
Plastids are absent?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: In all plant cells and in euglenoids, plastids can be found. Plastids are small yet easily observable under microscope. These are double membrane organelles. They are majorly responsible for manufacturing and storing of food. They bear some specific or certain kind of pigments used in photosynthesis which impart specific colors to the plants or plant cells.
Complete Explanation:
As we discussed above plastids are present only in plants and some lower eukaryotic organisms. So, they are absent in animal cells and higher eukaryotic cells.
Plastids may be divided into chloroplasts, chromoplast and leucoplasts on the basis of the type of pigments.
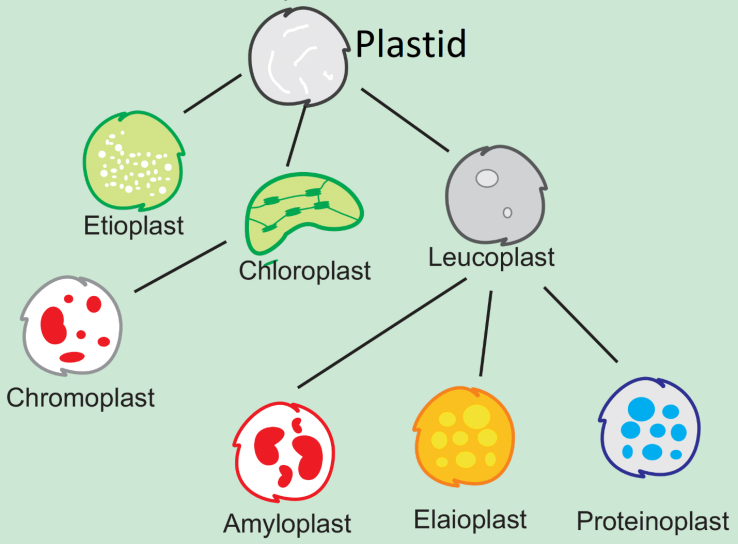
The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments that are essential for photosynthesis and trapping light energy. In chromoplasts fat soluble carotenoid pigments like carotene, xanthophylls and others are present, this gives the plant parts a yellow, orange or red color. Then the last pigment leucoplasts- as the name suggests leucoma means colorless hence, they are colorless plastids of various shapes and sizes with stored nutrients. Amyloplasts store carbohydrates (starch) like- potato. Etioplasts store oils and fats whereas the leucoplasts store proteins.
Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. They were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel. They are also sites for storage and manufacture of chemical compounds of cells like-autotrophic eukaryotes. They have a circular double-stranded DNA molecule.
All plastids come from proplastids present in the plant's meristematic areas. Proplastids are usually separated by binary fission, a mode of asexual reproduction. Plastids have the capacity to differentiate or redifferentiate depending on their morphology and function.
Each plastid creates several copies of a circular plastome of \[10 - 250\] kilobases. Plastid DNA exists as large protein DNA complexes associated with the inner envelope membrane and called plastid nucleoids. Each nucleoid particle may contain more than the \[10\] copies of the plastid DNA.
Note:
Plastids are thought to know that endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Archaeplastida's main endosymbiosis is assumed to occur approximately \[1.5\] billion years ago and has allowed eukaryotes to perform oxygenic photosynthesis. Hence plastids are important for plant cells as they impart colors to plants.
Complete Explanation:
As we discussed above plastids are present only in plants and some lower eukaryotic organisms. So, they are absent in animal cells and higher eukaryotic cells.
Plastids may be divided into chloroplasts, chromoplast and leucoplasts on the basis of the type of pigments.

The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments that are essential for photosynthesis and trapping light energy. In chromoplasts fat soluble carotenoid pigments like carotene, xanthophylls and others are present, this gives the plant parts a yellow, orange or red color. Then the last pigment leucoplasts- as the name suggests leucoma means colorless hence, they are colorless plastids of various shapes and sizes with stored nutrients. Amyloplasts store carbohydrates (starch) like- potato. Etioplasts store oils and fats whereas the leucoplasts store proteins.
Plastids are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. They were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel. They are also sites for storage and manufacture of chemical compounds of cells like-autotrophic eukaryotes. They have a circular double-stranded DNA molecule.
All plastids come from proplastids present in the plant's meristematic areas. Proplastids are usually separated by binary fission, a mode of asexual reproduction. Plastids have the capacity to differentiate or redifferentiate depending on their morphology and function.
Each plastid creates several copies of a circular plastome of \[10 - 250\] kilobases. Plastid DNA exists as large protein DNA complexes associated with the inner envelope membrane and called plastid nucleoids. Each nucleoid particle may contain more than the \[10\] copies of the plastid DNA.
Note:
Plastids are thought to know that endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Archaeplastida's main endosymbiosis is assumed to occur approximately \[1.5\] billion years ago and has allowed eukaryotes to perform oxygenic photosynthesis. Hence plastids are important for plant cells as they impart colors to plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




