
Pure silicon doped with phosphorus is:
(A) Amorphous
(B) p-type semiconductor
(C) n-type semiconductor
(D) Insulator
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: p-type semiconductor has impurity of atoms which belong to group 13 of periodic table i.e. atoms having three electrons in outermost shell. For Ex. $Ga, In$ and $Al$. n-type semiconductor has impurity of atoms which belong to group 15 of periodic table i.e. atoms having five electrons in the outermost shell. For ex. Arsenic, antimony etc.
Complete answer:
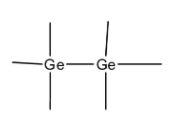
-In pure state, Ge atoms share four outermost electrons with adjacent $Ge$ atoms. Hence there are no free electrons at room temperature. This is an example of intrinsic or pure semiconductor.
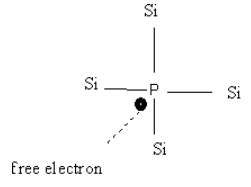
 -When pentavalent impurity (atom having five electrons in outermost shell Ex. P, As, Sb) is added to an intrinsic semiconductor, Ge atom is replaced with pentavalent atom which creates an extra Electron often called as free electron.
-When pentavalent impurity (atom having five electrons in outermost shell Ex. P, As, Sb) is added to an intrinsic semiconductor, Ge atom is replaced with pentavalent atom which creates an extra Electron often called as free electron.
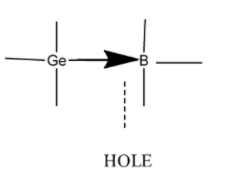
- When trivalent impurity (atom having three electrons in outermost shell Ex. $Ga, In, Al$) is added to an intrinsic semiconductor, $Ge$ atom is replaced with trivalent atom which creates a vacant state for Electron often called as hole.
-The process of adding impurities in pure semiconductors is called doping which leads to formation of Extrinsic semiconductors.
So Pure silicon doped with phosphorus is (C ) n-type semiconductor.
Note:
Group IV Elements like $Si, Ge$ are semiconductors which have conductivity between Conductors and Insulators. They have Four Valence electrons, when trivalent (Group lll) impurity is added, it forms three covalent bonds and leaves a hole leading to formation of. P-type or Positive Semiconductor. When pentavalent impurity (group V) is added, it forms four covalent bonds which give free electrons to the semiconductor. As electrons are negative, it produces n type semiconductor. P-type impurities are called acceptors and n-type semiconductors are called donors as it gives free electrons to the semiconductor.
Complete answer:
-In pure state, Ge atoms share four outermost electrons with adjacent $Ge$ atoms. Hence there are no free electrons at room temperature. This is an example of intrinsic or pure semiconductor.


- When trivalent impurity (atom having three electrons in outermost shell Ex. $Ga, In, Al$) is added to an intrinsic semiconductor, $Ge$ atom is replaced with trivalent atom which creates a vacant state for Electron often called as hole.

-The process of adding impurities in pure semiconductors is called doping which leads to formation of Extrinsic semiconductors.
So Pure silicon doped with phosphorus is (C ) n-type semiconductor.
Note:
Group IV Elements like $Si, Ge$ are semiconductors which have conductivity between Conductors and Insulators. They have Four Valence electrons, when trivalent (Group lll) impurity is added, it forms three covalent bonds and leaves a hole leading to formation of. P-type or Positive Semiconductor. When pentavalent impurity (group V) is added, it forms four covalent bonds which give free electrons to the semiconductor. As electrons are negative, it produces n type semiconductor. P-type impurities are called acceptors and n-type semiconductors are called donors as it gives free electrons to the semiconductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




