
Peacock eats a snake, a snake eats a frog and a frog eats insect, while insects eat the green plant, then the position of the peacock is:
(a) Primary Producer
(b) Secondary Producer
(c) Decomposer
(d) top at the apex of the food pyramid
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Food pyramid is a graphical representation which shows the common parameters like biomass transfer or transfer of food energy at any trophic level. The trophic level of peacocks is the same as eagles in a tree ecosystem. Humans also belong to this trophic level.
Complete answer:
In a food chain, a sequence of living organisms involves the transfer of food energy from producers, through a series of organisms with repeated eating and being eaten. Each level or step in a food chain where the transfer of energy takes place is called a trophic level. In most ecosystems, the transfer of energy starts from the primary producers that are the plants. Producers thus support herbivores that are primary consumers like insects and small herbivores which comprise the second trophic level. Primary carnivores or secondary consumers are the animals that feed on herbivores like frogs, small birds, etc and form third trophic level. Secondary carnivores or tertiary consumers like the large birds, lions, etc feed on primary carnivores and constitute the fourth trophic levels.
According to the question, plants are the primary producers that are eaten by the insect. Thus, the insect constitutes the second trophic level (primary producers). The insect is eaten by the frog so they constitute the second trophic level (primary carnivores). The frog is eaten by the snake, so it constitutes the fourth trophic level (secondary carnivore). At last, the snake is eaten by the peacock which comes at the top of the food pyramid.
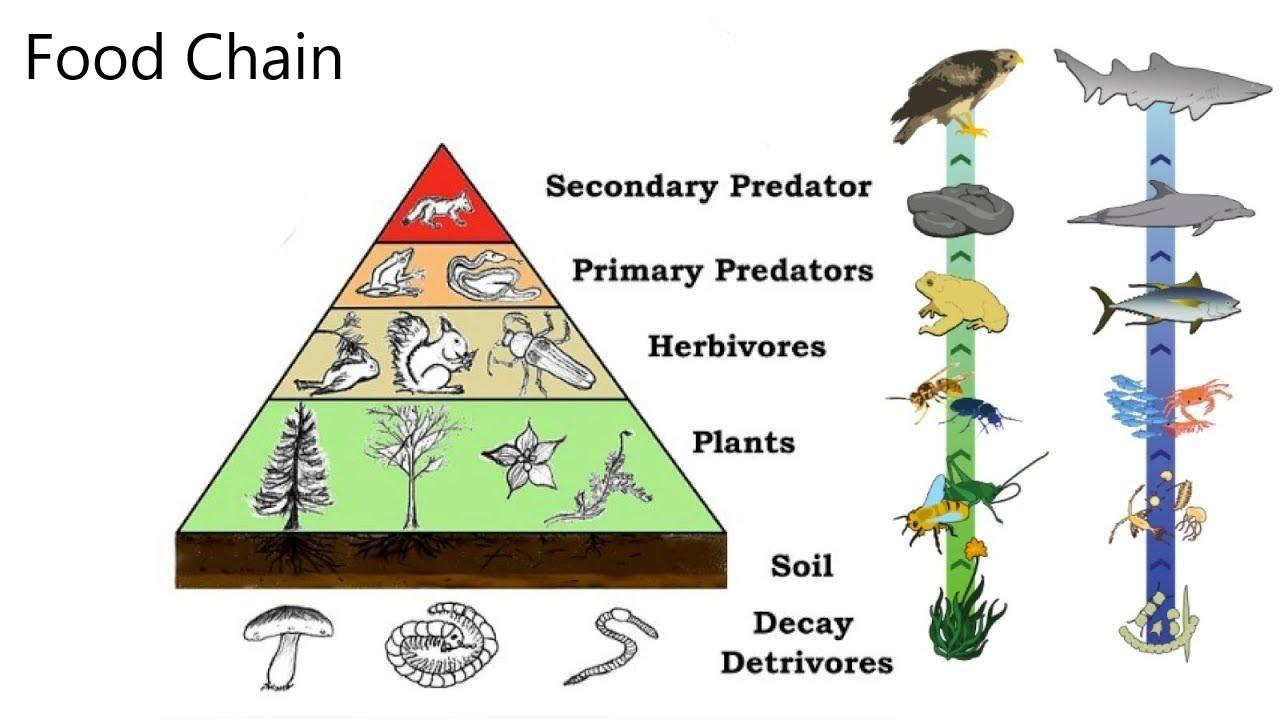
So, the answer is, ‘top at the apex of the food pyramid.’
Note:
- The above example is of a grazing food chain or a predator food chain as it consists of producer, consumer, and decomposers. The Source of energy for such a food chain is the sun. - The grazing food chain is a major conduit of energy flow in the aquatic ecosystem. - In the terrestrial ecosystem, the major conduit of energy is the detritus food chain. - The energy transfer is always unidirectional in a food chain. The size of the organism commonly increases at a higher trophic level.
Complete answer:
In a food chain, a sequence of living organisms involves the transfer of food energy from producers, through a series of organisms with repeated eating and being eaten. Each level or step in a food chain where the transfer of energy takes place is called a trophic level. In most ecosystems, the transfer of energy starts from the primary producers that are the plants. Producers thus support herbivores that are primary consumers like insects and small herbivores which comprise the second trophic level. Primary carnivores or secondary consumers are the animals that feed on herbivores like frogs, small birds, etc and form third trophic level. Secondary carnivores or tertiary consumers like the large birds, lions, etc feed on primary carnivores and constitute the fourth trophic levels.
According to the question, plants are the primary producers that are eaten by the insect. Thus, the insect constitutes the second trophic level (primary producers). The insect is eaten by the frog so they constitute the second trophic level (primary carnivores). The frog is eaten by the snake, so it constitutes the fourth trophic level (secondary carnivore). At last, the snake is eaten by the peacock which comes at the top of the food pyramid.

So, the answer is, ‘top at the apex of the food pyramid.’
Note:
- The above example is of a grazing food chain or a predator food chain as it consists of producer, consumer, and decomposers. The Source of energy for such a food chain is the sun. - The grazing food chain is a major conduit of energy flow in the aquatic ecosystem. - In the terrestrial ecosystem, the major conduit of energy is the detritus food chain. - The energy transfer is always unidirectional in a food chain. The size of the organism commonly increases at a higher trophic level.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




