
Propyne and propene can be distinguished by:
A. Conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$
B. $B{r_2}$ in $CC{l_4}$.
C. Dil. ${KMn{O_4}}$
D. $AgN{O_3}$ in ammonia.
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: Silver nitrate in ammonia is actually Tollen’s reagent. It also reacts with acidic hydrogens to give precipitates.
Complete step by step answer:
To get the answer, let us check each reaction one by one:
Conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\]:
Propyne on reaction with conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$ produces a ketone.
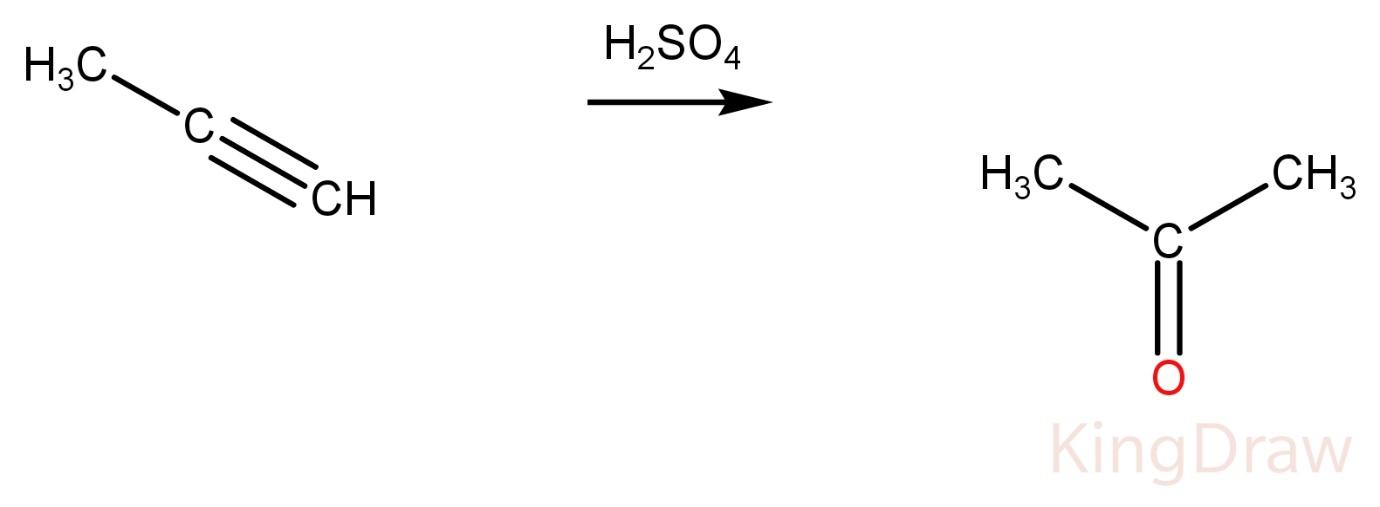 Propene on reaction with conc. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ produces alcohol.
Propene on reaction with conc. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ produces alcohol.
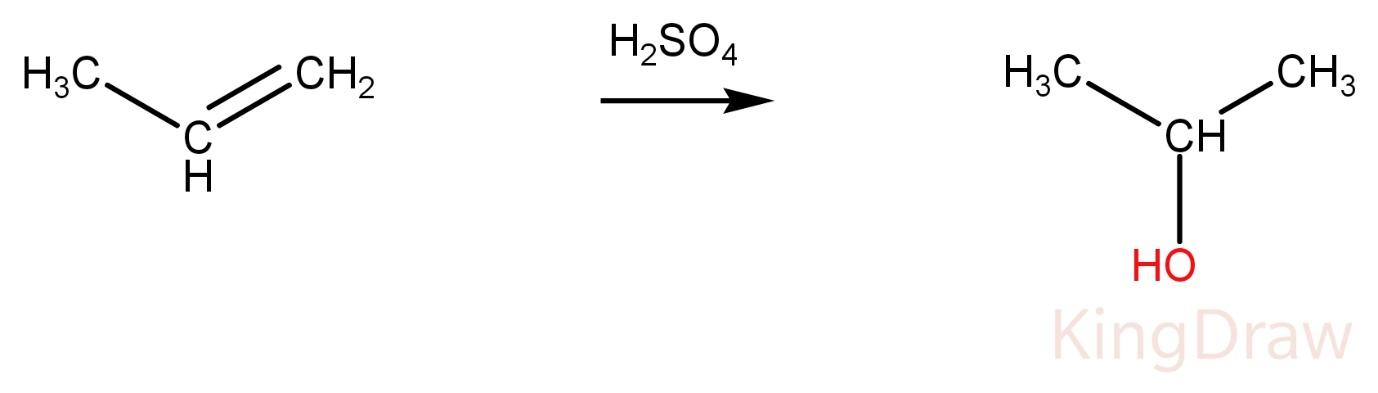 Ketone and alcohol can’t be distinguished at this condition without adding any other reagent. Hence, it is not the correct option.
