
What is photophosphorylation? Distinguish between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation. Give schematic sketches of both.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: Photophosphorylation is the production of ATP by the light-dependent reactions that use light as an energy source. Photophosphorylation occurs either in a cyclic manner or a non-cyclic manner.
Complete answer:
Photophosphorylation is the process of utilizing photosynthetic light energy to convert ADP to ATP. It is the process of formation of energy-rich ATP molecules by transferring the phosphate group into ADP molecules in the presence of light.
Photophosphorylation is of two types:
> Cyclic Photophosphorylation
> Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation
As the name mentions, cyclic photophosphorylation is the process that results in the movement of the electrons in a cyclic manner for synthesizing ATP molecules.
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation differs from cyclic photophosphorylation. It is the process that results in the movement of the electrons in a non-cyclic manner for the synthesis of ATP molecules using the energy from excited electrons provided by photosystem II.
Difference between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation:

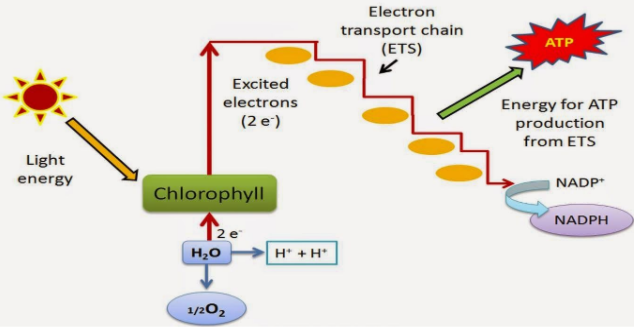
Note: During the pathway of electrons through the ETS (Electron Transport System), photophosphorylation reaction occurs at specific points which results in synthesis of energy rich ATP molecules. When this phosphorylation is occuring in presence of light, it is called photophosphorylation.
Complete answer:
Photophosphorylation is the process of utilizing photosynthetic light energy to convert ADP to ATP. It is the process of formation of energy-rich ATP molecules by transferring the phosphate group into ADP molecules in the presence of light.
Photophosphorylation is of two types:
> Cyclic Photophosphorylation
> Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation
As the name mentions, cyclic photophosphorylation is the process that results in the movement of the electrons in a cyclic manner for synthesizing ATP molecules.
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation differs from cyclic photophosphorylation. It is the process that results in the movement of the electrons in a non-cyclic manner for the synthesis of ATP molecules using the energy from excited electrons provided by photosystem II.
Difference between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation:
| S.No. | Cyclic photophosphorylation | Non-cyclic photophosphorylation |
| 1. | It is performed by the photosystem I is involved. | It is performed by collaboration of both photosystem I and II. |
| 2. | P700 is the active reaction centre. | P680 is the active reaction centre. |
| 3. | An external source of electrons is required because the same electrons get recycled. | The electrons require an external electron donor. |
| 4. | It is not connected with photolysis of water, thus no oxygen is produced. | It is connected with photolysis of water, therefore oxygen is eliminated. |
| 5. | Here, only ATP molecules are produced. | Here, both NADPH and ATP molecules are produced. |
| 6. | It occurs under low light intensity, anaerobic conditions or CO2 availability is poor. | It operates under optimum light intensity, aerobic conditions and in presence of CO2. |
| 7. | It occurs mostly in stromal or intergranal thylakoids. | It occurs in the granal thylakoids. |
| 8. | This process is predominant only in bacteria. | This process is predominant in all green plants. |


Note: During the pathway of electrons through the ETS (Electron Transport System), photophosphorylation reaction occurs at specific points which results in synthesis of energy rich ATP molecules. When this phosphorylation is occuring in presence of light, it is called photophosphorylation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




