
How is propene converted into 1−bromopropane and 2−bromopropane?
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of an electrophilic addition of halogens to a double bond. Markovnikov rule is an important rule for the prediction of products of addition reaction of unsymmetrical alkenes in organic chemistry.
Complete step by step solution:
Addition of \[HBr\] to propene gives 2-bromopropane. The hydrogen of \[HBr\] adds to carbon 1 of propene and bromine adds to carbon 2.
The addition of hydrogen halide to an unsymmetrical alkene gives two products. Propene when undergoes reaction with hydrogen bromide forms \[80{\text{ }}\% \] 2- bromopropane (isopropyl bromide) and \[20\% \] 1-bromopropane (n-propyl bromide) due to Markovnikov rule.
When reacted with \[HBr\] in the presence of peroxide, it gives 1-Bromopropane. The addition is according to Anti Markovnikov's rule.
Addition of \[HBr\] to propene without the presence of peroxides gives 2- bromopropane. The hydrogen of \[HBr\] adds to Carbon 1 of propene and bromine adds to Carbon 2. According to Markovnikov rule, addition reaction of alkenes follows the electrophilic addition reaction mechanism. The general mechanism is explained below:
1. An electrophile, H+ is generated from hydrogen bromide which attacks the double bond to form a carbocation.
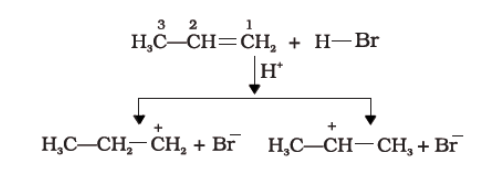
2. Since the secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation, the secondary carbocation predominates the formation of ions.

3. Finally,\[B{r^-}\] attacks the carbocation to form alkyl halides.
Note: Anti-Markovnikov rule explains the regiochemistry where the substituent is bonded to a less substituted carbon, rather than the more substituted carbon. This process is quite unusual, as carbocations which are commonly formed during alkene, or alkyne reactions tend to favour the more substituted carbon. Anti Markovnikov addition reaction is found to follow a free radical mechanism. The peroxide compound involved helps in the generation of free radicals. A general mechanism of anti-Markovnikov addition reaction is discussed below:
1. Generation of free radical through homolytic cleavage of peroxide compound.
2. Attack of generated free radical on hydrogen halide to form halide radical through homolysis
3. Attack of generated halide radical on alkene molecule to form alkyl radical through homolysis.
4. Attack of a generated alkyl radical on hydrogen halide to form alkyl halide through homolytic cleavage of hydrogen halide bond.
Complete step by step solution:
Addition of \[HBr\] to propene gives 2-bromopropane. The hydrogen of \[HBr\] adds to carbon 1 of propene and bromine adds to carbon 2.
The addition of hydrogen halide to an unsymmetrical alkene gives two products. Propene when undergoes reaction with hydrogen bromide forms \[80{\text{ }}\% \] 2- bromopropane (isopropyl bromide) and \[20\% \] 1-bromopropane (n-propyl bromide) due to Markovnikov rule.
When reacted with \[HBr\] in the presence of peroxide, it gives 1-Bromopropane. The addition is according to Anti Markovnikov's rule.
Addition of \[HBr\] to propene without the presence of peroxides gives 2- bromopropane. The hydrogen of \[HBr\] adds to Carbon 1 of propene and bromine adds to Carbon 2. According to Markovnikov rule, addition reaction of alkenes follows the electrophilic addition reaction mechanism. The general mechanism is explained below:
1. An electrophile, H+ is generated from hydrogen bromide which attacks the double bond to form a carbocation.

2. Since the secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation, the secondary carbocation predominates the formation of ions.

3. Finally,\[B{r^-}\] attacks the carbocation to form alkyl halides.
Note: Anti-Markovnikov rule explains the regiochemistry where the substituent is bonded to a less substituted carbon, rather than the more substituted carbon. This process is quite unusual, as carbocations which are commonly formed during alkene, or alkyne reactions tend to favour the more substituted carbon. Anti Markovnikov addition reaction is found to follow a free radical mechanism. The peroxide compound involved helps in the generation of free radicals. A general mechanism of anti-Markovnikov addition reaction is discussed below:
1. Generation of free radical through homolytic cleavage of peroxide compound.
2. Attack of generated free radical on hydrogen halide to form halide radical through homolysis
3. Attack of generated halide radical on alkene molecule to form alkyl radical through homolysis.
4. Attack of a generated alkyl radical on hydrogen halide to form alkyl halide through homolytic cleavage of hydrogen halide bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