Ketone and alcohol can’t be distinguished at this condition without adding any other reagent. Hence, it is not the correct option.
$B{r_2}] in [CC{l_4}$:
Propyne on reaction with $B{r_2}$ in $CC{l_4}$ produces a vicinal dibromo alkene whereas propene on reaction with $B{r_2}$ in $CC{l_4}$ produces a vicinal dibromo alkane.
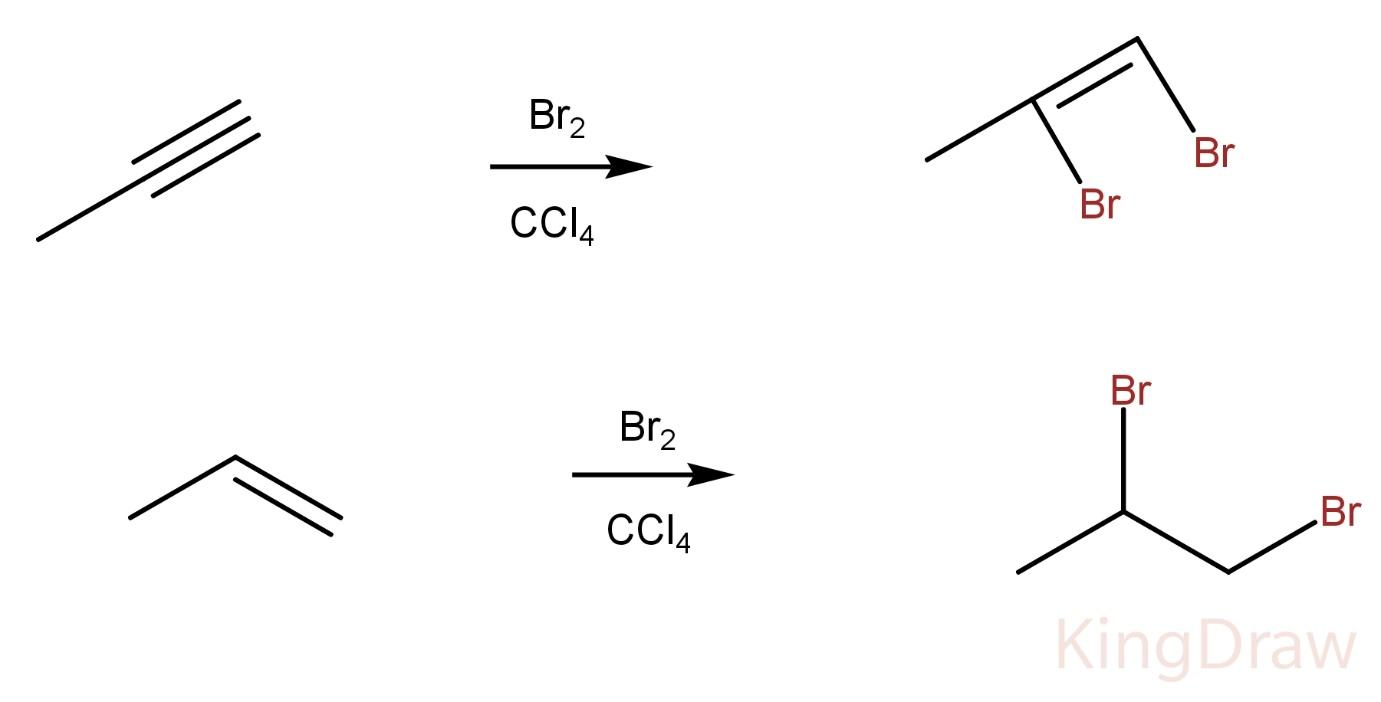 Hence, the two compounds can’t be distinguished by this process.
