
Periderm includes:
(a) Cork cambium (phellogen), cork (phellem), and secondary cortex (Phelloderm)
(b) Cork cambium and Cork
(c) Cork
(d) Cork and secondary phloem.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The periderm is made up of three protective layer cells that grow after the rupture of the epidermis and outer cortical layers of the primary plant body.
Complete answer:
As a result of the continued activity of vascular cambium, the girth of the stem goes on increasing. The continuous increase in the girth results in the rupture of the outermost layer i.e. epidermis and outer cortical layers (layers of cortex). Due to the ruptures, they need to be replaced to protect the stem. New protective cell layers are provided by another lateral meristem i.e. cork cambium. It is also called phellogen. It develops during the ongoing process of secondary growth. This meristematic tissue develops usually in the cortex region.
The outer cells of phellogen differentiate into the cork or phellem while the inner cells differentiate into the secondary cortex or phelloderm.
Cork or Phellem cells are compactly arranged and have thin cellulosic walls in the beginning. As they mature, there is a gradual loss of living matter and their cell walls become thick.
Phelloderm or the secondary cortex is a thin- walled parenchymatous cell. These are living cells that possess cellulosic cell walls.
Phellogen, Phellem, Phelloderm are collectively known as periderm. These all are the protective layers that grow due to the rupture of the epidermis and the outer layer of the cortex of the primary plant. Hence, secondary growth in the cortex with the help of cork cambium is the result of secondary growth by the vascular cambium.
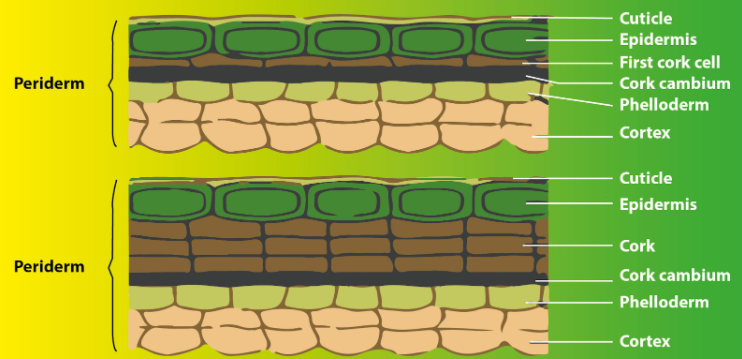
So, the answer is, ‘Cork cambium (phellogen), cork (phellem), and secondary cortex (Phelloderm)’..
Note: - Due to the origin outside the stele, the cork cambium is also called as extra- stellar cambium (stele comprises all the tissues on the inner side of the epidermis, i.e., pericycle, vascular bundles, and pith. - Phellogen is a couple of layers thick and has two layers of meristematic cells. - Cork becomes thick due to the deposition of a fatty substance caller suberin. The suberin deposition in the cell wall makes the cork impervious to water.
Complete answer:
As a result of the continued activity of vascular cambium, the girth of the stem goes on increasing. The continuous increase in the girth results in the rupture of the outermost layer i.e. epidermis and outer cortical layers (layers of cortex). Due to the ruptures, they need to be replaced to protect the stem. New protective cell layers are provided by another lateral meristem i.e. cork cambium. It is also called phellogen. It develops during the ongoing process of secondary growth. This meristematic tissue develops usually in the cortex region.
The outer cells of phellogen differentiate into the cork or phellem while the inner cells differentiate into the secondary cortex or phelloderm.
Cork or Phellem cells are compactly arranged and have thin cellulosic walls in the beginning. As they mature, there is a gradual loss of living matter and their cell walls become thick.
Phelloderm or the secondary cortex is a thin- walled parenchymatous cell. These are living cells that possess cellulosic cell walls.
Phellogen, Phellem, Phelloderm are collectively known as periderm. These all are the protective layers that grow due to the rupture of the epidermis and the outer layer of the cortex of the primary plant. Hence, secondary growth in the cortex with the help of cork cambium is the result of secondary growth by the vascular cambium.

So, the answer is, ‘Cork cambium (phellogen), cork (phellem), and secondary cortex (Phelloderm)’..
Note: - Due to the origin outside the stele, the cork cambium is also called as extra- stellar cambium (stele comprises all the tissues on the inner side of the epidermis, i.e., pericycle, vascular bundles, and pith. - Phellogen is a couple of layers thick and has two layers of meristematic cells. - Cork becomes thick due to the deposition of a fatty substance caller suberin. The suberin deposition in the cell wall makes the cork impervious to water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




