
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ in
(a)Type of movement and placement
(b)Location and mode of functioning
(c)Microtubular structure and function
(d)Microtubular and type of movement
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Flagellum is defined as a long appendage or tail that is used as a whip. It is found attached to the cell body of bacteria and sperm cells. The main difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic flagella lies in the arrangement of a structure which also helps in cytoskeleton formation.
Complete answer:
Additional Information:
-Flagella are filamentous protein structures attached to the cell surface that provide the swimming movement for most motile prokaryotes and in some eukaryotes.
-The structure of a flagellum can only be seen in the electron microscope because the size is 20 nm and up to 15 or 20m long.
So, the correct answer is ‘Microtubular and type of movement’.
Note: -In the 9+2 microtubule arrangement, there are nine fused pairs of microtubules on the outside of a cylinder and the two fused microtubules in the center.
-Monotrichous bacteria are those bacteria that have one flagellum located at the end thus also known as a polar flagellum.
-Amphitrichous bacteria are those bacteria that have a cluster of flagella at one or both ends.
Complete answer:
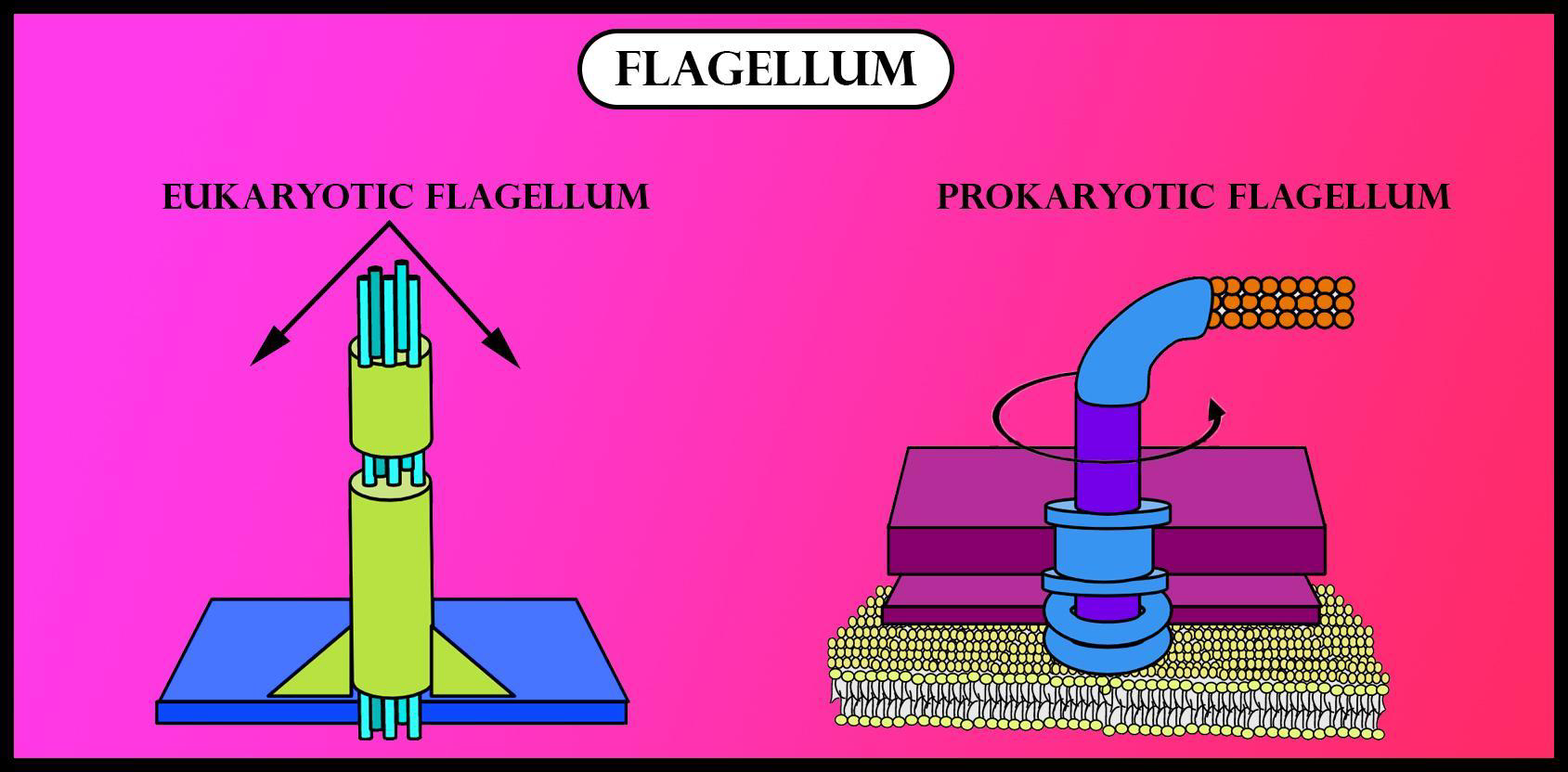
| Eukaryotic flagellum | Prokaryotic Flagellum |
| - Eukaryotes have thick flagella. | -Prokaryotes have thinner flagella |
| -It shows the bending movement. | -It shows rotary motion. |
| -They have a complex sliding filament system. | -They have a rotary motor |
| -The movement is driven by the use of ATP. | -The movement is driven by the proton. |
| -They have a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules. | -They don't have a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules. |

Additional Information:
-Flagella are filamentous protein structures attached to the cell surface that provide the swimming movement for most motile prokaryotes and in some eukaryotes.
-The structure of a flagellum can only be seen in the electron microscope because the size is 20 nm and up to 15 or 20m long.
So, the correct answer is ‘Microtubular and type of movement’.
Note: -In the 9+2 microtubule arrangement, there are nine fused pairs of microtubules on the outside of a cylinder and the two fused microtubules in the center.
-Monotrichous bacteria are those bacteria that have one flagellum located at the end thus also known as a polar flagellum.
-Amphitrichous bacteria are those bacteria that have a cluster of flagella at one or both ends.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




