
Phenol on oxidation in air gives:
A. Quinone
B. Catechol
C. Resorcinol
D. o-cresol
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Phenol is an aromatic compound having a hydroxyl group $\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)$ attached to the aromatic ring. The hydroxyl group is an electron-donating substituent. Oxidation of phenol in air means reaction of phenol with ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Phenol is an aromatic compound having a hydroxyl group $\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)$ attached to the aromatic ring. The hydroxyl group is an electron-donating substituent. As an electron-donating substituent is attached, the nucleophilic character of the aromatic ring increases.
Thus, the oxidation of phenol in air is as follows:
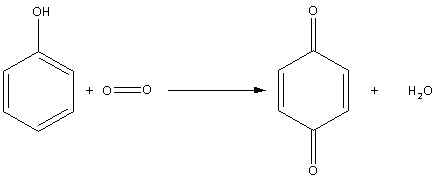
During oxidation of phenol in air, quinone (1,4-benzoquinone) is produced.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional Information:
Catechol is dihydroxybenzene. Oxidation of catechol in air also produces quinone (1,2-benzoquinone). The oxidation of catechol in air is as follows:
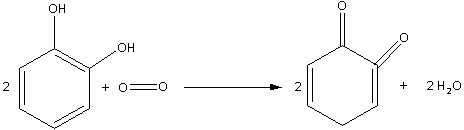
Note:
Quinones are oxidative derivatives of phenols. Quinones are not aromatic in nature as its bond lengths are different. The carbonyl $\left( {{\text{C}} = {\text{O}}} \right)$ bonds in quinone are always double bonds and the carbon-carbon bonds \[\left( {{\text{C}} - {\text{C}}} \right)\] next to the carbonyl bonds are always single bonds. Quinones are not aromatic but they are conjugated.
Phenol when stored in air turns pink in color. Because when stored in air phenol oxidized to quinone. The color of quinone is pink.
Complete step by step answer:
Phenol is an aromatic compound having a hydroxyl group $\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)$ attached to the aromatic ring. The hydroxyl group is an electron-donating substituent. As an electron-donating substituent is attached, the nucleophilic character of the aromatic ring increases.
Thus, the oxidation of phenol in air is as follows:

During oxidation of phenol in air, quinone (1,4-benzoquinone) is produced.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Additional Information:
Catechol is dihydroxybenzene. Oxidation of catechol in air also produces quinone (1,2-benzoquinone). The oxidation of catechol in air is as follows:

Note:
Quinones are oxidative derivatives of phenols. Quinones are not aromatic in nature as its bond lengths are different. The carbonyl $\left( {{\text{C}} = {\text{O}}} \right)$ bonds in quinone are always double bonds and the carbon-carbon bonds \[\left( {{\text{C}} - {\text{C}}} \right)\] next to the carbonyl bonds are always single bonds. Quinones are not aromatic but they are conjugated.
Phenol when stored in air turns pink in color. Because when stored in air phenol oxidized to quinone. The color of quinone is pink.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




