
Pear fruit contains abundant
(a) Fibers
(b) Aerenchyma
(c) Stone cells
(d) Vascular tissues
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: These are a reduced form of sclerenchyma cells. They are highly thickened, lignified cellular walls and form small bundles of durable layers of tissue in most plants.
Complete answer:
Pear fruit contains non-living cells known as stone cells that form the grit in a pear fruit from the genus Pyrus. They give the pear its texture and the cells die in patchy clusters. The pear sclereids and the sclereids within the fruit form bordered pits when the cell wall thickens. The main function of these cells is mechanical support and protection. Sclereids are variable in shape and can be generally classified as Brachysclereids, Macrosclereids, Osteosclereids, Astrosclereids, and Trichosclereids. Sclereid can be found in bundles, can be found in periphery forming complete tubes, or can occur as a small group of cells. They are found in the epidermis, ground tissue, and vascular tissue. Brachysclereids are also known as stone cells. The inner portion of the cell is known as Lumen and is an empty space bounded by secondary cell walls in the center of a cell. These cells are in charge of opposing the water uptake by the hard seed legumes. The presence of this forms the core of the apple and produces a gritty texture for guava. In 1885 the word sclereid was introduced by Alexander Tschirch.
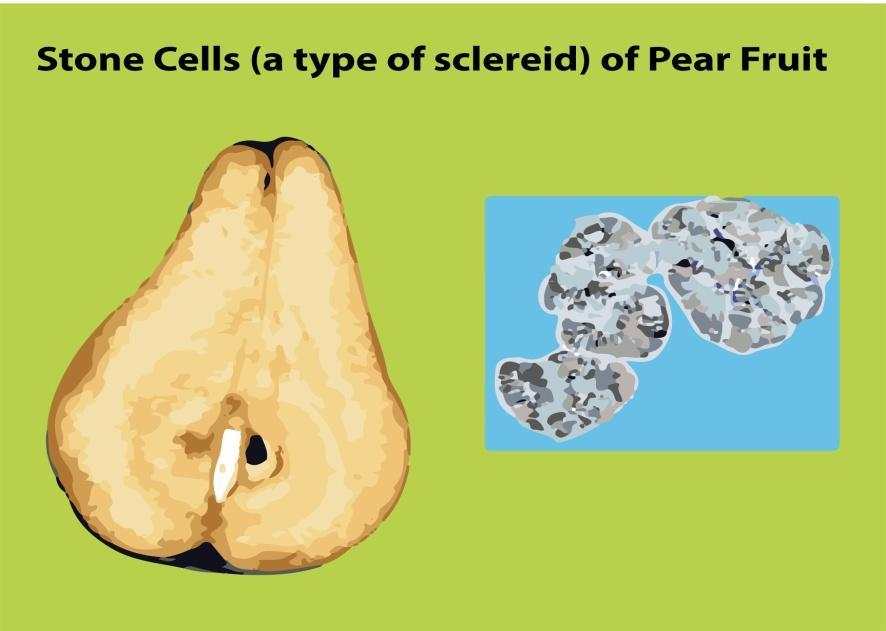
So, the correct answer is 'Stone cells'.
Note:
Pears contain fibers of 5.5 grams in medium-size pear. Aerenchyma is present in aquatic plants which gives buoyancy as the cells have large air cavities and this is not needed in pear fruit. Vascular tissues are complex conducting tissues that are a part of the transport system and are a collection of tube-like tissues that flow through plants, transporting critical substances to various parts of the plant.
Complete answer:
Pear fruit contains non-living cells known as stone cells that form the grit in a pear fruit from the genus Pyrus. They give the pear its texture and the cells die in patchy clusters. The pear sclereids and the sclereids within the fruit form bordered pits when the cell wall thickens. The main function of these cells is mechanical support and protection. Sclereids are variable in shape and can be generally classified as Brachysclereids, Macrosclereids, Osteosclereids, Astrosclereids, and Trichosclereids. Sclereid can be found in bundles, can be found in periphery forming complete tubes, or can occur as a small group of cells. They are found in the epidermis, ground tissue, and vascular tissue. Brachysclereids are also known as stone cells. The inner portion of the cell is known as Lumen and is an empty space bounded by secondary cell walls in the center of a cell. These cells are in charge of opposing the water uptake by the hard seed legumes. The presence of this forms the core of the apple and produces a gritty texture for guava. In 1885 the word sclereid was introduced by Alexander Tschirch.

So, the correct answer is 'Stone cells'.
Note:
Pears contain fibers of 5.5 grams in medium-size pear. Aerenchyma is present in aquatic plants which gives buoyancy as the cells have large air cavities and this is not needed in pear fruit. Vascular tissues are complex conducting tissues that are a part of the transport system and are a collection of tube-like tissues that flow through plants, transporting critical substances to various parts of the plant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




