
Predict the major products for the given reactions:
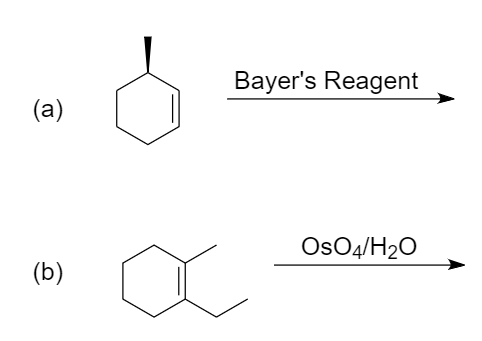

Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: In the presence of Bayer’s reagent and osmium tetroxide, the oxidation of alkene takes place and vicinal diol i.e., a compound having OH group at two adjacent carbon atoms, is formed. These reactions are categorized under the addition reaction of alkenes.
Complete answer:
(a) Bayer’s reagent: It is an alkaline solution of cold and dilute potassium permanganate i.e., $ KMn{{O}_{4}} $ . It is used for the qualitative tests for unsaturation because when it reacts with unsaturated compounds like alkene or alkyne, its colour changes from pink to colourless.
The mechanism followed for given reaction conditions is as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of $ KMn{{O}_{4}} $ takes place in the dilute solution.
$ KMn{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons {{K}^{+}}+Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-} $
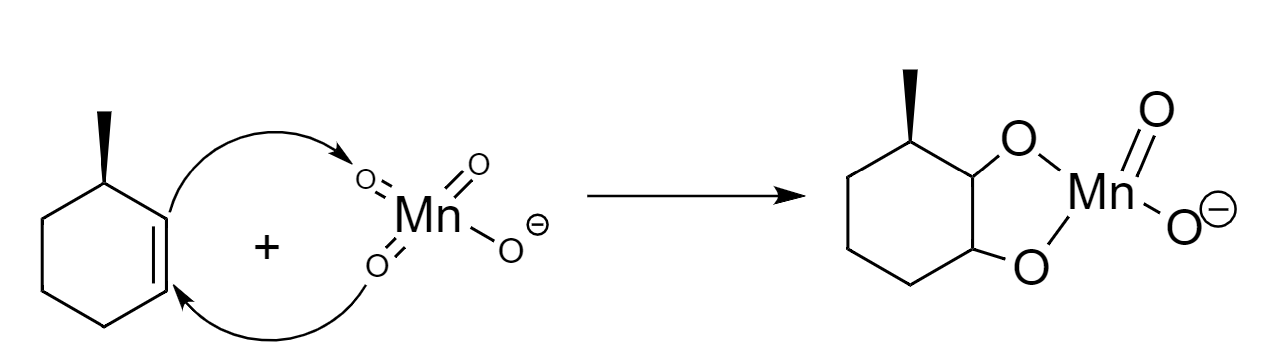
Step-2: Attack of $ Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-} $ on the unsaturated carbon atoms to form a cyclic intermediate.
Step-3: On hydrolysis, the cyclic intermediate converts into vicinal diol.
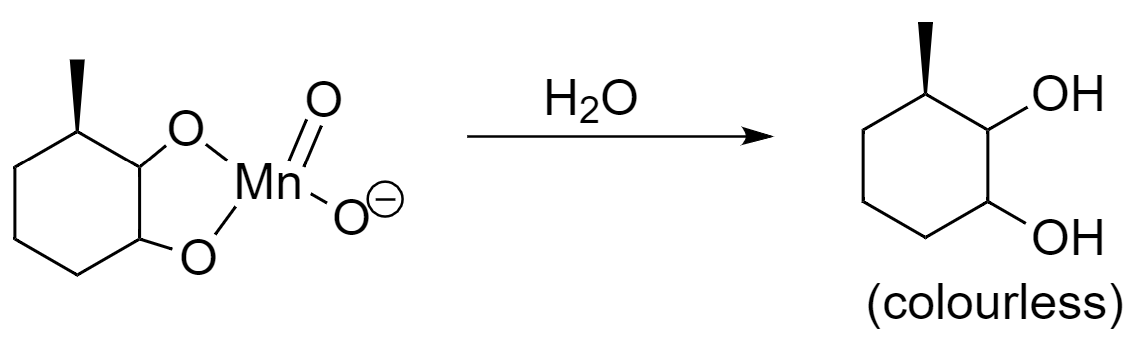
Hence, the major product that is formed after the reaction is $ 3-\text{methylcyclohexane-1,2-diol} $ .
(b) Osmium tetroxide: Its molecular formula is $ Os{{O}_{4}} $ . It shows electrophilic nature and when it reacts with alkene, a formation of cyclic intermediate takes place which on further hydrolysis yields a diol.
The mechanism followed for given reaction conditions is as follows:
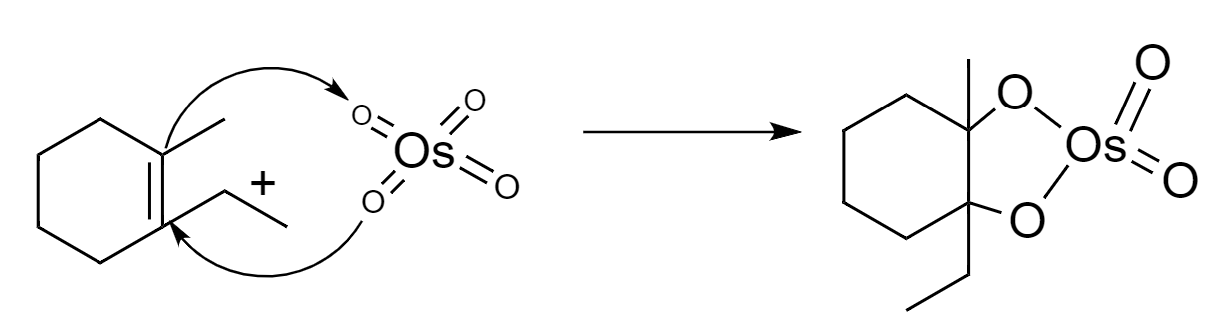
Step-1: The $ \pi $ bonds of alkene acts as a nucleophile and reacts with osmium tetroxide to give a cyclic intermediate.
Step-2: The cyclic intermediate form will undergo hydrolysis to yield a vicinal diol.
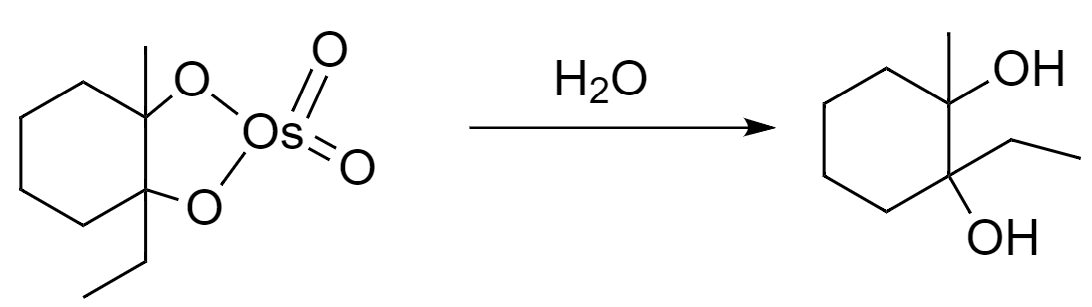
Hence, the major product that is formed after the reaction is $ 1-\text{ethyl2-methylcyclohexane-1,2-diol} $
Note:
