
Pneumotaxic center is present in
A. Medulla region of brain
B. Pons region of brain
C. Both A and B
D. Cerebellum of brain
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: Pneumotaxic center is located in the upper part of the pons, in the brain and it controls both the rate and pattern of the respiration.
Complete answer:
The Pneumotaxic center is a neural center present in the pons region of the brain that provides inhibitory impulses on inspiration and thus prevents overdistension of the lungs and helps to maintain alternately recurrent inspiration and expiration. It is considered as the antagonist of the apneustic center that produces abnormal inspiratory breaths. The apneustic center is located in the lower pons region of the brain that promotes inhalation by constant stimulation of the neurons in the medulla oblongata. It manages the intensity of breathing, giving positive impulses to the neurons which are involved in inhalation.
Functions of Pneumotaxic center –
- The neural signal from this center reduces the rate of inspiration and thus affects the respiratory rate and the actions of this center avoid the lungs from over-inflating.
- A chemosensitive area is located near to the rhythm center which is highly sensitive to $CO_2$ and hydrogen ions.
- The pneumotaxic center controls the amount of air that can be inhaled into the body with each breath.
- This center signals the dorsal respiratory group to speed up the rate when a faster rate of breathing is required.
So, the correct answer is the ‘Pons region of the brain’.
Note:
- The respiratory center is a special center in the medulla region of the brain that produces rhythmic nerve impulses that contract the muscles (diaphragm and external intercostal muscle) responsible for inspiration.
- It receives signals from chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, the cerebral cortex, and the hypothalamus in order to regulate the rate and depth of breathing.
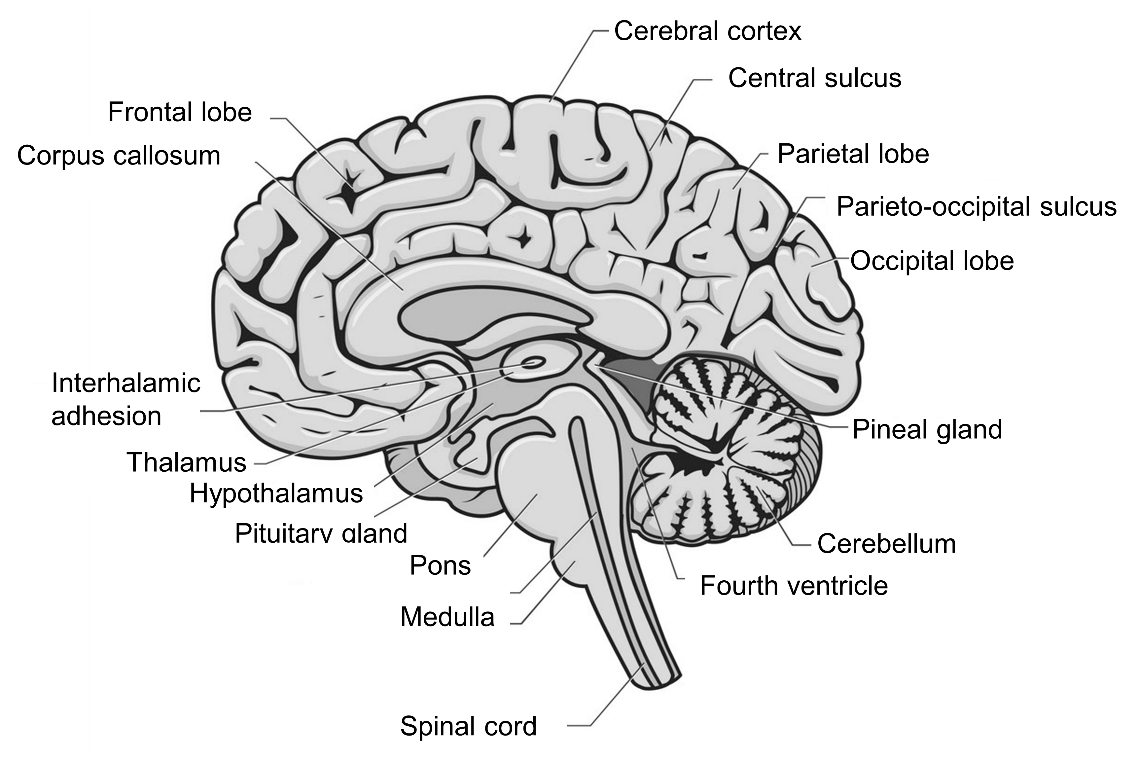
Figure: Parts of the human brain
Complete answer:
The Pneumotaxic center is a neural center present in the pons region of the brain that provides inhibitory impulses on inspiration and thus prevents overdistension of the lungs and helps to maintain alternately recurrent inspiration and expiration. It is considered as the antagonist of the apneustic center that produces abnormal inspiratory breaths. The apneustic center is located in the lower pons region of the brain that promotes inhalation by constant stimulation of the neurons in the medulla oblongata. It manages the intensity of breathing, giving positive impulses to the neurons which are involved in inhalation.
Functions of Pneumotaxic center –
- The neural signal from this center reduces the rate of inspiration and thus affects the respiratory rate and the actions of this center avoid the lungs from over-inflating.
- A chemosensitive area is located near to the rhythm center which is highly sensitive to $CO_2$ and hydrogen ions.
- The pneumotaxic center controls the amount of air that can be inhaled into the body with each breath.
- This center signals the dorsal respiratory group to speed up the rate when a faster rate of breathing is required.
So, the correct answer is the ‘Pons region of the brain’.
Note:
- The respiratory center is a special center in the medulla region of the brain that produces rhythmic nerve impulses that contract the muscles (diaphragm and external intercostal muscle) responsible for inspiration.
- It receives signals from chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, the cerebral cortex, and the hypothalamus in order to regulate the rate and depth of breathing.

Figure: Parts of the human brain
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




