
Phenol reacts with $PC{l_5}$ , the main product is:
A.
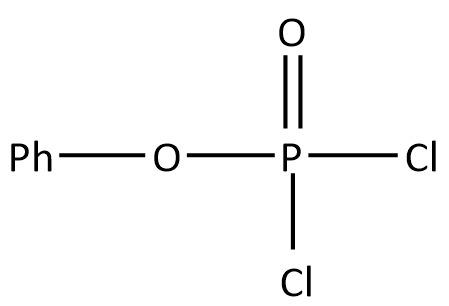
B.
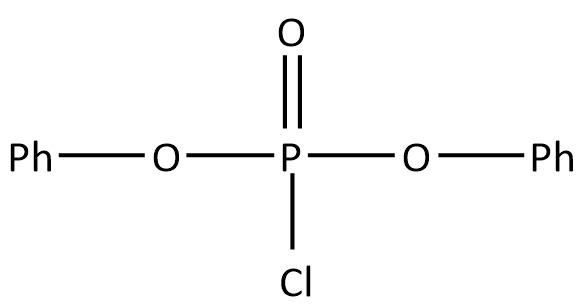
C.
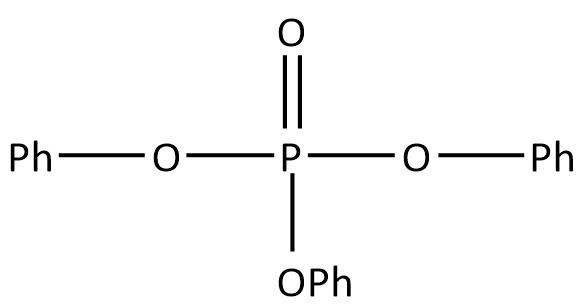
D. None of these



Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: We know that in general, phosphorus pentachloride can be used for preparing alkyl chlorides from alcohol.
Complete step by step answer:
Functional groups impart specific characteristics as it is evident from the name itself. Based on the functional groups, we can have different categories of compounds. Let’s have a look at some of them.
Alkanes are simple hydrocarbons made up of only carbon and hydrogen atoms with a general formula of ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ where $n$ is an integer.
Alkyl groups: These are derived from alkanes by removing one hydrogen atom and are present as substituents. We generally represent them with $R - $ which has been derived from the alkane $RH$ .
Haloalkanes: These are also derived from alkanes by substituting hydrogen atom(s) with halogen(s). Halogens come under functional groups and are usually represented by \[X\] . So, we can use \[RX\] for haloalkanes. As it is evident that there is one alkyl group connected to halogen which gives rise to another name for these compounds to be alkyl halides.
Alcohols: In this category, the functional group is represented by $OH - $ . Here also, hydrogen atom(s) in alkanes are replaced and we get $ROH$ .
As we can see that all of these are inter-related this led us to devise methods for preparing one from another. It has been found that generally, alcohols reacting with $PC{l_5}$ give alkyl chlorides. We can write the involved reaction as follows:
$R - OH + PC{l_5} \to R - Cl + POC{l_3} + HCl$
However, when phenol in which the alcohol group is attached to the benzene ring, is treated with $PC{l_5}$, it is quite different because in phenol, the $C - O$ bond is much stronger. So, when phenol reacts with $PC{l_5}$, following reaction takes place:
$PhO - H + PC{l_5} \to PhO - PC{l_4} + HCl$
We can draw the structure for as follows:
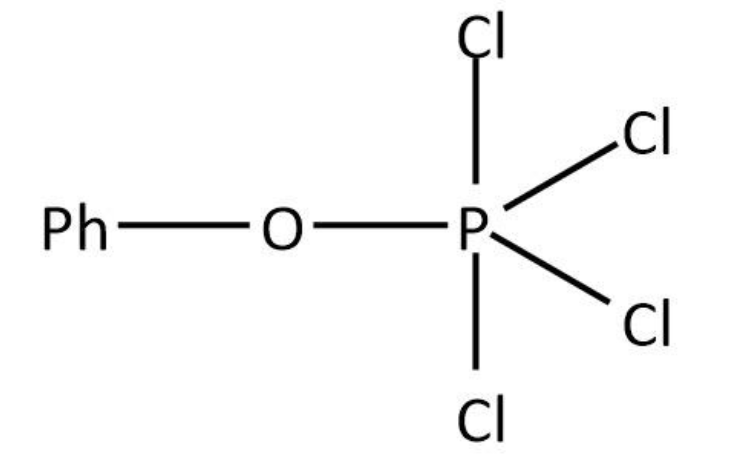
Therefore, the correct option is option (D).
Note:
We have to keep in mind that even though the functional group is the same, alkyl alcohols and aryl alcohols react differently.
Complete step by step answer:
Functional groups impart specific characteristics as it is evident from the name itself. Based on the functional groups, we can have different categories of compounds. Let’s have a look at some of them.
Alkanes are simple hydrocarbons made up of only carbon and hydrogen atoms with a general formula of ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ where $n$ is an integer.
Alkyl groups: These are derived from alkanes by removing one hydrogen atom and are present as substituents. We generally represent them with $R - $ which has been derived from the alkane $RH$ .
Haloalkanes: These are also derived from alkanes by substituting hydrogen atom(s) with halogen(s). Halogens come under functional groups and are usually represented by \[X\] . So, we can use \[RX\] for haloalkanes. As it is evident that there is one alkyl group connected to halogen which gives rise to another name for these compounds to be alkyl halides.
Alcohols: In this category, the functional group is represented by $OH - $ . Here also, hydrogen atom(s) in alkanes are replaced and we get $ROH$ .
As we can see that all of these are inter-related this led us to devise methods for preparing one from another. It has been found that generally, alcohols reacting with $PC{l_5}$ give alkyl chlorides. We can write the involved reaction as follows:
$R - OH + PC{l_5} \to R - Cl + POC{l_3} + HCl$
However, when phenol in which the alcohol group is attached to the benzene ring, is treated with $PC{l_5}$, it is quite different because in phenol, the $C - O$ bond is much stronger. So, when phenol reacts with $PC{l_5}$, following reaction takes place:
$PhO - H + PC{l_5} \to PhO - PC{l_4} + HCl$
We can draw the structure for as follows:

Therefore, the correct option is option (D).
Note:
We have to keep in mind that even though the functional group is the same, alkyl alcohols and aryl alcohols react differently.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




