nature is possible due to the presence of the more electronegative chlorine which attracts the shared electrons bond pair away from phosphorus making it partially positive. Whereas, the availability of the lone pair on phosphorus atoms, makes it act as a Lewis base or nucleophile. In the hydrolysis of phosphorus trichloride with water, it is the nucleophilic substitution of the -OH group by the -Cl group. We have the water molecule acting as the nucleophile and attacking the partially positive phosphorus atom with its electronegative oxygen atom and simultaneously losing a chloride ion. This is followed by the abstraction of a proton from the hydronium group attached to phosphorus by the chloride ion and forming HCl. Similarly, the other two chlorine atoms are also replaced by the hydroxide ion and we get phosphorous acid, $P{{(OH)}_{3}}$ which is diprotic in nature. The trivalent phosphorous acid undergoes tautomerisation giving us pentavalent phosphoric acid, ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$ .
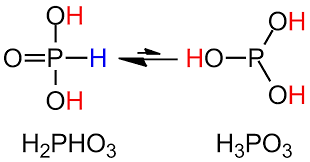
Therefore, the hydrolysis of $PC{{l}_{3}}$gives fumes of option (A)- ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}+HCl$.
Note: The phosphoric acid is a diprotic acid as it has only two ionizable hydrogens linked to the oxygen in O-H bond, whereas the hydrogen linked to the phosphorus atom is not ionisable.
Complete step by step answer:
Phosphorus trichloride, $PC{{l}_{3}}$ has one phosphorus atom having $(+3)$charge linked to three chlorine atoms having $(-1)$ charge on each atom. Thus, having a lone pair on the phosphorus atom leading to its trigonal pyramidal geometry from the VSEPR theory.
It acts as both an electrophile or nucleophile depending on the reaction condition, where the electrophilic nature is possible due to the presence of the more electronegative chlorine which attracts the shared electrons bond pair away from phosphorus making it partially positive. Whereas, the availability of the lone pair on phosphorus atoms, makes it act as a Lewis base or nucleophile. In the hydrolysis of phosphorus trichloride with water, it is the nucleophilic substitution of the -OH group by the -Cl group. We have the water molecule acting as the nucleophile and attacking the partially positive phosphorus atom with its electronegative oxygen atom and simultaneously losing a chloride ion. This is followed by the abstraction of a proton from the hydronium group attached to phosphorus by the chloride ion and forming HCl. Similarly, the other two chlorine atoms are also replaced by the hydroxide ion and we get phosphorous acid, $P{{(OH)}_{3}}$ which is diprotic in nature. The trivalent phosphorous acid undergoes tautomerisation giving us pentavalent phosphoric acid, ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$ .

Therefore, the hydrolysis of $PC{{l}_{3}}$gives fumes of option (A)- ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}+HCl$.
Note: The phosphoric acid is a diprotic acid as it has only two ionizable hydrogens linked to the oxygen in O-H bond, whereas the hydrogen linked to the phosphorus atom is not ionisable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




