
Proteinaceous infectious particles causing diseases are
A. Prions
B. Viroids
C. Viruses
D. Chlamydia
Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: Proteinaceous infectious particles are misfolded proteins which have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto the normal variants of the same protein. They are characterized by several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in people and animals.
Complete Answer:
The word prion derives from "proteinaceous infectious particle". The hypothetical role of a protein as an infectious agent stands in contrast to all other known infectious agents like viroids, viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites; all of these contain nucleic acids (DNA, RNA, or both).
The protein that constitutes prion (PrP) is found throughout the body. The normal form of the protein is called PrPC, while the infectious form is called PrPSc – the C refers to 'cellular' PrP, while the Sc refers to 'scrapie' which is the prototypic prion disease that occurs in sheep.
PrPC (cellular prion protein) is a normal protein found on the membranes of cells. It has 209 amino acids (in humans), one disulphide bond, a molecular mass of 35–36 kDa and a mainly alpha-helical structure. PrP plays an important role in cell-cell adhesion and intracellular signalling in vivo, and therefore be involved in cell-cell communication in the brain. Protease-resistant PrPSc-like protein (PrPres) is the name given to any isoform of PrPc that has been structurally altered and converted into misfolded proteinase K-resistant form in vitro. The term "PrPres" has been used to distinguish between PrPSc, which is isolated from infectious tissue. Unlike PrPSc, PrPres may not necessarily be infectious.
The infectious isoform of PrP is known as PrPSc, or simply the prion. It is capable of converting normal PrPC proteins into infectious isoform by changing their conformation, or shape which in turn, alters the way the proteins interconnect. PrPSc always causes prion disease. Although the exact 3D structure of PrPSc is not yet known, it has a higher proportion of β-sheet structure. A clump of these abnormal isoforms form highly structured amyloid fibres. These fibres accumulate to form plaques. The end of each fibre acts as a template onto which free protein molecules attach, allowing the fibre to grow. Under most circumstances, only PrP molecules with a similar amino acid sequence as the infectious PrPSc are incorporated into the growing fibre.
So, the correct answer to this question is option A. Prions
Note:
Prions lead to neurodegenerative disease called amyloids, which disrupt the normal tissue structure. This disruption is characterized by "holes" in the tissue. Other histological changes include astrogliosis and the absence of an inflammatory reaction. While the incubation period for prion diseases is relatively 5 to 20 years, once symptoms appear the disease will progress rapidly. This leads to brain damage and death. Neurodegenerative symptoms include convulsions, dementia, ataxia (balance and coordination dysfunction) and behavioural or personality changes.
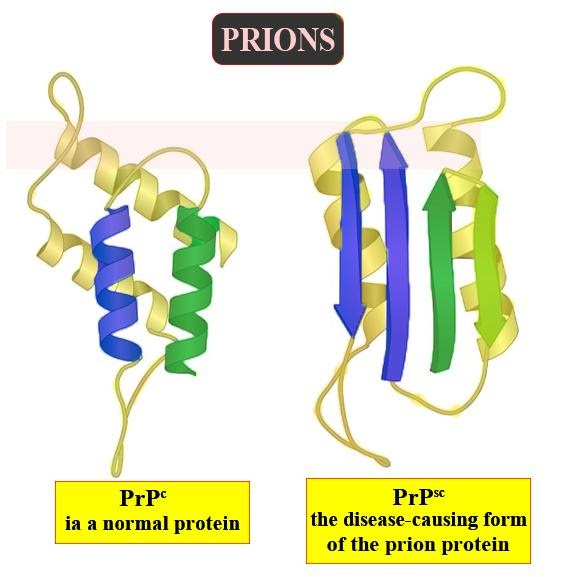
Figure: Prion
Complete Answer:
The word prion derives from "proteinaceous infectious particle". The hypothetical role of a protein as an infectious agent stands in contrast to all other known infectious agents like viroids, viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites; all of these contain nucleic acids (DNA, RNA, or both).
The protein that constitutes prion (PrP) is found throughout the body. The normal form of the protein is called PrPC, while the infectious form is called PrPSc – the C refers to 'cellular' PrP, while the Sc refers to 'scrapie' which is the prototypic prion disease that occurs in sheep.
PrPC (cellular prion protein) is a normal protein found on the membranes of cells. It has 209 amino acids (in humans), one disulphide bond, a molecular mass of 35–36 kDa and a mainly alpha-helical structure. PrP plays an important role in cell-cell adhesion and intracellular signalling in vivo, and therefore be involved in cell-cell communication in the brain. Protease-resistant PrPSc-like protein (PrPres) is the name given to any isoform of PrPc that has been structurally altered and converted into misfolded proteinase K-resistant form in vitro. The term "PrPres" has been used to distinguish between PrPSc, which is isolated from infectious tissue. Unlike PrPSc, PrPres may not necessarily be infectious.
The infectious isoform of PrP is known as PrPSc, or simply the prion. It is capable of converting normal PrPC proteins into infectious isoform by changing their conformation, or shape which in turn, alters the way the proteins interconnect. PrPSc always causes prion disease. Although the exact 3D structure of PrPSc is not yet known, it has a higher proportion of β-sheet structure. A clump of these abnormal isoforms form highly structured amyloid fibres. These fibres accumulate to form plaques. The end of each fibre acts as a template onto which free protein molecules attach, allowing the fibre to grow. Under most circumstances, only PrP molecules with a similar amino acid sequence as the infectious PrPSc are incorporated into the growing fibre.
So, the correct answer to this question is option A. Prions
Note:
Prions lead to neurodegenerative disease called amyloids, which disrupt the normal tissue structure. This disruption is characterized by "holes" in the tissue. Other histological changes include astrogliosis and the absence of an inflammatory reaction. While the incubation period for prion diseases is relatively 5 to 20 years, once symptoms appear the disease will progress rapidly. This leads to brain damage and death. Neurodegenerative symptoms include convulsions, dementia, ataxia (balance and coordination dysfunction) and behavioural or personality changes.

Figure: Prion
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




