
Pulp cavity of teeth opens
(a) Below the teeth
(b) In front of teeth
(c) Behind the teeth
(d) None of the above
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The pulp of the teeth is enclosed within the teeth. The four key functions of the pulp are dentin formation and nutrition, as well as innervation and tooth defense. Dentin formation is one of the most critical roles of the pulp and is formed by the odontoblast.
Complete answer:
The pulp cavity of the teeth opens below the teeth. The dental pulp is the entry portion of a tooth consisting of living connective tissue and cells occupy each tooth's central pulp cavity. As the root canal that opens into the periodontium through the apical foramen, it will pass down through the root of the tooth.
- The dental pulp is an unmineralized oral tissue that consists of soft connective tissue, vascular, lymphatic, and nervous elements that occupy each tooth's central pulp cavity. Pulp has a thick consistency and is gelatinous. Much (75- 80 percent) of the pulp in water. There is no inorganic portion in normal dental pulp beside the presence of pulp stones contained pathologically inside the pulp cavity of aging teeth.
- Adult dentition consists of a total of 32 pulp glands. The molar teeth pulp cavities are about four times larger than those of incisors.
- The pulp cavity extends as the root canal that opens into the periodontium through the apical foramen down through the root of the tooth. The dental pulp blood vessels, nerves, etc. enter and exit the tooth through this foramen. This provides a means of contact between the pulp and the surrounding tissue- which is clinically critical in spreading inflammation from the pulp into the surrounding periodontium.
- Pulp and dentin are closely related to both developmentally and functionally. Both are products of the neural crest connective tissue which formed the dental papilla.
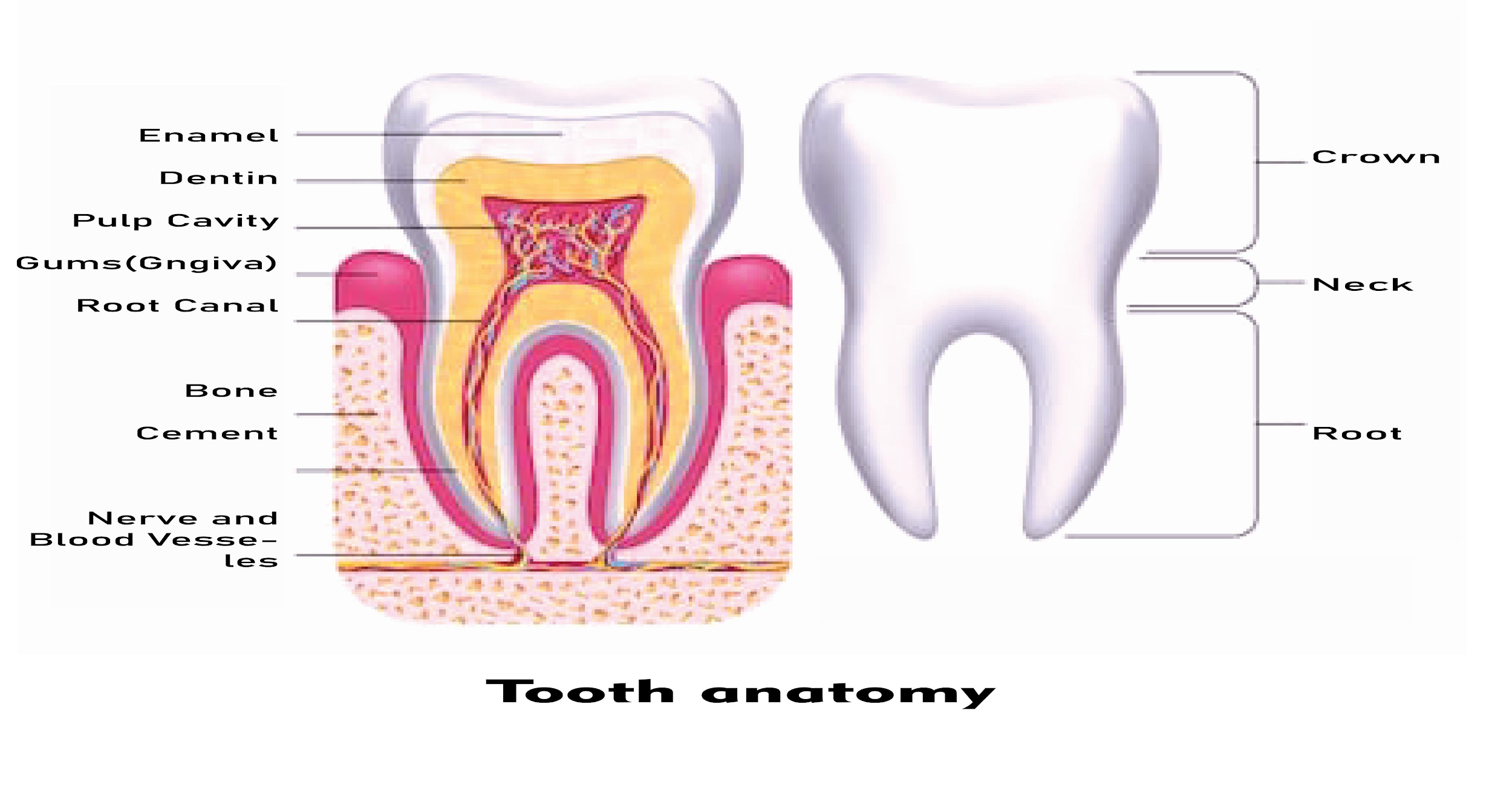
So, the correct answer is, ‘Below the teeth’.
Note: The decay enters the dentine where it is able to spread and weaken the enamel. If decay is left untreated, it can enter the pulp of the tooth, which includes blood vessels and nerves. Pulp gets infected. In the soft tissues, an abscess (swelling) or a fistula (opening to the gum surface) may develop.
Complete answer:
The pulp cavity of the teeth opens below the teeth. The dental pulp is the entry portion of a tooth consisting of living connective tissue and cells occupy each tooth's central pulp cavity. As the root canal that opens into the periodontium through the apical foramen, it will pass down through the root of the tooth.
- The dental pulp is an unmineralized oral tissue that consists of soft connective tissue, vascular, lymphatic, and nervous elements that occupy each tooth's central pulp cavity. Pulp has a thick consistency and is gelatinous. Much (75- 80 percent) of the pulp in water. There is no inorganic portion in normal dental pulp beside the presence of pulp stones contained pathologically inside the pulp cavity of aging teeth.
- Adult dentition consists of a total of 32 pulp glands. The molar teeth pulp cavities are about four times larger than those of incisors.
- The pulp cavity extends as the root canal that opens into the periodontium through the apical foramen down through the root of the tooth. The dental pulp blood vessels, nerves, etc. enter and exit the tooth through this foramen. This provides a means of contact between the pulp and the surrounding tissue- which is clinically critical in spreading inflammation from the pulp into the surrounding periodontium.
- Pulp and dentin are closely related to both developmentally and functionally. Both are products of the neural crest connective tissue which formed the dental papilla.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Below the teeth’.
Note: The decay enters the dentine where it is able to spread and weaken the enamel. If decay is left untreated, it can enter the pulp of the tooth, which includes blood vessels and nerves. Pulp gets infected. In the soft tissues, an abscess (swelling) or a fistula (opening to the gum surface) may develop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