It is important to note that the product formed in both the cases will be the syn product i.e., both the hydroxyl group attached to the carbon atoms will be in the same plane which can be either above the plane or below the plane with respect to the plane in which the substituted groups are present.
Complete answer:
(a) Bayer’s reagent: It is an alkaline solution of cold and dilute potassium permanganate i.e., $ KMn{{O}_{4}} $ . It is used for the qualitative tests for unsaturation because when it reacts with unsaturated compounds like alkene or alkyne, its colour changes from pink to colourless.
The mechanism followed for given reaction conditions is as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of $ KMn{{O}_{4}} $ takes place in the dilute solution.
$ KMn{{O}_{4}}\rightleftharpoons {{K}^{+}}+Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-} $
Step-2: Attack of $ Mn{{O}_{4}}^{-} $ on the unsaturated carbon atoms to form a cyclic intermediate.

Step-3: On hydrolysis, the cyclic intermediate converts into vicinal diol.

Hence, the major product that is formed after the reaction is $ 3-\text{methylcyclohexane-1,2-diol} $ .
(b) Osmium tetroxide: Its molecular formula is $ Os{{O}_{4}} $ . It shows electrophilic nature and when it reacts with alkene, a formation of cyclic intermediate takes place which on further hydrolysis yields a diol.
The mechanism followed for given reaction conditions is as follows:
Step-1: The $ \pi $ bonds of alkene acts as a nucleophile and reacts with osmium tetroxide to give a cyclic intermediate.

Step-2: The cyclic intermediate form will undergo hydrolysis to yield a vicinal diol.

Hence, the major product that is formed after the reaction is $ 1-\text{ethyl2-methylcyclohexane-1,2-diol} $
Note:
It is important to note that the product formed in both the cases will be the syn product i.e., both the hydroxyl group attached to the carbon atoms will be in the same plane which can be either above the plane or below the plane with respect to the plane in which the substituted groups are present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




