
How do you prove Ptolemy's Theorem that in a cyclic quadrilateral, the sum of the products of opposite pairs of sides is equal to the product of the diagonals?
In cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, \[AB \times CD + BC \times AD = AC \times BD\].
Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: To prove the Ptolemy's Theorem, draw a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, in which AC and BD are its diagonals which intersect at P. Considering its respective angles and triangles whose corresponding sides are proportional. Hence, by this we can prove the theorem.
Complete step by step answer:
Ptolemy's Theorem states that in a cyclic quadrilateral, the sum of the products of opposite pairs of sides is equal to the product of the diagonals.
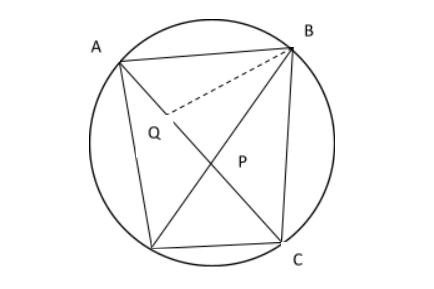
In the figure, ABCD is the cyclic quadrilateral inscribed in a circle as described below. Let us also join its diagonals AC and BD to intersect at P.
To prove that \[AB \times CD + BC \times AD = AC \times BD\], let us draw an angle
\[\angle ABQ = \angle CBD\] to intersect AC at Q as shown in the figure.
In \[\Delta ABQ\]and \[\Delta CBD\], we have
By construction we have
\[\angle ABQ = \angle CBD\]
Angles in the same arc we have
\[\angle BAQ = \angle CDB\]
Therefore,
\[\Delta ABQ \sim \Delta CBD\]
As we can see in the adjoining figure that both the obtained triangles are almost similar, hence the corresponding sides are proportional to each other
\[\dfrac{{AB}}{{BD}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{CD}}\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[AB \times CD = BD \times AQ\] ……………….. 1
Similarly, as \[\angle ABQ = \angle CBD\] we have
\[\angle ABQ + \angle QBP = \angle CBD + \angle QBP\]
And in \[\Delta ABD\]and \[\Delta QBC\], we have angles in the same arc AB as
\[\angle ABD = \angle QBC\]
\[\angle ADB = \angle QCB\]
Hence, this implies that
\[\Delta ABD \sim \Delta QBC\]
As we can see in the adjoining figure that both the obtained triangles are almost similar, hence the corresponding sides are proportional to each other
\[\dfrac{{AD}}{{QC}} = \dfrac{{BD}}{{BC}}\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[AD \times BC = BD \times QC\] ……………….. 2
Adding equation 1 and 2, we get
Equation 1 is
\[AB \times CD = BD \times AQ\]
Equation 2 is
\[AD \times BC = BD \times QC\]
Simplifying we get
\[AB \times CD + BC \times AD = \left( {AQ + QC} \right) \times BD\]
\[AB \times CD + BC \times AD = AC \times BD\]
Note: To prove Ptolemy's Theorem as it is a relation between the four sides and two diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral, considering its respective angles and triangles whose corresponding sides are proportional we can prove the theorem. In a quadrilateral, if the sum of the products of the lengths of its two pairs of opposite sides is equal to the product of the lengths of its diagonals, then the quadrilateral can be inscribed in a circle i.e., it is a cyclic quadrilateral.

Complete step by step answer:
Ptolemy's Theorem states that in a cyclic quadrilateral, the sum of the products of opposite pairs of sides is equal to the product of the diagonals.
In the figure, ABCD is the cyclic quadrilateral inscribed in a circle as described below. Let us also join its diagonals AC and BD to intersect at P.
To prove that \[AB \times CD + BC \times AD = AC \times BD\], let us draw an angle
\[\angle ABQ = \angle CBD\] to intersect AC at Q as shown in the figure.
In \[\Delta ABQ\]and \[\Delta CBD\], we have
By construction we have
\[\angle ABQ = \angle CBD\]
Angles in the same arc we have
\[\angle BAQ = \angle CDB\]
Therefore,
\[\Delta ABQ \sim \Delta CBD\]
As we can see in the adjoining figure that both the obtained triangles are almost similar, hence the corresponding sides are proportional to each other
\[\dfrac{{AB}}{{BD}} = \dfrac{{AQ}}{{CD}}\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[AB \times CD = BD \times AQ\] ……………….. 1
Similarly, as \[\angle ABQ = \angle CBD\] we have
\[\angle ABQ + \angle QBP = \angle CBD + \angle QBP\]
And in \[\Delta ABD\]and \[\Delta QBC\], we have angles in the same arc AB as
\[\angle ABD = \angle QBC\]
\[\angle ADB = \angle QCB\]
Hence, this implies that
\[\Delta ABD \sim \Delta QBC\]
As we can see in the adjoining figure that both the obtained triangles are almost similar, hence the corresponding sides are proportional to each other
\[\dfrac{{AD}}{{QC}} = \dfrac{{BD}}{{BC}}\]
Simplifying the terms, we get
\[AD \times BC = BD \times QC\] ……………….. 2
Adding equation 1 and 2, we get
Equation 1 is
\[AB \times CD = BD \times AQ\]
Equation 2 is
\[AD \times BC = BD \times QC\]
Simplifying we get
\[AB \times CD + BC \times AD = \left( {AQ + QC} \right) \times BD\]
\[AB \times CD + BC \times AD = AC \times BD\]
Note: To prove Ptolemy's Theorem as it is a relation between the four sides and two diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral, considering its respective angles and triangles whose corresponding sides are proportional we can prove the theorem. In a quadrilateral, if the sum of the products of the lengths of its two pairs of opposite sides is equal to the product of the lengths of its diagonals, then the quadrilateral can be inscribed in a circle i.e., it is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




