
What is the product of the following reaction?
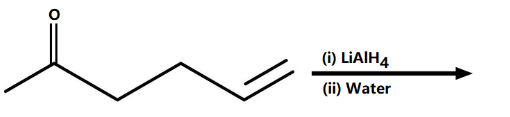
A.
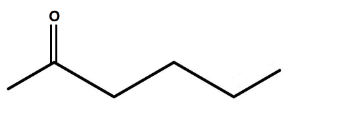
B.
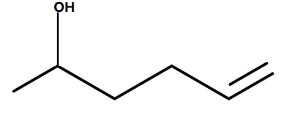
C.
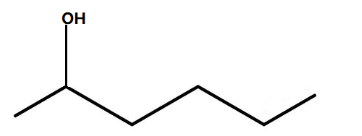
D.
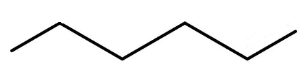





Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: In the reaction, the reactants provided to us is an unsaturated ketone. The reagent given is lithium aluminum hydride \[\left( LiAl{{H}_{4}} \right)\]. \[\left( LiAl{{H}_{4}} \right)\]is a very strong reducing reagent. It is generally a grey solid and is widely used to reduce different carboxyl groups from one form to the other.
Complete step-by-step answer: Lithium Aluminum hydride is majorly used in organic chemistry as a strong reducing agent. It is more strong and powerful as compared with the sodium borohydride. This is because the Al-H bond is generally weak as compared with the B-H bond.
In diether solution it reduces esters, carboxylic acids, acyl chlorides, aldehydes and ketones to the corresponding alcohols. Similarly, it converts amide, nitro, nitrile, oxime and imine into the amines. It also reduces the quaternary ammonium cation to the corresponding tertiary amines.
In the question, it is given that the ketone with a double bond is treated with the lithium aluminum hydride. In this reaction the lithium aluminum hydride will act as a strong reducing agent and thus converts the ketones into the alcohol (C=O group changes to C-OH).
The reaction will occur as follows:
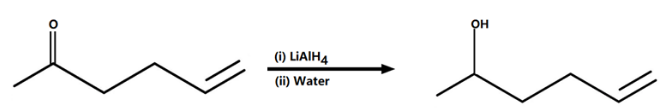
Lithium Aluminum hydride also reduces alkyl halides to the alkanes. This should be noted that here the reagent will not reduce the double bonds. The double bonds will remain as it is. Therefore, these reagents are reduced in nature but they do not reduce the double bonds.
Hence, the correct option is option B.
Note: It should be noted that $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$is more reactive than $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. $NaB{{H}_{4}}$reduces only aldehydes, ketones, acid chlorides, alkyl halides. On the other hand, $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$reduces aldehydes, ketones, acid chlorides, alkyl halides, esters, amides, nitriles, nitro compounds etc. thus it is more reactive and more expensive than the sodium borohydride.
Complete step-by-step answer: Lithium Aluminum hydride is majorly used in organic chemistry as a strong reducing agent. It is more strong and powerful as compared with the sodium borohydride. This is because the Al-H bond is generally weak as compared with the B-H bond.
In diether solution it reduces esters, carboxylic acids, acyl chlorides, aldehydes and ketones to the corresponding alcohols. Similarly, it converts amide, nitro, nitrile, oxime and imine into the amines. It also reduces the quaternary ammonium cation to the corresponding tertiary amines.
In the question, it is given that the ketone with a double bond is treated with the lithium aluminum hydride. In this reaction the lithium aluminum hydride will act as a strong reducing agent and thus converts the ketones into the alcohol (C=O group changes to C-OH).
The reaction will occur as follows:

Lithium Aluminum hydride also reduces alkyl halides to the alkanes. This should be noted that here the reagent will not reduce the double bonds. The double bonds will remain as it is. Therefore, these reagents are reduced in nature but they do not reduce the double bonds.
Hence, the correct option is option B.
Note: It should be noted that $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$is more reactive than $NaB{{H}_{4}}$. $NaB{{H}_{4}}$reduces only aldehydes, ketones, acid chlorides, alkyl halides. On the other hand, $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$reduces aldehydes, ketones, acid chlorides, alkyl halides, esters, amides, nitriles, nitro compounds etc. thus it is more reactive and more expensive than the sodium borohydride.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




