
Prove in a triangle ABC, if $AB>AC$ and D is any point on the side BC, then prove that $AB>AD$?
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:We start solving the problem by drawing all the given information to get a better view. We use the fact that the angle opposite to the larger side is large to get the relation between angles $\angle ACB$ and $\angle CBA$. We then find the relation between angle $\angle ADB$ and $\angle ACD$ using the fact that some of the angles in a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ and the angle in a straight line is ${{180}^{\circ }}$. Using this relation we find the relation between the angles $\angle ADB$ and $\angle CBA$, which leads us to the desired result.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem we have a triangle $ABC$ with sides $AB>AC$ and D is any point on the side BC. We need to prove $AB>AD$.
Let us draw the given information to get a better view.
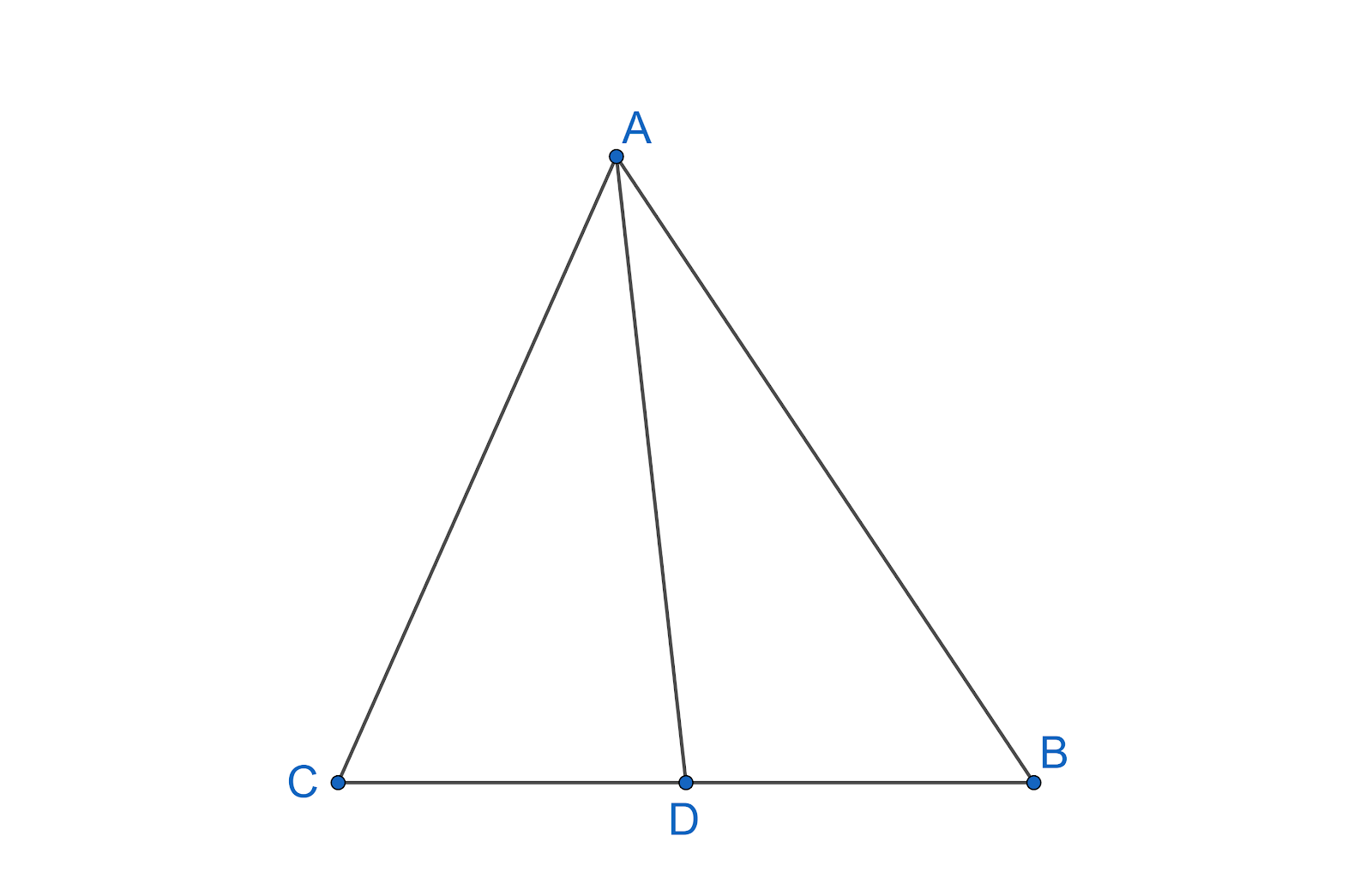
According to the problem, we have a relation between sides AB and AC as $AB>AC$. We know that the angle opposite to the larger side is large. Applying this fact in $\Delta ABC$, we get the relation between the angles as $\angle ACB>\angle CBA$ ---(1).
