
What is 'Pulvinus' in leaves? In which plants is it found? What are their functions?
Answer
504.6k+ views
Hint: A pulvinus is a joint-like thickening situated at the base of a plant leaf or a leaflet that facilitates growth-independent nyctinastic and thigmonastic movement. Pulvini can be present at the base or apex of the petiole or even where the leaflets of a compound leaf are inserted into the rachis.
Complete answer:
A pulvinus is also sometimes called a geniculum. Pulvinus is a swollen leaf base.This type of leaves is seen in legume plants. The swelling results due to change in the turgor pressure. Night closure movement of legume leaves shows this pulvinar movement.
The pulvinus protects the young axillary bud. They are autonomous organs, which perform induced movements also when they are detached from stem and leaf. All pulvini consist of thick-walled water conducting vascular tissue that are surrounded by thin-walled motor cells which can undergo visible swelling and shrinking. Pulvini-based leaf movements occur in many plants of the bean family, the fastest responses can be found in Mimosa pudica, and Desmodium gyrans. While most plants can move their leaves only up and down, lupines can move them in any direction.
The diagram below shows a plant with different parts including the Pulvinus.
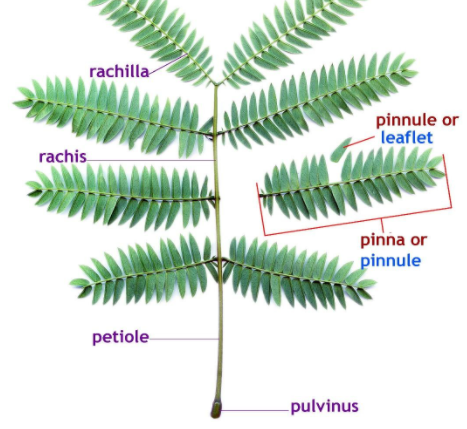
Note: Using nuclear magnetic resonance, upward movement of water within the pulvinus joint in response to electrical stimulation can be observed in the pulvinus at the base of the petiole. Movement of water to the upper or lower part of the pulvinus can cause asymmetric swelling thereby causing the petiole to either droop or rise and contributes to the characteristic displacement of the petioles.
Complete answer:
A pulvinus is also sometimes called a geniculum. Pulvinus is a swollen leaf base.This type of leaves is seen in legume plants. The swelling results due to change in the turgor pressure. Night closure movement of legume leaves shows this pulvinar movement.
The pulvinus protects the young axillary bud. They are autonomous organs, which perform induced movements also when they are detached from stem and leaf. All pulvini consist of thick-walled water conducting vascular tissue that are surrounded by thin-walled motor cells which can undergo visible swelling and shrinking. Pulvini-based leaf movements occur in many plants of the bean family, the fastest responses can be found in Mimosa pudica, and Desmodium gyrans. While most plants can move their leaves only up and down, lupines can move them in any direction.
The diagram below shows a plant with different parts including the Pulvinus.

Note: Using nuclear magnetic resonance, upward movement of water within the pulvinus joint in response to electrical stimulation can be observed in the pulvinus at the base of the petiole. Movement of water to the upper or lower part of the pulvinus can cause asymmetric swelling thereby causing the petiole to either droop or rise and contributes to the characteristic displacement of the petioles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




