
What is the position of the center of gravity of a rectangular lamina?
A. At the midpoint of the longer side
B. At the midpoint of the shorter side
C. At the point of intersection of its diagonals
D. At one of the corners
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: In regular shaped bodies, the center of mass and the center of gravity both are at the same point due to the uniform distribution of masses. In an irregular shaped body, there is a difference in position between the center of mass and the center of gravity. This is because of the irregular distribution of masses over the body.
Complete answer:
Centre of gravity is defined as the point from which the weight of the entire body or a system is acting. The center of gravity is the center of mass of the body when the gravity of the place is uniform. The center of a regular shaped body will be the center of gravity of that body.
The center of mass is the mean point of mass in the object while the center of gravity is the point on which gravity seems to act. They are not the same.
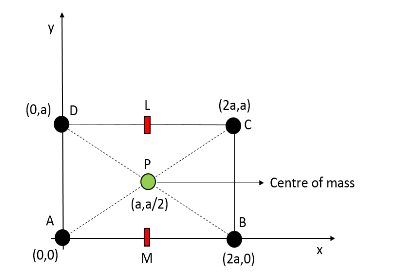
Let us take a rectangular lamina ABCD, where point A is situated at the origin of a Cartesian plane.
Now, length of the lamina is taken as 2a and breadth is taken as a.
Assume that the mass of the lamina are equally distributed at four corners and taken as m.
So, the centre of mass due to masses at A and B will be situated at M which is the midpoint of the length 2a. i.e. (a, 0)
And the centre of mass due to masses at C and D will be situated at L which is the midpoint of the length 2a. i.e. (a, a)
Now, find the centre of mass of masses located at L and M using the formula,
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{m{{x}_{l}}+m{{x}_{m}}}{m+m}=\dfrac{{{x}_{l}}+{{x}_{m}}}{2} \\
& y=\dfrac{m{{y}_{l}}+m{{y}_{m}}}{m+m}=\dfrac{{{y}_{l}}+{{y}_{m}}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the values for x and y for respective masses and we get,
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{{{x}_{l}}+{{x}_{m}}}{2}=\dfrac{a+a}{2}=a \\
& y=\dfrac{{{y}_{l}}+{{y}_{m}}}{2}=\dfrac{a+0}{2}=\dfrac{a}{2} \\
\end{align}$
So, we got the point where centre of mass of the lamina is situated as $\left( a,\dfrac{a}{2} \right)$ which is same as the point of intersection of diagonals for a rectangle having length 2a and breadth a.
Hence, for a rectangular lamina center of gravity is the point of intersection of the diagonals.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Another method for calculating mass element $dm$ for the calculation of center of gravity of irregular objects are as follows:
First we need to find surface mass density which is nothing but total mass per unit area and then multiplying it by total area.
i.e., $\sigma =\dfrac{M}{A}$
Where, $\sigma $ is mass density.
M and A are total mass and total area of the body respectively.
Then, $dM=\sigma dA$ and $dM=\sigma dA$ .
Complete answer:
Centre of gravity is defined as the point from which the weight of the entire body or a system is acting. The center of gravity is the center of mass of the body when the gravity of the place is uniform. The center of a regular shaped body will be the center of gravity of that body.
The center of mass is the mean point of mass in the object while the center of gravity is the point on which gravity seems to act. They are not the same.

Let us take a rectangular lamina ABCD, where point A is situated at the origin of a Cartesian plane.
Now, length of the lamina is taken as 2a and breadth is taken as a.
Assume that the mass of the lamina are equally distributed at four corners and taken as m.
So, the centre of mass due to masses at A and B will be situated at M which is the midpoint of the length 2a. i.e. (a, 0)
And the centre of mass due to masses at C and D will be situated at L which is the midpoint of the length 2a. i.e. (a, a)
Now, find the centre of mass of masses located at L and M using the formula,
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{m{{x}_{l}}+m{{x}_{m}}}{m+m}=\dfrac{{{x}_{l}}+{{x}_{m}}}{2} \\
& y=\dfrac{m{{y}_{l}}+m{{y}_{m}}}{m+m}=\dfrac{{{y}_{l}}+{{y}_{m}}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the values for x and y for respective masses and we get,
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{{{x}_{l}}+{{x}_{m}}}{2}=\dfrac{a+a}{2}=a \\
& y=\dfrac{{{y}_{l}}+{{y}_{m}}}{2}=\dfrac{a+0}{2}=\dfrac{a}{2} \\
\end{align}$
So, we got the point where centre of mass of the lamina is situated as $\left( a,\dfrac{a}{2} \right)$ which is same as the point of intersection of diagonals for a rectangle having length 2a and breadth a.
Hence, for a rectangular lamina center of gravity is the point of intersection of the diagonals.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Another method for calculating mass element $dm$ for the calculation of center of gravity of irregular objects are as follows:
First we need to find surface mass density which is nothing but total mass per unit area and then multiplying it by total area.
i.e., $\sigma =\dfrac{M}{A}$
Where, $\sigma $ is mass density.
M and A are total mass and total area of the body respectively.
Then, $dM=\sigma dA$ and $dM=\sigma dA$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




