
Phenolphthalein indicator is used in the pH range:
(A) 3.2 - 4.4
(B) 4.8 - 6.0
(C) 6.8 - 8.4
(D) 8.2 - 10.0
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: This range is specific for phenolphthalein indicator. It lies in the basic value (i.e, between 7 and 14) among the pH values. Phenolphthalein indicator is colourless in acidic medium whereas it shows magenta colour in basic medium.
Complete step by step answer:
- Acid - base indicators / pH indicators are weak organic acids or bases which can change colour with change in pH.
- Let us now consider a weak acid indicator, HIn. At equilibrium, the following chemical equation is established.
\[HIn+{{H}_{2}}O\to I{{n}^{-}}+{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}\]
- The acid (HIn) and its conjugate base (In-) have different colours.
- At low pH, the concentration of H+ (we can write H3O+ ion as H+ ion) will be high and so according to the Le-Chatelier’s principle, equilibrium shifts towards the left. Then the equilibrium solution will show the colour 1.
- At high pH, the concentration of H+ will be low and so the equilibrium shifts towards right and the equilibrium solution has colour 2.
-Phenolphthalein is a colourless, weak acid indicator. Under acidic conditions, the equilibrium is to the left, and the concentration of the anions is too low for the magenta colour to be observed. However, under alkaline conditions, the equilibrium is to the right, and the concentration of the anion becomes sufficient for the magenta colour to be observed.
- When we apply this equilibrium law in general for a weak acid indicator, we get:
\[{{K}_{In}}=\dfrac{[{{H}^{+}}][I{{n}^{-}}]}{[HIn]}\]
- ${{K}_{In}}$ is known as the indicator dissociation constant. The colour of the indicator turns from colour 1 to colour 2 or vice versa at its turning point. At this point: \[\left[ HIn \right]\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ I{{n}^{-}} \right]\]
- So from the equilibrium expression we get, ${{K}_{In}}=[{{H}^{+}}]$
- The pH of the solution at its turning point is $p{{K}_{In}}$ and is the pH at which half of the indicator is in its acid form and the other half in the form of its conjugate base.
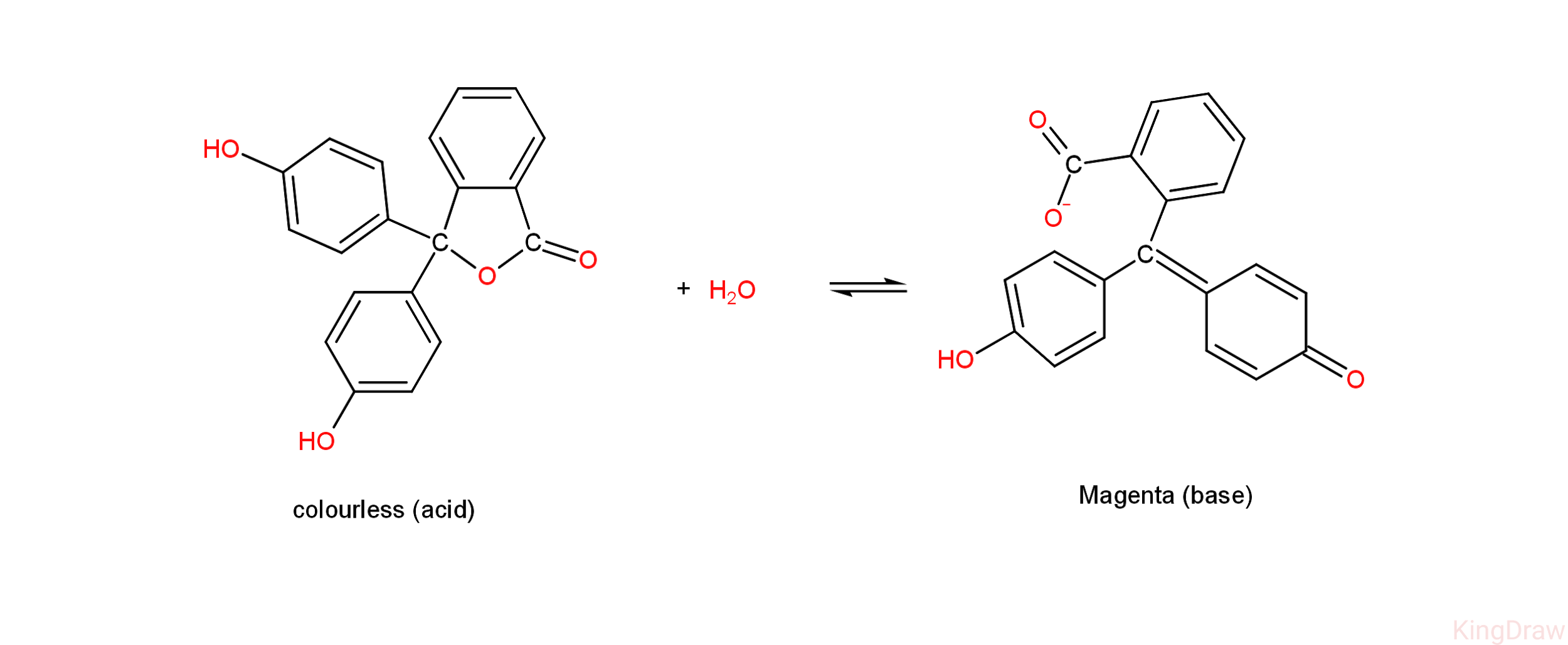
- Given above is the diagram representing the behaviour of phenolphthalein indicators in acidic and basic medium.
