
Phellem, phelloderm and phellogen together form………….
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: Periderm is a result of secondary growth observed mainly in dicot plants. Periderm includes a group of secondary tissues that acts as a protective layer and replaces the epidermis of the stems or roots of a plant body.
Complete answer:
Dicot stems produce cork cambium or phellogen in the outer area of the cortex to increase the girth of the stem. The periclinal division of phellogen produces a set of the outer layers of cells and an inner set of layers. The outer layer is known as cork or phellem while the layer inner to phellogen is referred to as the secondary cortex or phelloderm.
Therefore, Phellem (cork), Phellogen (cork cambium), and Phelloderm together make up the periderm.
Additional information
-The periderm is cylindrical tissue covering the surfaces of stems and roots of perennial plants during early secondary growth; therefore it's not found in monocots and is confined to plants where secondary growth occurs like the dicots.
-During the secondary growth in dicots, some of the cells in the cortex region become meristematic. These are then termed phellogen or cork cambium. Then, the thin-walled and rectangular phellogen cells cut off cells on either side. The cells of the outer side produce the phellem or cork which due to the deposition of suberin in its cell membrane is impervious to water. The inner layer is known as the secondary cortex or phelloderm and it is filled with parenchymatous cells.
-The terrestrial plants with great height have a larger transpiration rate. Cork solves this problem by preventing this loss of water. The inner tender cells are also protected from any attack of pests or mechanical injury. The protection of inner tissues from extreme temperatures is also the function of cork. In some trees, the corks cells are found to be storing tannins, resins, etc.
Note:
-A cell may divide by periclinal division or anticlinal division. When a cell divides in a parallel fashion to the plane of division, then such a division is known as periclinal division. It increases the height or length of a plant.
-If a cell divides perpendicularly or at 90 degrees to the plane of division, it is known as anticlinal division. An increase in the diameter or thickness of a plant has been a result of the anticlinal division.
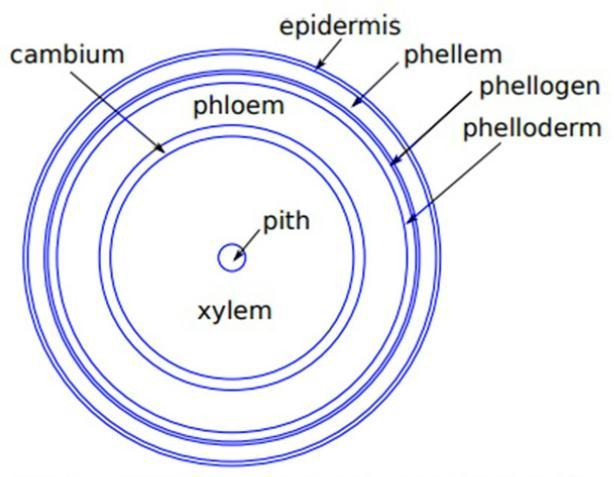
Complete answer:
Dicot stems produce cork cambium or phellogen in the outer area of the cortex to increase the girth of the stem. The periclinal division of phellogen produces a set of the outer layers of cells and an inner set of layers. The outer layer is known as cork or phellem while the layer inner to phellogen is referred to as the secondary cortex or phelloderm.
Therefore, Phellem (cork), Phellogen (cork cambium), and Phelloderm together make up the periderm.
Additional information
-The periderm is cylindrical tissue covering the surfaces of stems and roots of perennial plants during early secondary growth; therefore it's not found in monocots and is confined to plants where secondary growth occurs like the dicots.
-During the secondary growth in dicots, some of the cells in the cortex region become meristematic. These are then termed phellogen or cork cambium. Then, the thin-walled and rectangular phellogen cells cut off cells on either side. The cells of the outer side produce the phellem or cork which due to the deposition of suberin in its cell membrane is impervious to water. The inner layer is known as the secondary cortex or phelloderm and it is filled with parenchymatous cells.
-The terrestrial plants with great height have a larger transpiration rate. Cork solves this problem by preventing this loss of water. The inner tender cells are also protected from any attack of pests or mechanical injury. The protection of inner tissues from extreme temperatures is also the function of cork. In some trees, the corks cells are found to be storing tannins, resins, etc.
Note:
-A cell may divide by periclinal division or anticlinal division. When a cell divides in a parallel fashion to the plane of division, then such a division is known as periclinal division. It increases the height or length of a plant.
-If a cell divides perpendicularly or at 90 degrees to the plane of division, it is known as anticlinal division. An increase in the diameter or thickness of a plant has been a result of the anticlinal division.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




