
Pheretima can be associated with which of the following terms?
(a) Sterile
(b) Hermaphrodite
(c) Radially symmetrical
(d) Dioecious
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Pheretima is the genus of earthworms which belong to the phylum Annelida. Earthworms have both male and female organs in the form of testes and ovaries in the same body.
Complete answer:
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate exhibiting a tube-within-a-tube body plan. They are monoecious organisms with bilateral symmetry. "Earthworm" is the common name for the largest members of class Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they were classified under the order Opisthopora, since their male pores lie posterior to the female pores, although the internal male segments are present anterior to the female segments.
Earthworms are hermaphrodite animals, i.e., each individual carries both male and female sex organs. As invertebrates, they lack a true skeleton, but they maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelomic chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.
The sexual organs in an earthworm are located through segments 9 to 15. Pheretima has one or two pairs of testes that are contained within sacs. They have two or four pairs of seminal vesicles that produce, store, and release sperms via the male pores. Ovaries and oviducts are seen in segment 13 that release eggs via the female pores on segment 14, while the sperm is expelled from segment 15. One or more pairs of spermathecae are seen in segments 9 and 10 which are internal sacs that receive and store sperm from the other worm during copulation.
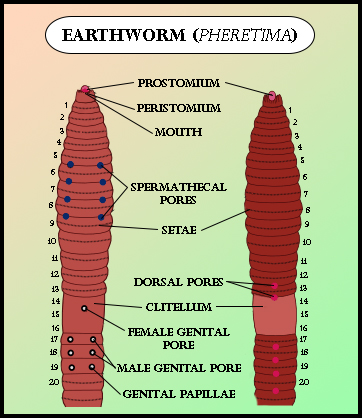
So, the answer is, ‘Hermaphrodite.’
Note: Copulation and reproduction are two separate processes in earthworms. Though they are hermaphrodites, each earthworm obtains sperms from a different worm. So, each earthworm is the father to offspring of a different worm and mother to its own. This ensures genetic variation.
Complete answer:
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate exhibiting a tube-within-a-tube body plan. They are monoecious organisms with bilateral symmetry. "Earthworm" is the common name for the largest members of class Oligochaeta. In classical systems, they were classified under the order Opisthopora, since their male pores lie posterior to the female pores, although the internal male segments are present anterior to the female segments.
Earthworms are hermaphrodite animals, i.e., each individual carries both male and female sex organs. As invertebrates, they lack a true skeleton, but they maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelomic chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.
The sexual organs in an earthworm are located through segments 9 to 15. Pheretima has one or two pairs of testes that are contained within sacs. They have two or four pairs of seminal vesicles that produce, store, and release sperms via the male pores. Ovaries and oviducts are seen in segment 13 that release eggs via the female pores on segment 14, while the sperm is expelled from segment 15. One or more pairs of spermathecae are seen in segments 9 and 10 which are internal sacs that receive and store sperm from the other worm during copulation.

So, the answer is, ‘Hermaphrodite.’
Note: Copulation and reproduction are two separate processes in earthworms. Though they are hermaphrodites, each earthworm obtains sperms from a different worm. So, each earthworm is the father to offspring of a different worm and mother to its own. This ensures genetic variation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




