
PEP is the primary ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ acceptor in
(a) ${ C }_{ 4 }$
(b) ${ C }_{ 3 }$
(c) ${ C }_{ 2 }$
(d) Both ${ C }_{ 3 }$ and ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants.
Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: PEP is an organic compound that is present as a carbon dioxide acceptor in a particular set of plants that have distinguished leaf anatomy and biochemistry. These plants are present in tropical and dry climates.
Complete answer:
- PEP stands for the three-carbon compound phosphoenolpyruvate. This compound is the primary ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ acceptor in ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase is the enzyme catalyzes the addition of bicarbonate (${ HCO }_{ 3 }^{ - }$) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), forming the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate and inorganic phosphate.
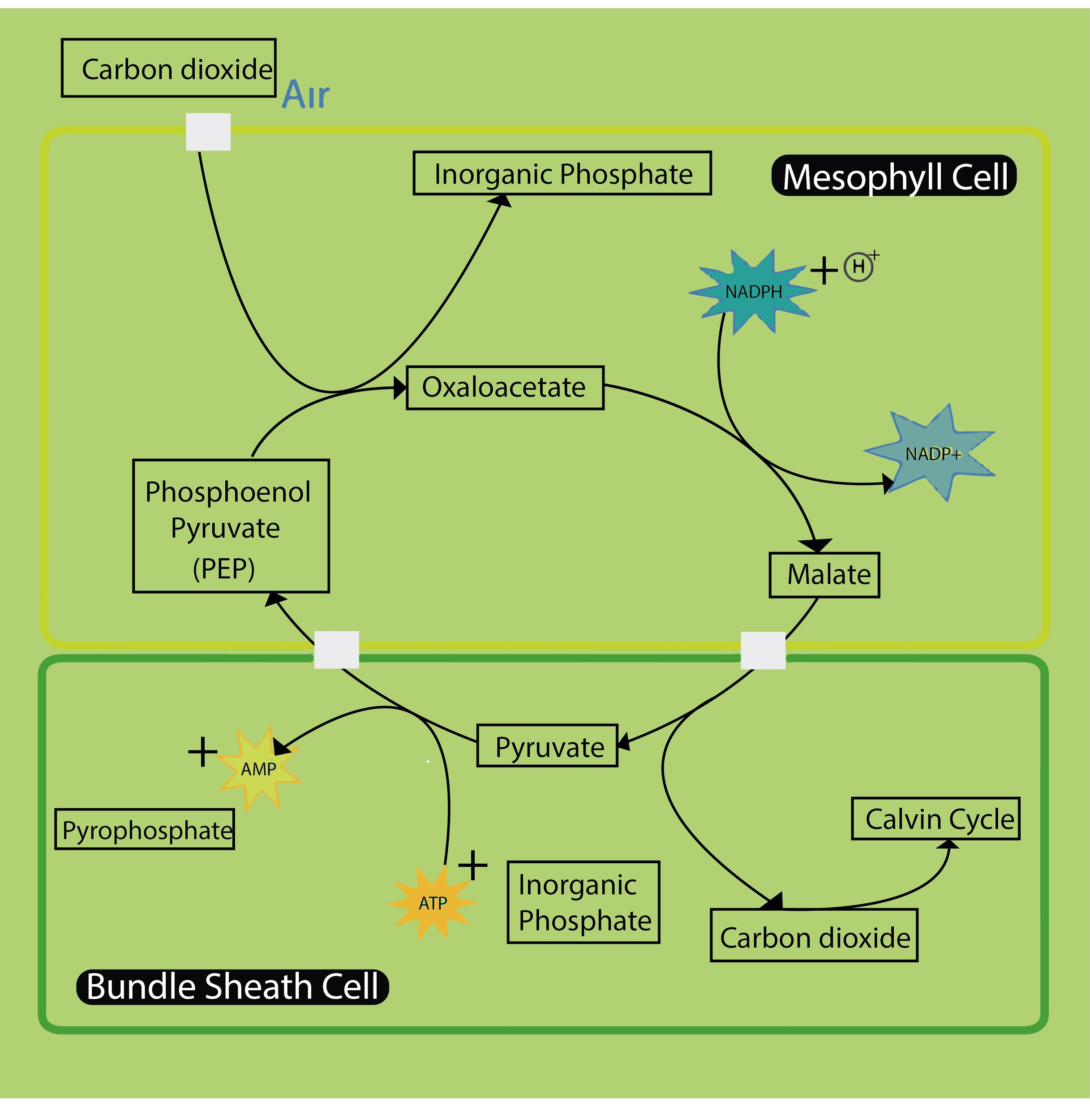
- In ${ C }_{ 3 }$ plants, ribulose bisphosphate acts as a primary acceptor and gets converted into phosphoglycerate (PGA). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme RuBisCO.
- ${ C }_{ 2 }$ is also known as the oxidative photosynthetic carbon cycle. Here, the RuBisCO enzyme oxygenates ribulose bisphosphate instead of adding carbon dioxide. This causes wastage of energy produced from photosynthesis.
Additional Information:
- ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants have the pathway to adapt to growth in tropical areas as it minimizes photorespiration. The leaf of the plant contains different anatomy than ${ C }_{ 3 }$ plants. Carbon fixation is carried by both the bundle sheath cells and mesophyll cells.
- In ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants, carbon dioxide is converted into bicarbonate in the mesophyll cells and is added to phosphoenolpyruvate through the PEPc enzyme.
- ${ C }_{ 4 }$ pathway is named after the observed plants showed the 4C compound malate as the storage molecule. The first stable carbon compound in the pathway is the 4C oxaloacetic acid.
So, the correct answer is ‘(a) ${ C }_{ 4 }$’.
Note:
- Examples of ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants are maize, sugarcane, sorghum, etc. Examples of CAM plants are aloe, agave, pineapple, etc.
- ${ C }_{ 4 }$ pathway is also known as the Hatch-Slack pathway.
Complete answer:
- PEP stands for the three-carbon compound phosphoenolpyruvate. This compound is the primary ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ acceptor in ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase is the enzyme catalyzes the addition of bicarbonate (${ HCO }_{ 3 }^{ - }$) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), forming the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate and inorganic phosphate.

- In ${ C }_{ 3 }$ plants, ribulose bisphosphate acts as a primary acceptor and gets converted into phosphoglycerate (PGA). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme RuBisCO.
- ${ C }_{ 2 }$ is also known as the oxidative photosynthetic carbon cycle. Here, the RuBisCO enzyme oxygenates ribulose bisphosphate instead of adding carbon dioxide. This causes wastage of energy produced from photosynthesis.
Additional Information:
- ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants have the pathway to adapt to growth in tropical areas as it minimizes photorespiration. The leaf of the plant contains different anatomy than ${ C }_{ 3 }$ plants. Carbon fixation is carried by both the bundle sheath cells and mesophyll cells.
- In ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants, carbon dioxide is converted into bicarbonate in the mesophyll cells and is added to phosphoenolpyruvate through the PEPc enzyme.
- ${ C }_{ 4 }$ pathway is named after the observed plants showed the 4C compound malate as the storage molecule. The first stable carbon compound in the pathway is the 4C oxaloacetic acid.
So, the correct answer is ‘(a) ${ C }_{ 4 }$’.
Note:
- Examples of ${ C }_{ 4 }$ plants are maize, sugarcane, sorghum, etc. Examples of CAM plants are aloe, agave, pineapple, etc.
- ${ C }_{ 4 }$ pathway is also known as the Hatch-Slack pathway.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




