
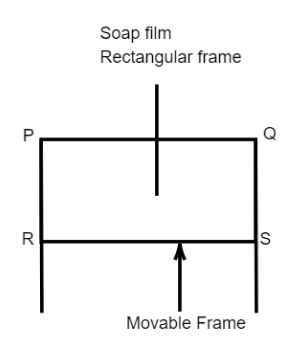
PQSR is a rectangular frame of copper wire shown in fig. The side RS of the frame is movable. If a soap film is formed on it then what is the diameter of the wire to maintain equilibrium? (Given that surface tension of soap solution=\[0.045\,N{m^{ - 1}}\] and density of copper=\[8.96 \times {10^3}kg{m^{ - 3}}\])

Answer
507.3k+ views
Hint: A system is said to be at equilibrium if the total force acting on the system is zero. Find the forces acting on the copper wire to find the equilibrium state of the system. The total surface tension due to the film is equal to the product of the product of the tension force times the length of interaction.
Formula used:
Net force acting on a system at equilibrium is given by,
\[{F_{net}} = 0\]
where, \[{F_{net}}\] is the total force acting on the system.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given here that, PQSR is a rectangular frame of copper wire the side RS of the frame is movable. And a soap film is formed on it. We have to find the diameter of the wire to maintain the equilibrium meaning the film should not snap. Now, the forces acting on the wire are, the weight of the wire and the tension force of the film.
Now, at equilibrium these two forces must be equal. So, the tension force acting on the wire is, \[2Tl\]. And the weight of the wire is, \[mg\].
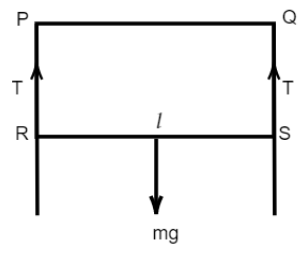
Hence, at equilibrium, \[2Tl - mg = 0\].
Now, the mass of the wire is equal to,
\[m = \rho \pi {r^2}l\]
where, \[\rho \] is the density of copper, $r$ is the radius and $l$ is the length which interacts with the film.
So, we have,
\[2Tl - \rho \pi {r^2}lg = 0\]
\[\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2T}}{{\pi \rho g}}} \]
Putting the values of \[\rho = 8.96 \times {10^3}kg{m^{ - 3}}\] , \[T = 0.045\,N{m^{ - 1}}\] and \[g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}\]we will have,
\[r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 0.045}}{{\pi \times 8.96 \times {{10}^3} \times 9.8}}} \]
\[\therefore r = 5.71 \times {10^{ - 4}}\]
So, the radius of the wire is, \[5.71 \times {10^{ - 4}}m\] or \[0.571mm\].
So, the diameter of the wire will be, \[1.142\,mm\].
Note: To solve this type of problem, find the forces acting and equate them to zero to find the required expression. Note that the radius is proportional to the tension due to the film. Since tension is a contact force the same amount of force will be applied to the film. So, if the radius is larger the tension is larger also and if the tension is greater than the intermolecular force of the film then the film will snap.
Formula used:
Net force acting on a system at equilibrium is given by,
\[{F_{net}} = 0\]
where, \[{F_{net}}\] is the total force acting on the system.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given here that, PQSR is a rectangular frame of copper wire the side RS of the frame is movable. And a soap film is formed on it. We have to find the diameter of the wire to maintain the equilibrium meaning the film should not snap. Now, the forces acting on the wire are, the weight of the wire and the tension force of the film.
Now, at equilibrium these two forces must be equal. So, the tension force acting on the wire is, \[2Tl\]. And the weight of the wire is, \[mg\].

Hence, at equilibrium, \[2Tl - mg = 0\].
Now, the mass of the wire is equal to,
\[m = \rho \pi {r^2}l\]
where, \[\rho \] is the density of copper, $r$ is the radius and $l$ is the length which interacts with the film.
So, we have,
\[2Tl - \rho \pi {r^2}lg = 0\]
\[\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2T}}{{\pi \rho g}}} \]
Putting the values of \[\rho = 8.96 \times {10^3}kg{m^{ - 3}}\] , \[T = 0.045\,N{m^{ - 1}}\] and \[g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}\]we will have,
\[r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2 \times 0.045}}{{\pi \times 8.96 \times {{10}^3} \times 9.8}}} \]
\[\therefore r = 5.71 \times {10^{ - 4}}\]
So, the radius of the wire is, \[5.71 \times {10^{ - 4}}m\] or \[0.571mm\].
So, the diameter of the wire will be, \[1.142\,mm\].
Note: To solve this type of problem, find the forces acting and equate them to zero to find the required expression. Note that the radius is proportional to the tension due to the film. Since tension is a contact force the same amount of force will be applied to the film. So, if the radius is larger the tension is larger also and if the tension is greater than the intermolecular force of the film then the film will snap.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




