
Prop or pillar root are
(a)Fasciculated roots
(b)Taproots
(c) Adventitious roots
(d) Secondary roots
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: These are short-lived roots that grow from any part of the plant other than the radicle such as branches, leaves, etc., which are shallow and the growth can be either underground or aerial.
Complete answer:
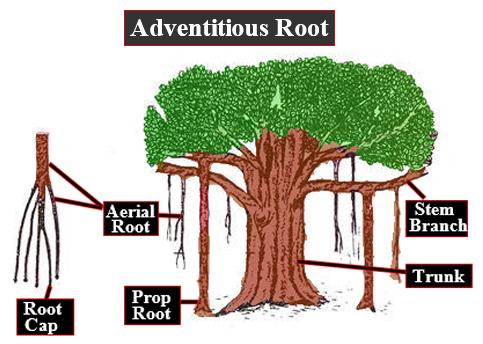
Prop root or pillar root is thick pillar-like adventitious roots. They are modified roots for support. As the plant grows the branches become very heavy. To provide additional support, there arise prop roots from branches of the stem which grow vertically downward. These roots develop from the branches of the tree. Initially, roots are aerial and hygroscopic. They become red in the moistened state. Root caps are present at their tips; they hang downwards, and on reaching the ground, they enter the soil and penetrate the ground thereby supporting the tree. They are also called pillar roots.
As the roots reach the soil, they become thick and pillar-like. The main trunk of the tree often becomes indistinguishable. Its death will not affect the growth of the tree because the crown is supported and nourished by prop roots. Example: Roots of the banyan tree and Rubber plant.
So, the correct answer is ’Adventitious roots’.
Note: -Banyan tree (Great Banyan Tree) growing in Indian Botanic Gardens, Howrah (Indian Botanical Gardens, Kolkata) has 1775 prop roots. Its main trunk has decayed. The crown of the tree has a circumference of 404 m.
-The tree is over 200 years old. The largest Banyan tree grows in Thimmamma Marrimanu village of Anantapur district in Andhra Pradesh. It is spread over an area of 5.2 acres. Two other famous trees are at Adyar in Chennai and Kethohalli village near Bangalore.
-Rhizophora a mangrove plant also possesses prop roots on which lenticels occur.
Complete answer:
Prop root or pillar root is thick pillar-like adventitious roots. They are modified roots for support. As the plant grows the branches become very heavy. To provide additional support, there arise prop roots from branches of the stem which grow vertically downward. These roots develop from the branches of the tree. Initially, roots are aerial and hygroscopic. They become red in the moistened state. Root caps are present at their tips; they hang downwards, and on reaching the ground, they enter the soil and penetrate the ground thereby supporting the tree. They are also called pillar roots.
As the roots reach the soil, they become thick and pillar-like. The main trunk of the tree often becomes indistinguishable. Its death will not affect the growth of the tree because the crown is supported and nourished by prop roots. Example: Roots of the banyan tree and Rubber plant.
So, the correct answer is ’Adventitious roots’.
Note: -Banyan tree (Great Banyan Tree) growing in Indian Botanic Gardens, Howrah (Indian Botanical Gardens, Kolkata) has 1775 prop roots. Its main trunk has decayed. The crown of the tree has a circumference of 404 m.
-The tree is over 200 years old. The largest Banyan tree grows in Thimmamma Marrimanu village of Anantapur district in Andhra Pradesh. It is spread over an area of 5.2 acres. Two other famous trees are at Adyar in Chennai and Kethohalli village near Bangalore.
-Rhizophora a mangrove plant also possesses prop roots on which lenticels occur.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