We know that the angle in a straight line at a point is ${{180}^{\circ }}$. We apply this at point D.
We get \[\angle ADB+\angle CDA={{180}^{\circ }}\].
\[\Rightarrow \angle ADB={{180}^{\circ }}-\angle CDA\] ---(2).
We know that the sum of the angles in a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$. We use this in $\Delta ADC$.
So, we get \[\angle ACD+\angle CDA+\angle DAC={{180}^{\circ }}\].
$\Rightarrow \angle ACD+\angle DAC={{180}^{\circ }}-\angle CDA$.
From equation (2), we get
$\Rightarrow \angle ACD+\angle DAC=\angle ADB$ ---(3).
From the figure, we can see that $\angle ACD=\angle ACB$. We use this in equation (3).
$\Rightarrow \angle ACB+\angle DAC=\angle ADB$ ---(4).
From equation (4), we can see that the value of the angle $\angle ADB$ greater than the angle $\angle ACB$.
So, we get $\angle ADB>\angle ACB$ ---(5).
From equation (1) and (5), we can clearly see that $\angle ADB>\angle CBA$ ---(6).
Now, let us consider $\Delta ADB$ and we have $\angle ADB>\angle CBA$. We know that the sides opposite to the larger angle is large. We can see that the side opposite to the angle $\angle ADB$ is AB and the side opposite to $\angle CBA$ is AD.
So, we get $AB>AD$.
∴ We have proved $AB>AD$.
Note:
We should not confuse with the notation of angles present inside the triangle. Whenever we get this type of problem, we should make use of the diagram and the fact that the angle opposite to the larger side is large. We should not assume the angle at point D as ${{90}^{\circ }}$. We should not consider the line segment AD as the angular bisector as this will not be possible always.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem we have a triangle $ABC$ with sides $AB>AC$ and D is any point on the side BC. We need to prove $AB>AD$.
Let us draw the given information to get a better view.

According to the problem, we have a relation between sides AB and AC as $AB>AC$. We know that the angle opposite to the larger side is large. Applying this fact in $\Delta ABC$, we get the relation between the angles as $\angle ACB>\angle CBA$ ---(1).
We know that the angle in a straight line at a point is ${{180}^{\circ }}$. We apply this at point D.
We get \[\angle ADB+\angle CDA={{180}^{\circ }}\].
\[\Rightarrow \angle ADB={{180}^{\circ }}-\angle CDA\] ---(2).
We know that the sum of the angles in a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$. We use this in $\Delta ADC$.
So, we get \[\angle ACD+\angle CDA+\angle DAC={{180}^{\circ }}\].
$\Rightarrow \angle ACD+\angle DAC={{180}^{\circ }}-\angle CDA$.
From equation (2), we get
$\Rightarrow \angle ACD+\angle DAC=\angle ADB$ ---(3).
From the figure, we can see that $\angle ACD=\angle ACB$. We use this in equation (3).
$\Rightarrow \angle ACB+\angle DAC=\angle ADB$ ---(4).
From equation (4), we can see that the value of the angle $\angle ADB$ greater than the angle $\angle ACB$.
So, we get $\angle ADB>\angle ACB$ ---(5).
From equation (1) and (5), we can clearly see that $\angle ADB>\angle CBA$ ---(6).
Now, let us consider $\Delta ADB$ and we have $\angle ADB>\angle CBA$. We know that the sides opposite to the larger angle is large. We can see that the side opposite to the angle $\angle ADB$ is AB and the side opposite to $\angle CBA$ is AD.
So, we get $AB>AD$.
∴ We have proved $AB>AD$.
Note:
We should not confuse with the notation of angles present inside the triangle. Whenever we get this type of problem, we should make use of the diagram and the fact that the angle opposite to the larger side is large. We should not assume the angle at point D as ${{90}^{\circ }}$. We should not consider the line segment AD as the angular bisector as this will not be possible always.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