Hence, the two compounds can’t be distinguished by this process.
Dil. $KMn{O_4}$:
Propynes on reaction with Dil. $KMn{O_4}$ produce -ketoacid.
Propene on reaction with Dil. $KMn{O_4}$ produce a vicinal diol.
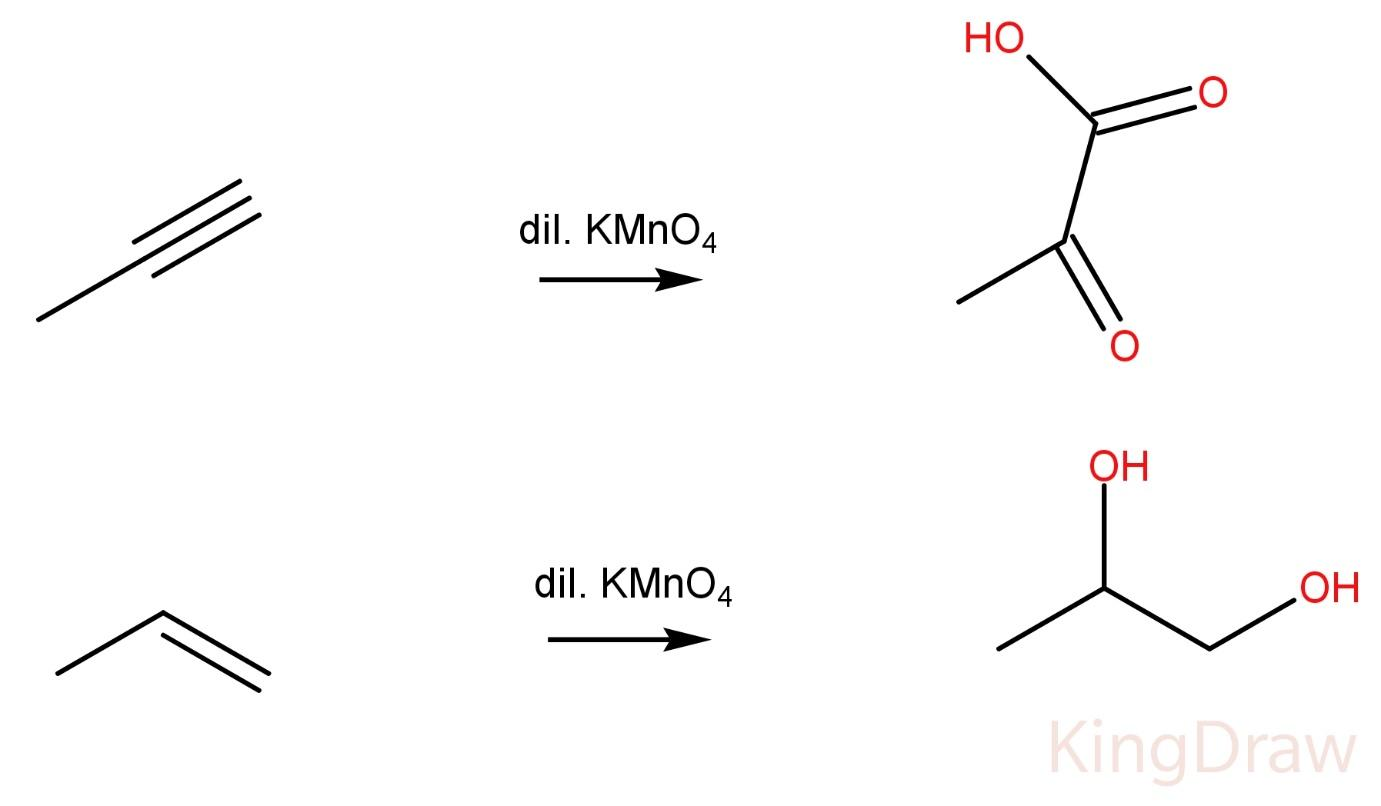 Hence, the two compounds cannot be distinguished by this method also.
Hence, the two compounds cannot be distinguished by this method also.
$AgN{O_3}$ in ammonia:
Propyne on reaction with $AgN{O_3}$ in ammonia produces a white precipitate, while propene does not show any reaction with the Tollen’s reagent.
