
Phloem parenchyma is absent in
(a) Dicot roots
(b) Dicot leaf
(c) Monocot stem
(d) Dicot stem
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Phloem parenchyma is composed of living parenchymatous cells. It stores food and organic materials and also helps in the transport of food material. These are absent in grass or grass-like plants whose seeds contain only one embryonic leaf.
Complete answer:
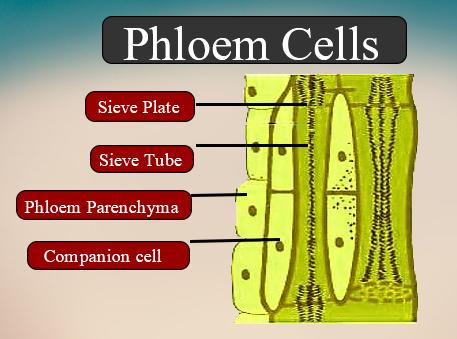
Phloem parenchyma are elongated cells that have tapering ends. They are cylindrical.
Phloem parenchyma is found in both primary and secondary phloem. It is a part of the phloem elements. These are found in dicot roots, leaves, and stems but are absent in monocot plants.
Additional Information: -Phloem is a living tissue that carries food materials, from the source to the sink. The phloem is made up of different elements. These are:
Sieve tube elements, phloem fibers, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma.
-Sieve tube elements are long thin-walled structures that lack nuclei in the mature state. These cells help in the food conduction.
-Companion cells are the specialized parenchymatous cells that are closely associated with sieve tube elements. They help in the maintenance of the pressure gradient in the sieve tube element.
Phloem fibers are the blast fibers that provide mechanical support.
-Phloem Parenchyma: These cells have dense cytoplasm and prominent nucleus. The cell walls are made up of cellulose and have pits. These elements store foods synthesized by the plants and also help to transport them to the various parts of the plants. These also contain organic materials like resins, tannins, mucilage, latex. These materials can be seen as an exudate.
So, the correct answer is, “Monocot stem.”
Note: -The pits present in the phloem parenchyma joins the adjacent cells to form a common connected wall. These form the plasmodesmata connection which is a microscopic channel through which the food and organic materials enter the Phloem.
-Xylem contains xylem parenchyma which is also a living tissue but is present in all vascular plants, unlike the phloem parenchyma.
Complete answer:
Phloem parenchyma are elongated cells that have tapering ends. They are cylindrical.
Phloem parenchyma is found in both primary and secondary phloem. It is a part of the phloem elements. These are found in dicot roots, leaves, and stems but are absent in monocot plants.
Additional Information: -Phloem is a living tissue that carries food materials, from the source to the sink. The phloem is made up of different elements. These are:
Sieve tube elements, phloem fibers, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma.
-Sieve tube elements are long thin-walled structures that lack nuclei in the mature state. These cells help in the food conduction.
-Companion cells are the specialized parenchymatous cells that are closely associated with sieve tube elements. They help in the maintenance of the pressure gradient in the sieve tube element.
Phloem fibers are the blast fibers that provide mechanical support.
-Phloem Parenchyma: These cells have dense cytoplasm and prominent nucleus. The cell walls are made up of cellulose and have pits. These elements store foods synthesized by the plants and also help to transport them to the various parts of the plants. These also contain organic materials like resins, tannins, mucilage, latex. These materials can be seen as an exudate.
So, the correct answer is, “Monocot stem.”
Note: -The pits present in the phloem parenchyma joins the adjacent cells to form a common connected wall. These form the plasmodesmata connection which is a microscopic channel through which the food and organic materials enter the Phloem.
-Xylem contains xylem parenchyma which is also a living tissue but is present in all vascular plants, unlike the phloem parenchyma.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




