
Prove that the chords equidistant from the center of a circle are equal in length.
Answer
609.9k+ views
Hint: First of all, draw a circle with center O and chords AB and CD at a distance of OX and OY from the center respectively. Now, join O to A and O to D. Now prove \[\Delta AOX\] and \[\Delta DOY\] congruent, and from this prove AX = DY. Now, from this prove AB = CD by using the theorem that perpendiculars from the center bisect the chord.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have to prove that the chords equidistant from the center of a circle are equal in length. First of all, construct a circle with center O
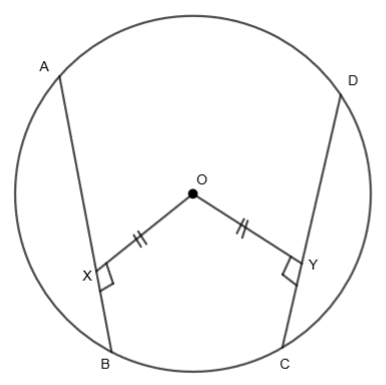
In the above circle, AB and CD are two chords of the circle where OX is the distance from the center of the chord AB that is \[OX\bot AB\]. Also, OY is the distance from the center of the chord CD that is \[OY\bot CD\]. We are given that the two chords are equidistant from the center of the circle. So, OX = OY. Now, we have to prove that the lengths of the given chords are equal or AB = CD. Let us join point A to O and point D to O.
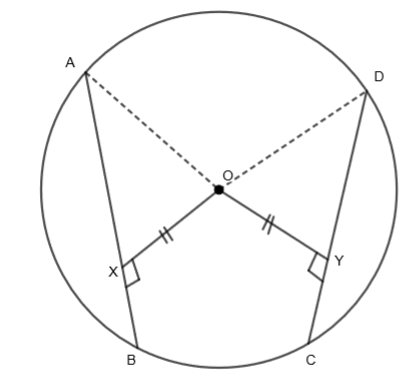
Consider \[\Delta AOX\] and \[\Delta DOY\]. We get, both \[\angle OXA\] and \[\angle OYD\] are equal to \[{{90}^{o}}\]. So,
\[\angle OXA=\angle OYD.....\left( i \right)\]
We know that in a circle, all radii are equal. So,
OA = OD …..(ii)
Also, we are given that OX = OY……(iii)
So, from right angle hypotenuse side (RHS) congruence criteria, we get,
\[\Delta AOX\cong \Delta DOY\]
We know that the corresponding parts of the congruent triangles are equal. So, we get,
AX = DY……(iv)
We know that the perpendicular from the center to a chord bisects the chord. So, we get,
For chord AB, X bisects AB, so AB = 2 AX.
\[\Rightarrow AX=\dfrac{AB}{2}.....\left( v \right)\]
For chord CD, Y bisects CD, so, CD = 2 DY
\[\Rightarrow DY=\dfrac{CD}{2}.....\left( vi \right)\]
Now by substituting the values of AX and DY from equation (v) and (vi) in equation (iv), we get,
\[\dfrac{AB}{2}=\dfrac{CD}{2}\]
AB = CD [Hence proved]
So, we have proved that chords equidistant from the center of the circle is equal in length.
Note: In this question, students must remember all the theorems discussed in the above solution as they are very useful while solving the questions related to the circle. Also, students can check these theorems practically by constructing a circle of a certain radius and making equidistant chords and perpendiculars on it from the center. Now, measure the lengths of both the chords if they are equal or not.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have to prove that the chords equidistant from the center of a circle are equal in length. First of all, construct a circle with center O

In the above circle, AB and CD are two chords of the circle where OX is the distance from the center of the chord AB that is \[OX\bot AB\]. Also, OY is the distance from the center of the chord CD that is \[OY\bot CD\]. We are given that the two chords are equidistant from the center of the circle. So, OX = OY. Now, we have to prove that the lengths of the given chords are equal or AB = CD. Let us join point A to O and point D to O.

Consider \[\Delta AOX\] and \[\Delta DOY\]. We get, both \[\angle OXA\] and \[\angle OYD\] are equal to \[{{90}^{o}}\]. So,
\[\angle OXA=\angle OYD.....\left( i \right)\]
We know that in a circle, all radii are equal. So,
OA = OD …..(ii)
Also, we are given that OX = OY……(iii)
So, from right angle hypotenuse side (RHS) congruence criteria, we get,
\[\Delta AOX\cong \Delta DOY\]
We know that the corresponding parts of the congruent triangles are equal. So, we get,
AX = DY……(iv)
We know that the perpendicular from the center to a chord bisects the chord. So, we get,
For chord AB, X bisects AB, so AB = 2 AX.
\[\Rightarrow AX=\dfrac{AB}{2}.....\left( v \right)\]
For chord CD, Y bisects CD, so, CD = 2 DY
\[\Rightarrow DY=\dfrac{CD}{2}.....\left( vi \right)\]
Now by substituting the values of AX and DY from equation (v) and (vi) in equation (iv), we get,
\[\dfrac{AB}{2}=\dfrac{CD}{2}\]
AB = CD [Hence proved]
So, we have proved that chords equidistant from the center of the circle is equal in length.
Note: In this question, students must remember all the theorems discussed in the above solution as they are very useful while solving the questions related to the circle. Also, students can check these theorems practically by constructing a circle of a certain radius and making equidistant chords and perpendiculars on it from the center. Now, measure the lengths of both the chords if they are equal or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




