
How many primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen atoms are present in isobutane?
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: In order to find the number of primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen atoms in certain compounds, we must know what are primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogen is. For that we must first have a clear idea about what primary, secondary and tertiary carbon are. Hydrogen atoms which are attached to these primary, secondary and tertiary carbons are said to be the primary, secondary and tertiary hydrogens respectively.
Complete Solution :
Before moving onto the question directly, let us see what primary, secondary and tertiary carbons are. Primary carbon is those carbon in which the carbon atoms are attached to one other carbon atom. The hydrogen which is attached to these carbon atoms is called primary hydrogen.
The secondary carbon atom is the carbon atom attached to two other carbon atoms called secondary carbon atoms. The hydrogen atoms which are attached to the secondary carbon atom are called secondary hydrogen.
Tertiary carbon atoms are those carbon atoms in which the carbon is attached to three other carbon atoms are called tertiary carbon atoms. The hydrogen atoms attached to such carbon are called tertiary carbon atoms.
Let us now see the structure of isobutane.
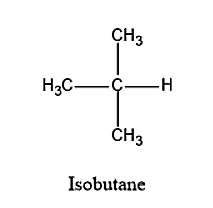
- From the structure, we can see that there are only two types of carbon atoms, i.e. primary and tertiary carbon atoms. It does not have any secondary carbon atom. Therefore, no secondary hydrogen will be present. There are three primary carbon atoms, each carbon atom having three hydrogen atoms and therefore, total nine primary hydrogen atoms are present. The number of tertiary carbon atoms is one. Therefore, it is having only one tertiary hydrogen.
The number of primary hydrogen atoms are 9. The number of tertiary hydrogen atoms are 1. The number of secondary carbon atoms is 0.
Additional information:
Let us see some of the characteristics of isobutane.
- Isobutane will have a tertiary carbon and will have a branched structure.
- the other names of isobutane are i-butane, methyl propane.
- Isobutane is colorless.
- It is odorless
- It is insoluble in water.
Note: Not only primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms are present but also quaternary carbon atoms are present too. For a carbon to be Quaternary, it has to be attached to four other carbon atoms. For example, Neopentane will be having a quaternary Carbon atom.
Complete Solution :
Before moving onto the question directly, let us see what primary, secondary and tertiary carbons are. Primary carbon is those carbon in which the carbon atoms are attached to one other carbon atom. The hydrogen which is attached to these carbon atoms is called primary hydrogen.
The secondary carbon atom is the carbon atom attached to two other carbon atoms called secondary carbon atoms. The hydrogen atoms which are attached to the secondary carbon atom are called secondary hydrogen.
Tertiary carbon atoms are those carbon atoms in which the carbon is attached to three other carbon atoms are called tertiary carbon atoms. The hydrogen atoms attached to such carbon are called tertiary carbon atoms.
Let us now see the structure of isobutane.

- From the structure, we can see that there are only two types of carbon atoms, i.e. primary and tertiary carbon atoms. It does not have any secondary carbon atom. Therefore, no secondary hydrogen will be present. There are three primary carbon atoms, each carbon atom having three hydrogen atoms and therefore, total nine primary hydrogen atoms are present. The number of tertiary carbon atoms is one. Therefore, it is having only one tertiary hydrogen.
The number of primary hydrogen atoms are 9. The number of tertiary hydrogen atoms are 1. The number of secondary carbon atoms is 0.
Additional information:
Let us see some of the characteristics of isobutane.
- Isobutane will have a tertiary carbon and will have a branched structure.
- the other names of isobutane are i-butane, methyl propane.
- Isobutane is colorless.
- It is odorless
- It is insoluble in water.
Note: Not only primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms are present but also quaternary carbon atoms are present too. For a carbon to be Quaternary, it has to be attached to four other carbon atoms. For example, Neopentane will be having a quaternary Carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




