
Pseudostratified epithelium is present in
a) Nephron and neuron
b) Larynx and pharynx
c) Trachea and bronchi
d) Urinary bladder and intestine
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: The pseudostratified epithelium is present mainly in the respiratory tract of humans as they need to collect the foreign substances entering the tract and block their passage. They are prominent in the upper part of the respiratory tract.
Complete answer
The nephron and neurons are a part of the nervous system which require only neural impulses to be transmitted and no movement at all. Since stratified epithelium has cilia which helps in movement of substances, they are of no use in the nerve cells, hence are not present along the nervous system.
The larynx and pharynx have epithelium but it is a columnar epithelium which is not pseudostratified by actual stratification. So, this option is out of bounds.
The upper respiratory tract is prone to the entry of foreign substances due to which it might get blocked. To keep the tract, clear of all the obstacles, small or big, the upper respiratory tract is filled with a layer of stratified epithelium. The pseudostratified epithelium is not stratified but the cells are arranged at different levels which give an illusion of stratification. It is present in the Trachea and Bronchi which form the upper respiratory tract.
The lining in the urinary bladder is that of a stratified epithelium which is known as the urothelium. It is not a pseudostratified tissue, which makes this option an incorrect answer.
Therefore, we can deduce that option C is the correct answer.
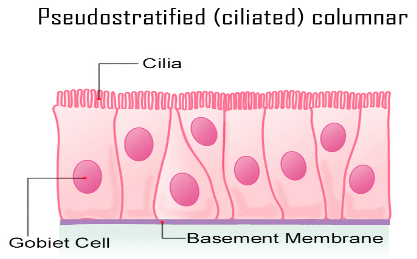
Note:
The epithelial tissue is one of the four types of animal tissue which forms the covering of the organs of the body, both from inside and outside. The types of epithelium are: Simple Squamous, Simple Cuboidal, Simple Columnar, Pseudostratified Columnar, Stratified Columnar, Stratified Squamous, Stratified Cuboidal and Transitional.
Complete answer
The nephron and neurons are a part of the nervous system which require only neural impulses to be transmitted and no movement at all. Since stratified epithelium has cilia which helps in movement of substances, they are of no use in the nerve cells, hence are not present along the nervous system.
The larynx and pharynx have epithelium but it is a columnar epithelium which is not pseudostratified by actual stratification. So, this option is out of bounds.
The upper respiratory tract is prone to the entry of foreign substances due to which it might get blocked. To keep the tract, clear of all the obstacles, small or big, the upper respiratory tract is filled with a layer of stratified epithelium. The pseudostratified epithelium is not stratified but the cells are arranged at different levels which give an illusion of stratification. It is present in the Trachea and Bronchi which form the upper respiratory tract.
The lining in the urinary bladder is that of a stratified epithelium which is known as the urothelium. It is not a pseudostratified tissue, which makes this option an incorrect answer.
Therefore, we can deduce that option C is the correct answer.

Note:
The epithelial tissue is one of the four types of animal tissue which forms the covering of the organs of the body, both from inside and outside. The types of epithelium are: Simple Squamous, Simple Cuboidal, Simple Columnar, Pseudostratified Columnar, Stratified Columnar, Stratified Squamous, Stratified Cuboidal and Transitional.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