- It is colourless in acidic medium and shows a magenta colour in alkaline.
- At a low pH, a weak acid indicator is in the HIn form, the colour of which predominates. As the pH increases, the intensity of the colour of HIn decreases and the equilibrium is shifted to the right. Therefore, the intensity of the colour of indicator ions increases.
- When an indicator is changing its colour in different mediums and it has a small range of pH, we can say it as an efficient indicator.
- For most of the indicators, the pH range is \[p{{K}_{In}}=\pm 1\]
- Phenolphthalein is used in the pH range of 8.2 - 10.0, which is satisfied by Option (D).
- Option (A) 3.2 - 4.4, this pH range is shown by the methyl orange indicator. It shows red colour in acidic medium and orange colour in alkaline medium.
- Option (B) 4.8 - 6.0, this pH range is shown by the chlorophenol red indicator. It shows yellow colour in acidic medium and red colour in alkaline medium.
- Option (C) 6.8 - 8.4, this pH range is shown by phenol red indicator. It shows yellow colour in acidic medium and red colour in alkaline medium.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Apart from being used as an acid base indicator, phenolphthalein has also other uses. It is used for producing magic graph patterns in certain art works, since it shows different colours in different mediums. It is also used as a potential laxative, which is a drug used for the treatment of constipation.
Complete step by step answer:
- Acid - base indicators / pH indicators are weak organic acids or bases which can change colour with change in pH.
- Let us now consider a weak acid indicator, HIn. At equilibrium, the following chemical equation is established.
\[HIn+{{H}_{2}}O\to I{{n}^{-}}+{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}\]
- The acid (HIn) and its conjugate base (In-) have different colours.
- At low pH, the concentration of H+ (we can write H3O+ ion as H+ ion) will be high and so according to the Le-Chatelier’s principle, equilibrium shifts towards the left. Then the equilibrium solution will show the colour 1.
- At high pH, the concentration of H+ will be low and so the equilibrium shifts towards right and the equilibrium solution has colour 2.
-Phenolphthalein is a colourless, weak acid indicator. Under acidic conditions, the equilibrium is to the left, and the concentration of the anions is too low for the magenta colour to be observed. However, under alkaline conditions, the equilibrium is to the right, and the concentration of the anion becomes sufficient for the magenta colour to be observed.
- When we apply this equilibrium law in general for a weak acid indicator, we get:
\[{{K}_{In}}=\dfrac{[{{H}^{+}}][I{{n}^{-}}]}{[HIn]}\]
- ${{K}_{In}}$ is known as the indicator dissociation constant. The colour of the indicator turns from colour 1 to colour 2 or vice versa at its turning point. At this point: \[\left[ HIn \right]\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ I{{n}^{-}} \right]\]
- So from the equilibrium expression we get, ${{K}_{In}}=[{{H}^{+}}]$
- The pH of the solution at its turning point is $p{{K}_{In}}$ and is the pH at which half of the indicator is in its acid form and the other half in the form of its conjugate base.

- Given above is the diagram representing the behaviour of phenolphthalein indicators in acidic and basic medium.
- It is colourless in acidic medium and shows a magenta colour in alkaline.
- At a low pH, a weak acid indicator is in the HIn form, the colour of which predominates. As the pH increases, the intensity of the colour of HIn decreases and the equilibrium is shifted to the right. Therefore, the intensity of the colour of indicator ions increases.
- When an indicator is changing its colour in different mediums and it has a small range of pH, we can say it as an efficient indicator.
- For most of the indicators, the pH range is \[p{{K}_{In}}=\pm 1\]
- Phenolphthalein is used in the pH range of 8.2 - 10.0, which is satisfied by Option (D).
- Option (A) 3.2 - 4.4, this pH range is shown by the methyl orange indicator. It shows red colour in acidic medium and orange colour in alkaline medium.
- Option (B) 4.8 - 6.0, this pH range is shown by the chlorophenol red indicator. It shows yellow colour in acidic medium and red colour in alkaline medium.
- Option (C) 6.8 - 8.4, this pH range is shown by phenol red indicator. It shows yellow colour in acidic medium and red colour in alkaline medium.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Apart from being used as an acid base indicator, phenolphthalein has also other uses. It is used for producing magic graph patterns in certain art works, since it shows different colours in different mediums. It is also used as a potential laxative, which is a drug used for the treatment of constipation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