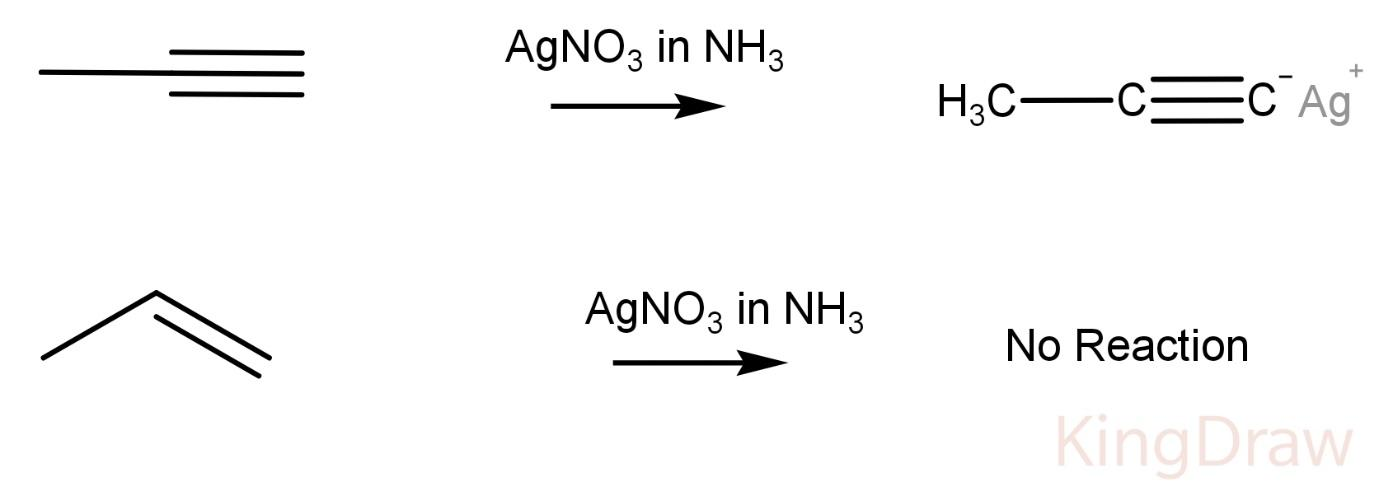
This is due to the fact that Tollen’s reagent reacts with an acidic hydrogen forming a precipitate like in a propyne. The hydrogen which is replaced is very acidic due to high electronegativity of an sp hybridized carbon.
Hence, this reagent can be used to distinguish between a propyne and a propene.
Therefore, the correct answer is (D) $AgN{O_3}$ in ammonia.
Note: When an alkyne is reacted with conc. Sulphuric acid, ketone is formed by the Markovnikov addition of -OH, followed by the rearrangement of the alcohol formed from enol form to keto.
Complete step by step answer:
To get the answer, let us check each reaction one by one:
Conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\]:
Propyne on reaction with conc. ${H_2}S{O_4}$ produces a ketone.


$B{r_2}] in [CC{l_4}$:
Propyne on reaction with $B{r_2}$ in $CC{l_4}$ produces a vicinal dibromo alkene whereas propene on reaction with $B{r_2}$ in $CC{l_4}$ produces a vicinal dibromo alkane.

Dil. $KMn{O_4}$:
Propynes on reaction with Dil. $KMn{O_4}$ produce -ketoacid.
Propene on reaction with Dil. $KMn{O_4}$ produce a vicinal diol.

$AgN{O_3}$ in ammonia:
Propyne on reaction with $AgN{O_3}$ in ammonia produces a white precipitate, while propene does not show any reaction with the Tollen’s reagent.

This is due to the fact that Tollen’s reagent reacts with an acidic hydrogen forming a precipitate like in a propyne. The hydrogen which is replaced is very acidic due to high electronegativity of an sp hybridized carbon.
Hence, this reagent can be used to distinguish between a propyne and a propene.
Therefore, the correct answer is (D) $AgN{O_3}$ in ammonia.
Note: When an alkyne is reacted with conc. Sulphuric acid, ketone is formed by the Markovnikov addition of -OH, followed by the rearrangement of the alcohol formed from enol form to keto.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




