
Petiole of Australian Acacia helps in?
(a) Respiration
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Transpiration
(d) Secretion
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: A leaf is a photosynthetic organ of a plant. It is basically of 3 parts- leaf base, petiole, and lamina. The leaf base is the part that is attached to the stem. The petiole is the part that connects the lamina to the stem. And lamina is the broad, flattened part of the leaf. There are several modifications of leaf i.e., modified structures of leaves that are produced to reduce water loss, trap insects, provide support, etc.
Complete answer:
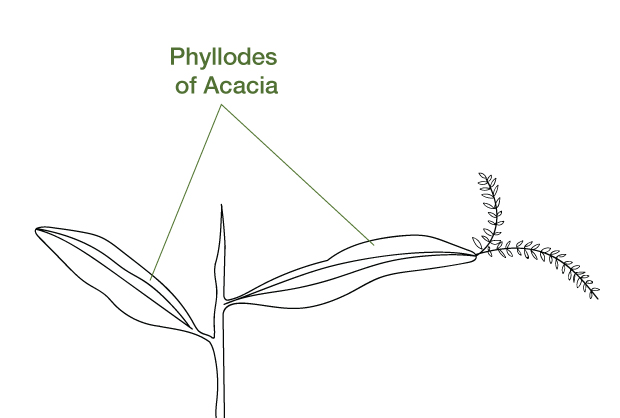
Petiole of Australian Acacia helps in photosynthesis. Petiole connects lamina to the stem and contains vascular tissues like xylem and phloem that allow the sap to flow through them. Thus, they provide a passage to plant sap, food, and nutrients to the leaf. Photosynthesis takes place in leaves so petiole is a part of the leaf photosynthesis and produces the products of photosynthesis.
Additional Information: - Petiole of Australian Acacia gets modified and becomes flat leaf-like and is called phyllode. The leaf itself gets reduced or vanishes and phyllode (petiole) takes over the photosynthetic function of the leaf.
- The vertical orientation of phyllodes protects them from the high intensity of sunlight and thus leaves are modified to protect themselves from sunlight.
- Plants are modified according to the conditions that they have to thrive in. Because they cannot move from one place to another to escape from danger so they have structural modifications.
So, the correct answer is `photosynthesis`.
Note: Leaf tendrils are modifications of leaf in which the whole leaf is modified into a thin wire-like structure for example in peas. Leaf spines are modified leaves to protect the plant from grazing animals as in Opuntia dilleni. Leaf pitcher is a modification wherein leaves are modified into pitcher shaped structures to trap insects to increase intake of phosphorus and nitrogen as in Nepenthes.
Complete answer:
Petiole of Australian Acacia helps in photosynthesis. Petiole connects lamina to the stem and contains vascular tissues like xylem and phloem that allow the sap to flow through them. Thus, they provide a passage to plant sap, food, and nutrients to the leaf. Photosynthesis takes place in leaves so petiole is a part of the leaf photosynthesis and produces the products of photosynthesis.
Additional Information: - Petiole of Australian Acacia gets modified and becomes flat leaf-like and is called phyllode. The leaf itself gets reduced or vanishes and phyllode (petiole) takes over the photosynthetic function of the leaf.
- The vertical orientation of phyllodes protects them from the high intensity of sunlight and thus leaves are modified to protect themselves from sunlight.
- Plants are modified according to the conditions that they have to thrive in. Because they cannot move from one place to another to escape from danger so they have structural modifications.
So, the correct answer is `photosynthesis`.

Note: Leaf tendrils are modifications of leaf in which the whole leaf is modified into a thin wire-like structure for example in peas. Leaf spines are modified leaves to protect the plant from grazing animals as in Opuntia dilleni. Leaf pitcher is a modification wherein leaves are modified into pitcher shaped structures to trap insects to increase intake of phosphorus and nitrogen as in Nepenthes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




